GDP Notes
advertisement

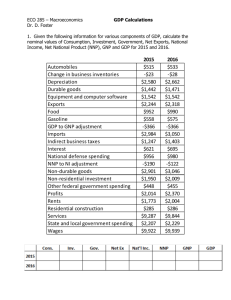
10/2 Macroeconomics - GDP, Unemployment, and Economic Business Cycle Current Issues are directly related to this unit Bureau of Labor Statistics is good website to research Job Projections GDP – Gross Domestic Product – measure of productivity A. Definition - the market value of all final goods and services produced in a country’s borders in a year. a. Final goods – goods purchased for final use – end product b. Intermediate goods – goods used in the production of final goods and services – wood to make desks, flour to make cakes, fabric to make clothes, etc - Not counted in GDP! Measuring GDP A. Income Approach – calculates GDP by adding up all the incomes in the economy. a. Does not include savings b. Does not take into effect unemployment B. Expenditure Approach - Calculates GDP by totaling the money spent on four major categories of goods and services: GDP = C + I + G + (x-m) Most Practical Approach C = Consumption (consumer expenditures - all of what we buy) a. Consumption – spending by households on goods and services b. Includes things such as cars, food, and visits to the dentist c. Makes up 2/3 of GDP spending I = Investment (businesses investing in capital goods) a. Investment – spending by businesses b. Includes things like new machinery, factories, equipment, tools, and construction of new buildings c. This is NOT investment in the stock market! G = Government Spending (largest consumer) ex: arms, teacher salaries a. Spending by all levels of government on goods and services b. Includes spending on military, schools, and highways among other public goods x = exports m = imports (x-m = net exports) ex: food, supplies a. Net Exports (X-M) – spending by people abroad on US goods and services (exports or X) MINUS spending by people in the US on foreign goods and services (imports or M) b. This is the smallest part of GDP, and has in recent years been negative because we import so much. Durable Good – goods that last for a relatively long time like refrigerator, washing machine, car, etc Nondurable Good – goods that last a short period of time, like food, light bulbs, clothes, etc Both durable and nondurable goods are included in GDP. 10/3 Nominal vs Real GDP A. Nominal GDP a. Measured in current prices b. Does not account for price level increases (inflation) from year to year. B. Real GDP a. expressed in constant, or unchanging, dollars. b. Includes adjustment for inflation therefore more accurate than Nominal GDP c. Multiply year 1 pricing by year 2 quantities C. Real GDP per Capita – a. takes into account inflation and population See WB pages 46 & 47 for work on Nominal vs Real GDP Problems/Limitations of GDP: GDP does not take into account certain economic activities which may include: A. Nonmarket activities a. goods/services people make/do themselves b. mowing lawns, childcare, changing your own oil, etc B. Underground Economy a. although income is generated with these activities, they are not reported and therefore not counted b. “under the table” wages not reported, scalping tickets (black market transactions) C. Government Payments a. payments to individuals from govt b. Social Security checks, Medicare, Medicaid, etc D. Financial Assets a. buying and selling stocks and bonds b. traded over and over again so cannot be counted E. Resold Goods a. goods that are resold or being sold for the second time b. used cars, houses that have been previously owned, etc