Organic Chemical Pathways for Esters
advertisement

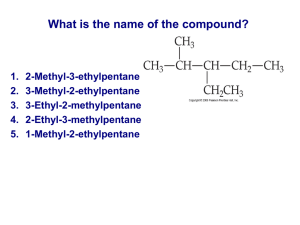
Organic Chemical Pathways Chemistry 3 & 4, Chapter 7 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1.When a mixture of ethane gas and chlorine gas is exposed to UV light, a number of products are detected, which can be separated by fractional distillation. Besides various chloroethanes, what other product will be present? A CH3Cl B CH4 C HCl D H2 2.Which of the following compounds could NOT be used as a starting material for the synthesis of CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3? I CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl II CH3CH2CHClCH3 III CH3CH2CH=CH2 IV CH3CH=CHCH3 A II only B I or II C II or III D II, III or IV 3.When propane, C3H8, undergoes cracking, which one of the following products will NOT be obtained? A CH4 B C2H2 C H2 D C4H10 4.Which one of the following amino acids is LEAST likely to be obtained from the hydrolysis of a protein in food? A NH2CH2CH(CH3)COOH B NH2CH(CH3)COOH C NH2CH2COOH D NH2CH(SH)COOH 5.Which molecule is always produced when triglycerides undergo hydrolysis? A CH2(CH2)14COOH B C6H12O6 C C3H8O3 D H2O 6.When a mixture of pentane and pent-2-ene, which are both colourless liquids, is mixed with liquid bromine, the red–brown colour of the bromine disappears. Which one of the following is the correctly balanced equation for the reaction that causes this colour change? A C5H12(l) + Br2(l) C5H12Br2(l) B CH3CH2CH=CHCH3(l) + Br2(l) CH3CH2CHBrCHBrCH3(l) C CH3CH2CH2CH=CH2(l) + Br2(l) CH3CH2CH2CHBrCH2Br(l) D C5H10(l) + C5H12(l) + 2Br2(l) 2C5H10Br2(l) + H2(g) 7.A compound that is present in ‘red delicious’ apples, and yet smells like bananas, is CH3COOCH2CH2CH2CH3. To synthesise this compound in the laboratory, you would need to react: A methanol and pentanoic acid. B ethanol and butanoic acid. C butan-1-ol and methanoic acid. D butan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. 8.The molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6 (Mr = 180.0 amu). If a disaccharide is produced from two glucose monomers: A its Mr will be 342.0 amu and it will contain an ester link. B its Mr will be 360.0 amu and it will contain an ester link. C its Mr will be 342.0 amu and it will contain a glycosidic link. D its Mr will be 360.0 amu and it will contain a glycosidic link. 9.Aspartame, which is marketed as ‘Equal’ or ‘Nutrasweet’, is a sugar substitute used in some low-calorie foods. The structure of Aspartame is shown below. What functional groups are likely to have interacted to form the –CO–NH– link at the centre of the molecule, if a H2O molecule was eliminated as this link formed? A –COOH and –NH2 B –COOH and –OH C –OH and –NH2 D –COCl and –NH2 10What substance would be produced if you were to react 2-chloropentane with .ammonia dissolved in ethanol? A CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3 B CH3CH2CH2CH(NH2)CH3 C CH3CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3 D NH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2 11One of the major constituents of palm oil is palmitic acid, which has the formula .CH3(CH2)14COOH. When this acid is reacted with potassium hydroxide, the main constituent of a well-known soap is produced. What will be the other product of the reaction? A Glycerol B Water C Carbon dioxide D An ester 12If you wish to commercially prepare ethanol from ethane derived from natural .gas, you would: A heat the ethane in NaOH solution, then distil off the ethanol. B react the ethane with Cl2 gas under UV light, then add NaOH solution to the product. C add yeast organisms, let the mixture ferment then distil off the ethanol. D dissolve the ethane in NaOH solution and then bubble O2 gas through the mixture. 13To prepare CH3CH2CH2COOH, the reaction pathway would involve: .A the oxidation of propan-1-ol B the hydrolysis of prop-1-ene C the oxidation of butan-1-ol D an addition reaction between oxygen and but-1-ene 14Look at the following diagram. . Substances P, Q and R will be, respectively: A C5H10, C5H10Br2, C5H12 B C5H11Cl, C5H11Br, C5H12 C C5H12, C5H10Br2, C5H10 D C5H12, C5H10Br2, C2H4 15A section of the structure of a polymer is shown below. To which of the .following families of polymers would this belong? –O–CH2–CH2–O–CO–CH2–CO–O–CH2–CH2–O–CO–CH2–CO– A Polyamide B Polyester C Polysaccharide D Protein 16Which of the following substances will be produced when CH3CH=CH2 is .subjected to high pressure and temperature in the presence of certain catalysts and undergoes a polymerisation reaction? A –CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2– B –CH2CH3CH2CH2CH3CH2CH2CH3– C –CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CH2– D –CH2OCOCH2CH2OCOCH2CH2OCOCH2– 17Ethanol can be produced industrially from propane that is derived from natural .gas. The flow chart for this production is shown below: Processes I, II and III are best described as, respectively: A fractional distillation; reduction; hydrolysis B fractional distillation; cracking; hydrolysis C cracking; reduction; fermentation D cracking; hydrogenation; oxidation 18Unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more C=C bonds. These can undergo an .addition reaction with hydrogen, using a nickel catalyst. Which of the following represents the molecular formula of a fatty acid that would react with hydrogen in this way in a mole ratio of 1:1? A C18H30O2 B C18H32O2 C C18H34O2 D C18H36O2 19The hydrogenation of alkenes is usually carried out in the presence of fine nickel .wire mesh. Which of the following is NOT a role played by this mesh in this reaction? A Hold one of the gaseous reactants in place B Lower the activation energy for the reaction C Lower the temperature required for the reaction D Slow down the reaction to make it safer and more easily controlled 20Examine the following protein segment. . How many different amino acids are present? A 3 B 4 C 5 D 6 ANSWERS 1.When a mixture of ethane gas and chlorine gas is exposed to UV light, a number of products are detected, which can be separated by fractional distillation. Besides various chloroethanes, what other product will be present? ACH3Cl B CH4 C HCl DH2 C ANSWER C : POINTS: 0 / 1 FEEDBA These are CK: substitut ion reaction s in which Cl atoms replace H atoms in the molecul e. The displace dH atoms combine with Cl atoms that result from splitting up the Cl2 molecul es, to produce HCl. pp202–3 REF: 2.Which of the following compounds could NOT be used as a starting material for the synthesis of CH3CH2CH(OH)CH3? I CH3CH2CH2CH2Cl II CH3CH2CHClCH3 III CH3CH2CH=CH2 IV CH3CH=CHCH3 A II only B I or II C II or III D II, III or IV C C ANSWER: D 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:All the molecules have four C atoms as in the required product, so none can be eliminated as possibilities on this basis. In the case of I and II, since these are saturated compounds, the OH can only replace the Cl present, so will be located on the same C atom as the Cl. This means that I will not produce the correct structural isomer. In the case of III and IV, an addition reaction across the C=C with H2O can attach an –OH group to one of the C atoms involved in the double bond, so theoretically both could yield the required product in an hydrolysis reaction. pp204, 211 REF: 3.When propane, C3H8, undergoes cracking, which one of the following products will NOT be obtained? A CH4 B C2H2 C H2 D C4H10 ANSWER: D 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:In the cracking process, a large molecule breaks up into smaller parts. Some C3H8 molecules will break up into C2H2 and CH4, and others will break up into C3H6 and H2. However, none will form larger molecules. p235 REF: 4.Which one of the following amino acids is LEAST likely to be obtained from the hydrolysis of a protein in food? A NH2CH2CH(CH3)COOH B NH2CH(CH3)COOH C NH2CH2COOH D NH2CH(SH)COOH ANSWER: A 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:All of the compounds are amino acids, but only alphaamino acids can act as monomers for proteins. That is, the amino functional group, –NH2, and the carboxyl functional group, –COOH, must be attached to the same carbon atom. In A, they are attached to two different carbon atoms. C C C pp227–8 REF: 5.Which molecule is always produced when triglycerides undergo hydrolysis? A CH2(CH2)14COOH B C6H12O6 C C3H8O3 D H2O ANSWER: C 1/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:Molecules of triglycerides are built up from glycerol and three fatty acids. A water molecule is eliminated as each ester link forms as a result of a condensation reaction between a hydroxyl group on the glycerol molecule and the carboxyl group on each fatty acid molecule. When a triglyceride undergoes hydrolysis, the reverse reaction occurs and glycerol, C3H8O3, and three fatty acids are produced. Answer A represents only one possible fatty acid. p216 REF: 6.When a mixture of pentane and pent-2-ene, which are both colourless liquids, is mixed with liquid bromine, the red–brown colour of the bromine disappears. Which one of the following is the correctly balanced equation for the reaction that causes this colour change? A C5H12(l) + Br2(l) C5H12Br2(l) B CH3CH2CH=CHCH3(l) + Br2(l) CH3CH2CHBrCHBrCH3(l) C CH3CH2CH2CH=CH2(l) + Br2(l) CH3CH2CH2CHBrCH2Br(l) D C5H10(l) + C5H12(l) + 2Br2(l) 2C5H10Br2(l) + H2(g) ANSWER: B 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:Bromine is only decolourised when it undergoes an addition reaction with unsaturated hydrocarbons, such as pent-2-ene. Hence the answer can only be B or C. Only B has the correct structure for pent-2-ene. The isomer reacting in C is pen-1-ene. p211 REF: 7.A compound that is present in ‘red delicious’ apples, and yet smells like bananas, is CH3COOCH2CH2CH2CH3. To synthesise this compound in the laboratory, you would need to react: A methanol and pentanoic acid. B ethanol and butanoic acid. C butan-1-ol and methanoic acid. D butan-1-ol and ethanoic acid. ANSWER: D 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:The start of the formula (CH3CO) contains two C atoms and tells us that the acid from which this ester is C C derived is ethanoic acid, CH3COOH. The last part of the formula contains four C atoms and tells us that the alcohol required is butan-1-ol, CH3CH2CH2CH2OH. If this isomer is not present, the –OH functional group will not be at the end of the molecule, which is where it must be if the required ester is to be produced. p213–4 REF: 8.The molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6 (Mr = 180.0 amu). If a disaccharide is produced from two glucose monomers: A its Mr will be 342.0 amu and it will contain an ester link. B its Mr will be 360.0 amu and it will contain an ester link. C its Mr will be 342.0 amu and it will contain a glycosidic link. D its Mr will be 360.0 amu and it will contain a glycosidic link. ANSWER: C 1/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:The condensation reaction between two glucose molecules results in the elimination of a H2O molecule at the link, so its Mr = (360.0 – 18.0) amu = 342 amu. The link present in disaccharides and polysaccharides is the glycosidic link, also known as an ether link. p230 REF: 9.Aspartame, which is marketed as ‘Equal’ or ‘Nutrasweet’, is a sugar substitute used in some low-calorie foods. The structure of Aspartame is shown below. What functional groups are likely to have interacted to form the – CO–NH– link at the centre of the molecule, if a H2O molecule was eliminated as this link formed? A –COOH and –NH2 B –COOH and –OH C –OH and –NH2 D –COCl and –NH2 ANSWER: A 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:The –CO–NH– group may be an amide link or a peptide link. But given that H2O was eliminated as the link formed, we can deduce that it is a peptide link and hence is formed as a result of a condensation reaction between a carboxyl group, –COOH, on one molecule (the first monomer) and an amine group, –NH2, on the C C C other. p228 REF: 10.What substance would be produced if you were to react 2chloropentane with ammonia dissolved in ethanol? A CH3CH(OH)CH2CH2CH3 B CH3CH2CH2CH(NH2)CH3 C CH3CH2CH2CH(OH)CH3 D NH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2NH2 ANSWER: B 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:This is the usual pathway by which an amine may be prepared. Since this is a direct substitution reaction, the starting chloroalkane must have the chloro group attached to the same carbon atom as the one to which the amino group is to be attached. p203 REF: 11.One of the major constituents of palm oil is palmitic acid, which has the formula CH3(CH2)14COOH. When this acid is reacted with potassium hydroxide, the main constituent of a well-known soap is produced. What will be the other product of the reaction? A Glycerol B Water C Carbon dioxide D An ester ANSWER: B 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:Normally, reacting NaOH solution or KOH solution with an oil will produce soaps (salts of the fatty acid molecules) and glycerol. To make an ester, this fatty acid would need to be reacted with an alcohol, not a base. But in this case the products will be the soap, CH3(CH2)14COOK, and H2O. pp213–4, 216 REF: 12.If you wish to commercially prepare ethanol from ethane derived from natural gas, you would: A heat the ethane in NaOH solution, then distil off the ethanol. B react the ethane with Cl2 gas under UV light, then add NaOH solution to the product. C add yeast organisms, let the mixture ferment then distil off the ethanol. D dissolve the ethane in NaOH solution and then bubble O2 gas through the mixture. ANSWER: B 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:Ethane is non-polar and hence will not react directly with, or even dissolve in, NaOH solution. But by converting the ethane to a chloroethane, it becomes C sufficiently polar to dissolve and react. The –OH group then replaced the –Cl atom in the molecule. Yeast organisms require a sugar, not an alkane, for fermentation to occur. pp195, 202–4 REF: 13.To prepare CH3CH2CH2COOH, the reaction pathway would involve: A the oxidation of propan-1-ol B the hydrolysis of prop-1-ene C the oxidation of butan-1-ol D an addition reaction between oxygen and but-1-ene ANSWER: C 1/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:An alcohol is oxidised by an oxidant such as oxygen or acidified potassium dichromate to its corresponding carboxylic acid. Since the carboxylic acid contained four C atoms in a straight chain, with the carboxyl group at the end, we had to start with butan-1-ol. p205 REF: 14.Look at the following diagram. C Substances P, Q and R will be, respectively: A C5H10, C5H10Br2, C5H12 B C5H11Cl, C5H11Br, C5H12 C C5H12, C5H10Br2, C5H10 D C5H12, C5H10Br2, C2H4 ANSWER: A 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:Alkenes undergo an addition reaction with water, hydrogen and bromine, so P is an alkene. Since it must contain the same number of C atoms as the alcohol, it can only be pentene. When H2O is added to C5H10, we obtain C5H12O. This rearranges to C5H11OH, which shows the hydroxyl group. Similarly the addition of Br2 and H2 to C5H10 produces the formulas C5H10Br2 and C5H12 respectively. pp209–11 REF: C C C 15.A section of the structure of a polymer is shown below. To which of the following families of polymers would this belong? –O–CH2–CH2–O–CO–CH2–CO–O–CH2–CH2–O–CO–CH2–CO– A Polyamide B Polyester C Polysaccharide D Protein ANSWER: B 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:The links shown are –O–CO–, which are ester links. Hence it is a polyester. The monomers would be the diol HO–CH2–CH2–OH and the dicarboxylic acid HOOC–CH2–COOH. pp223–4 REF: 16.Which of the following substances will be produced when CH3CH=CH2 is subjected to high pressure and temperature in the presence of certain catalysts and undergoes a polymerisation reaction? A –CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2– B –CH2CH3CH2CH2CH3CH2CH2CH3– C –CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CH2– D –CH2OCOCH2CH2OCOCH2CH2OCOCH2– ANSWER: C 1/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:Propene, CH3CH=CH2, undergoes an addition polymerisation. This occurs across the double bond of each monomer. The CH3 group attached to one of the C atoms involved in the double bond then becomes a side group in the polymer. Answer D can only be a condensation polymer, since it contains ester links, and can only form from monomers that have two functional groups. p222 REF: 17.Ethanol can be produced industrially from propane that is derived from natural gas. The flow chart for this production is shown below: Processes I, II and III are best described as, respectively: A fractional distillation; reduction; hydrolysis B fractional distillation; cracking; hydrolysis C cracking; reduction; fermentation D cracking; hydrogenation; oxidation ANSWER: POINTS: B 0/1 C C FEEDBACK:Propane is separated from the other components of natural gas (methane, ethane and butane) by fractional distillation. Propane contains three carbon atoms and ethene only contains two carbon atoms. The breaking up of a larger hydrocarbon into a smaller one is termed cracking. Water is added to ethene to convert it to ethanol. This is an addition reaction, not a redox reaction. The production of ethanol by fermentation requires sugar and yeast organisms, not ethene. pp195, 233–5 REF: 18.Unsaturated fatty acids contain one or more C=C bonds. These can undergo an addition reaction with hydrogen, using a nickel catalyst. Which of the following represents the molecular formula of a fatty acid that would react with hydrogen in this way in a mole ratio of 1:1? A C18H30O2 B C18H32O2 C C18H34O2 D C18H36O2 ANSWER: C 1/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:A saturated carboxylic acid, which will not undergo an addition reaction with H2, contains only single C–C bonds. This means that it will consist of an alkyl group attached to the carboxyl group and it will have the general formula CnH2n+1COOH. For an unsaturated fatty acid to undergo an addition reaction with H2 in the ratio 1:1, which means that one mol of the acid reacts with one mol H2, it must have just one C=C bond. Hence it will have two H atoms less than the saturated acid; these will be added in when it reacts with H2. Thus its general formula will be CnH2n-1COOH. Of n =17, the formula of the acid will be C17H33COOH, which rearranges to C18H34O2. p209 REF: 19.The hydrogenation of alkenes is usually carried out in the presence of fine nickel wire mesh. Which of the following is NOT a role played by this mesh in this reaction? A Hold one of the gaseous reactants in place B Lower the activation energy for the reaction C Lower the temperature required for the reaction D Slow down the reaction to make it safer and more easily controlled ANSWER: D 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:The nickel gauze acts as a catalyst. It speeds up the reaction by lowering the activation energy, which means more particles have sufficient energy for a successful collision, and helps ‘pin down’ one of the reactants so the collision rate is greater. In addition, it lowers the temperature required. p210 REF: 20.Examine the following protein segment. C How many different amino acids are present? A3 B 4 C 5 D6 ANSWER: B 0/1 POINTS: FEEDBACK:We first break up the polymer into its monomers by ‘cutting’ through the peptide links. This produces six monomers. However, two sets of monomers have the same R group, so there are really only four different amino acids present. pp227–8 REF: