Dissociation vs. Ionization
advertisement

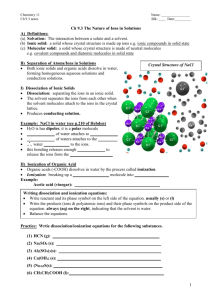
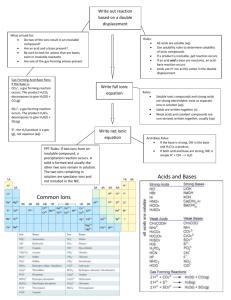
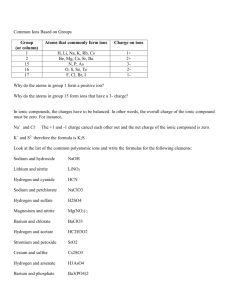
Dissociation In 1887, Svante August Arrhenius proposed that when a substance dissolves in water, particles of the substance separate from each other and disperse into the solution (called dissociation). Non-electrolytes disperse electrically neutral particles (therefore don’t conduct electricity) Electrolytes disperse electrically charged particles called ions (therefore do conduct electricity) Why do ionic compounds disperse electrically charged particles? The positive ions are surrounded by the negative end of the polar water molecules. The negative ions are surrounded by the positive end of the polar water molecules. RESULT: The ions at the edges of the ionic crystal are tugged and dislodged until each one is surrounded by water molecules and is floating around as an independent entity DISSOCIATION – the separation of ions that occurs when an ionic compound dissolves in water Dissociation Equations Remember: There are two requirements of dissociation: it must be soluble in water and must be ionic Dissociation Equations: shows the separation of ions in a chemical equation H20(l) is not shown because it is a solvent and is NOT consumed nor changed. It is shown in the aqueous states for the products (aq means “dissolved in water”) Examples: (you still need to make sure the equations are balanced) NaCl(s) Na + (aq) + Cl – (aq) K3PO4(s) 3 K +(aq) + PO43- (aq) Try it on your own.... Pg. 198 #2 Arrhenius acids and bases Arrhenius extended his dissociation theory to include acids and bases Bases – ionic compounds containing the hydroxide ion (OH-) that dissolve into cations and OH– (aq) in water Ba(OH)2 (s) Ba 2+ (aq) + 2 OH-(aq) NOTE: All bases are ionic, so all bases could dissociate if soluble in H2O Acids – molecular compounds containing hydrogen that yield H+ (aq) ions when they dissolve in water - Acids behave as molecular substances; CH3COOH (l) – does not conduct electricity or change the color of litmus paper - As soon as acids are dissolved in water, their acid properties appear; CH3COOH (aq) will conduct electricity and changes litmus paper from blue to red NOTE: Acids are not ionic, so they DO NOT dissociate. They IONIZE. Arrhenius came up with the idea of ionization to explain why acids are electrolytic: The non-electrolytic molecular compound separates into ions when dissolved in water, becoming electrolytic HCl (g) H+ (aq) + Cl-(aq) IONIZATION – the reaction of neutral molecular compounds forming charged ions Dissociation vs. Ionization What is the difference between dissociation and ionization? Both produce (aq) ions... Dissociation, however, is the separation of ions that already exist before dissolving in water M+X- (s) M+ (aq) + X-(aq) Ionization involves the production of new ions, specifically hydrogen ions HX0 (aq) H+ (aq) + X-(aq) SUMMARY Substance Process General Equation XY (s/l/g) XY (aq) Molecular Disperse as individual, neutral molecules Ionic Dissociate into individual ions MX (s) M+ (aq) + X-(aq) Base (ionic hydroxide) Dissociate into positive ions and hydroxide ions MOH (s) M+ (aq) + OH-(aq) Acid Ionize to form hydrogen ions and anions HX (s/l/g) H+ (aq) + X-(aq) Reference pg. 201 Solubility IONIC Use solubility table MOLECULAR Memorize ACIDS All soluble BASES Ionics Try it on your own... Pg. 202 #1-3 Pg 195 Lab Exersice 5.A Complete Analysis - Identities of solutions Pg 195 Section 5.1 questions Q 3,5-7 Pg. 202 Q 1-4,8