The World of Poetry
advertisement

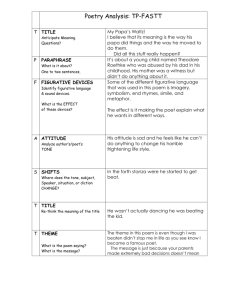
The World of Poetry Poetry Terms and Techniques Bear Creek High School Mr. Bernstein Why poetry? The poet doesn’t invent. He listens. ~Jean Cocteau Poetry is important because it reflects the emotions and character of society. It is a mirror to humanity, just like all literature and fine art. Sound + Meaning = Poetry A You must look at meaning and sound elements to truly take meaning from a poem. collage of images, thoughts and sounds that evoke feeling and meaning. Why is poetry difficult to read and understand? Denotation (the literal) vs. Connotation (the understood) “You’re on fire!” “That’s Sick!” Meaning Denotative (Literal) Connotative Language: (Figurative) Language: A basic, strict Using language that is dictionary meaning of not meant to be taken a word or phrase. literally, but has underlying meaning. This is my home. This is where I live, sleep and eat. This is my shelter from the elements. This is my home. It feels natural to be here and this is where my heart belongs. Sound In many ways, poetry is like music. A poet will use and manipulate their language to make certain sound qualities that are not usually found in prose. Prose is any form of writing that is not poetry or drama. Imagery: Language that evokes the senses. Visual – Sight Aural – Hearing Tactile – Touch Gustatory – Taste Olfactory – Smell What types of imagery are the following lines? The dry scent of a dying garden in September. ~Hart Crane The iron kettle sings on the stove. ~Elizabeth Bishop I’ve been driving over back roads, fringed with queen anne’s lace. ~Adrienne Rich Similes and Metaphors Simile : A figure of speech likening one thing to another by the use of “like” or “as”. Metaphor: A figure of speech in which one thing is spoken of as if it were another. Extended Metaphor: A metaphor in which the initial comparison between two unlike things is made, and then additional comparisons are made based on that initial comparison. Similes and Metaphors My faith is a steel bridge. My faith is as strong as a steel bridge. Personification: Giving living characteristics to non-living things. Fog The fog comes On little cat feet. It sits looking Over harbor and city On silent haunches And then moves on. ~Carl Sandburg Symbolism Symbolism: When a thing or object actually represents a concept, emotion or idea. What might the following image symbolize for you? Vagabonds We are the desperate Mood: The Who do not care, feeling the The hungry reader gets from Who have nowhere the poem. To eat, Tone: The tone No place to sleep, of voice the The tearless author is using. Who cannot Weep. Langston Hughes Theme: Theme: the universal message about humanity and human nature that the poem explores. Like every novel, short story, and film each poem has many themes that you can relate to. It makes you FEEL and CONNECT. Have you ever experienced loss, first love, fear of death, the tragedies of war? So has the poet. Theme: What is the main subject of the work? + What is the author saying about the subject? __________________ = Theme Statement Rhyme Internal vs. End Line Internal: Two or more words found inside one line that rhyme. End Line: Words at the end of lines that rhyme. My mind is not kind. My name I have signed. Rhyme Perfect vs. Slant Perfect: Words that have the same end sound. Smart/Heart Slant: Words that are have the same first and last sounds but different vowels in the middle. Ball/Bell Rhyme Pattern The pattern of rhyme is determined and labeled using letters. So sweet, My love, My dove, When we meet. A B B A Meter and Rhythm Meter: The counted syllables in a line. Poems without a set pattern are called free verse. Meter can be used to help set mood or feeling. Is the beat strong and fast or soft and slow? Meter and Rhythm We Real Cool We real cool. We Left school. We Lurk late. We Strike Straight. We Sing sin. We Thin gin. We Jazz June. We Die Soon. ~ Gwendolyn Brooks Alliteration, Assonance, Consonance and Onomatopoeia Alliteration: the repetition of the same beginning consonants Assonance: the repetition of the same vowel sounds in the middle of words Consonance: the repetition of the same ending consonants Onomatopoeia: words that are spelled much like how they sound. What sound techniques are used in the following lines? I heard the crunch of bones. My dinner was decidedly delicious. I think we should crank up the funk. She is tall, gaunt and always around. TPCASTT Title- What do you think the poem will be about?. Paraphrase – What basically happens in the poem? Connotation – What figurative language exists in the poem? Attitude – Describe the mood and tone. Shift – Is there a shift in subject or tone? Title – After reading the poem, what does the title mean? Theme – What is one common human experience that this poem explores? “Interior” Her mind lives in a quiet room, A narrow room and tall, With pretty lamps to quench the gloom And mottos on the wall. There all things are waxen neat And set in decorous lines; And there are posies round and sweet , And little straightened vines. Her mind lives tidily; apart From cold and noise and pain, And bolts the door against her heart, Out wailing in the rain. Dorothy Parker 1928- Learning Objective: To understand concepts in poetry. English 9 Poetry Vocabulary Ventured Lamentation Venerable Sullen Infested Cursory Euphemism Adept Destitute Unwieldy Communal Conspicuous Assuage Hoodwink Impending Judicious Imploring Fettered Sordid Pervaded