Domains of Learning
advertisement

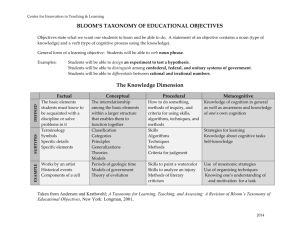
Three Learning Domains Bloom et al. are well known for dividing categories of learning into the cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. The cognitive domain involves the learning and application of knowledge. The affective domain addresses the acquisition of attitudes and values, and the psychomotor domain involves development of the body and skills it performs. Domain Taxonomies A taxonomy classifies information into a hierarchy of levels. Domain taxonomies reveal that what educators want students to accomplish (expressed by educational objectives) can be arranged into levels of complexity, and that those levels are best fulfilled sequentially. Example: The food guide pyramid is a taxonomy of levels based on number of servings, or relative contribution of a particular food group to total food intake. www.ncagr.com/agscool/ nutrition/pyramid.htm Cognitive Domain The cognitive domain involves the learning and application of knowledge. The taxonomy contains six levels that can be remembered by the following mnemonic device: www.chorley.gov.uk/.../ 1/BinThinking-logo.jpg Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation B. Bloom, ed., Taxonomy of educational objectives, handbook I: Cognitive domain. New York: McKay, 1956. Kickball Can Almost Always Seem Enjoyable Cognitive Domain Levels Level Description Knowledge To recall or recognize information in some pre-arranged form. Verbs Objective Define List Define levels of cognitive domain. Comprehen- To understand meaning of sion information based on prior learning. Describe Explain Interpret Explain purpose of cognitive domain. Application To utilize information to complete a task with limited direction. Compute Solve Use Write objective for levels of cognitive domain. Analysis To classify and relate assumptions or evidence. Contrast Examine Compare cognitive & affective domains. Synthesis To integrate or combine ideas into a new product or plan. Design Develop Organize Design way to write objectives that combines 3 domains. Evaluation Critique idea based on specific standards and criteria. Appraise Judge Justify Judge effectiveness of writing objectives using taxonomy. Cognitive Domain Levels Research over the last 40 years has confirmed the taxonomy as a hierarchy, with the exception of the last two levels. It is uncertain whether synthesis and evaluation should be reversed, or whether synthesis and evaluation are at the same level of difficulty, but use different cognitive processes. Creative Thinking Critical Thinking Synthesis Evaluation Analysis Application Comprehension Knowledge Affective Domain The affective domain addresses the acquisition of attitudes and values. The taxonomy contains five levels that can be remembered by the following mnemonic device: www.rhinocerospie.com/.../ archive-072004.html Receiving Responding Valuing Organization Characterization Krathwohl, D., et al. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives, handbook II: Affective domain. New York: McKay. Regular Rude Vices Offend Christ Affective Domain Levels Level Description Verbs Objective Receiving Being aware of, or attending to something in the environment. Listen Notice Tolerate Listen attentively to badminton introduction. Responding Showing some new behavior as a result of experience. Comply Enjoy Follow Voluntarily help set up badminton nets. Valuing Showing some definite involvement or commitment. Carry out Express Attend optional badminton match. Organization Integrating a new value into one's general set of values relative to other priorities. Choose Consider Prefer Purchase own badminton racket. Characterization Acting consistently with the new value; person is known by the value. Act on Depict Exemplify Join intramurals to play badminton twice per week. Psychomotor Domain The psychomotor domain involves development of the body and skills it performs. The taxonomy contains seven levels that can be remembered by the following mnemonic device: www.campdiscovery.com/ Specialist-04/Tennis-01.jpg Perceiving Patterning Accommodating Refining Varying Improvising Composing Bressan’s adaptations of Jewett et al., “Educational change through a taxonomy for writing physical education objectives,” Quest 15, 35-36, 1971. Premium Pandas Acquire Rare Value In China Psychomotor Domain Levels Level Description Verbs Objective Perceiving Recognizing movement position or pattern. Listen Observe Discover headstand movement principles. Patterning Reproducing movement position or pattern. Imitate Practice Perform headstand following modeling. Accommodating Using or modifying Adjust movement position or pattern. Modify Use headstand in routine. Refining Demonstrating efficient control in performing pattern. Perform headstand with pointed toes. Varying Performing movement pattern Design in different ways. Develop Perform headstand in three positions. Improvising Originating novel movement or movement combinations. Construct Invent Combine headstand with new skill. Composing Creating unique movement pattern. Create Invent Create floor exercise routine. Improve Master