Slides
advertisement

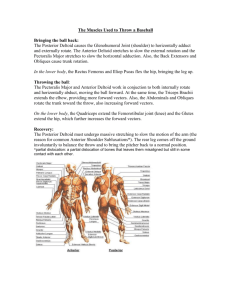
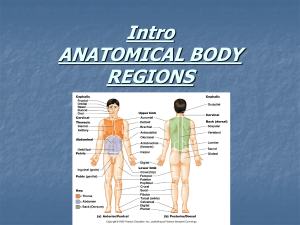
Helpful Tips for Learning Bones Do NOT learn bones based on size! EX: Just because a bone is big does not mean it is the femur! For bone quizzes check out lecture CD-ROM (skeletal system chapter) www.flashcardexchange.com Anatomical Terminology, Pg.4 Superior = above Inferior = below Anatomical Terminology, Pg.4 Anterior = front Posterior = back Anatomical Terminology, Pg.4 Medial = toward the Middle Lateral = toward the side Anatomical Terminology, Pg.4 Proximal = close to the trunk (Proximal ~ Proximity) Distal = Distant from the trunk Articulating the Skeleton Ligaments connect bones together Tendons join muscles to bone What type of tissue are ligaments & tendons? Scapula, Pg 147, Posterior View Glenoid Cavity Deltoid muscle attaches to the Spine Humerus articulates at the Glenoid Cavity Spine Spine Deltoid Scapula, Pg 147, Anterior View Suprascapular notch allows for nerve passage Suprascapular Notch Distinguishing Left & Right Bones 1. Look at the bone’s morphology 2. Think of how it articulates with other bones Humerus, Pg 148, Anterior View Intertubercular Sulcus Bicep tendon passes through the Intertubular Sulcus Deltoid Tuberosity Deltoid muscle attaches to the Deltoid Tuberosity Deltoid Intertubular Sulcus Bicep Deltoid Tuberosity Radius, Pg 149, Anterior View Radial Tuberosity Bicep attaches at the Radial Tuberosity Styloid Process Wrist ligaments attach to the Styloid Process Bicep Radial Tuberosity Ulna, Pg 149, Lateral View Styloid Process Wrist ligament attachment site Distinguishing the Radius & Ulna Radius is on the thumb side of the forearm The radius rotates when you twist your arm Ulna has a wrench-like trochlear notch Phalanges Metacarpals Carpals Do Activity 1 and Activity 2 Find the answers to the questions in your handout Pelvic Girdle, Pg 152, Lateral View Illium Pubis Ischium Pelvis, Pg. 152, Lateral View G. & L. Sciatic Notches allow for nerve and blood vessel passage Greater Sciatic Notch Lesser Sciatic Notch Greater Sciatic Nerve Look at a Pelvis at your Table Do Activity 3 – Pg. 152 Distinguish between male and female pelves Femur, Pg 154, Posterior View Greater Trochanter Lesser Trochanter Greater & Lesser Trochanters are attachment sites for buttock muscles Greater Trochanter Patella, Pg. 154, Anterior View The patella protects the knee joint Tibia, Pg. 155, Anterior View Tibial Tuberosity Attachment site for patellar ligament & quadriceps muscles Medial Malleolus Helps stabilize the ankle joint Tibial Tuberosity Fibula, Pg. 155, Anterior View The lateral malleolus helps to stabilize the ankle joint Lateral Malleolus Distinguishing between the Tibia & Fibula The Tibia is Tough The Fibula is Flimsy The Foot, Pg. 156, Lateral View Attachment site for the Achilles (Calcaneal) tendon Calcaneus Achilles Tendon Distinguishing the Carpals & Tarsals The Carpals are in the hand where some people suffer from “Carpal Tunnel Syndrome” The Tarsals are near the Toes Do Activity 5 – Pg. 156 Do Activity 6 - Construct a Skeleton