LEVERS
advertisement

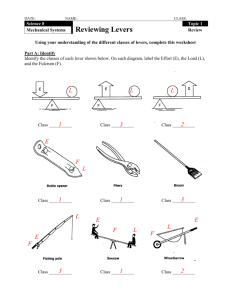
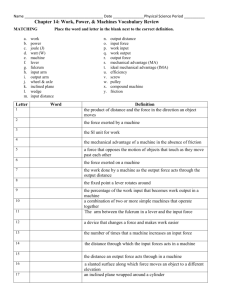
Rigid bar fulcrum Chaitali prabhudesai Forces The lever consist of two forces: 1) 2) An effort force: which will tend to rotate the bar around the fulcrum An resisting force: which will resist the movement These forces act around a supporting force which provides for a point of pivot known as the fulcrum effort Chaitali prabhudesai resistance Forces Force Arm: The distance from the effort to the fulcrum is known as the force arm Resistance Arm: The distance between the resistance and the fulcrum is known as the resistance arm effort Chaitali prabhudesai FA RA resistance Law Of Lever In order for the lever to be in equilibrium: Load(resistance) * Load Arm= Effort * Effort Arm E.g. 1 gm of feather has to be balanced by 1 kg of rock feathers Chaitali prabhudesai FA rock RA Mechanical Advantage Mechanical Advantage or leverage is defined as a ratio of force arm to resistance arm MA=FA/RA Mechanical Advantage can either be equal to 1, less than 1 or greater than 1 depending upon the type of lever Chaitali prabhudesai Types Of Levers Class I Levers: In these types of levers the fulcrum lies between the resistance and the effort effort FA RA Resistance The Mechanical advantage for these levers can be equal to 1,>1 or < 1 depending upon the position of the fulcrum. Chaitali prabhudesai Types Of Levers Class II levers: In these types of levers the resistance lies between the fulcrum and effort. Thus the effort(force) arm is always greater than the resistance arm Mechanical Advantage: Thus the mechanical advantage of this lever is always greater than 1 FA RA Chaitali prabhudesai Resistance effort Types Of Levers Class III levers: In these types of levers the effort lies between the fulcrum and resistance. Thus the resistance arm is always greater than the force arm Mechanical Advantage: Thus the mechanical advantage of this lever is always less than 1 effort FA RA Chaitali prabhudesai Resistance Levers In Human Body In human body the bones act as levers, the weight of that body part acts as the resistance and the associated muscular contraction(muscle attached to that bone) acts as the effort. Motion is produced only when the effort exceeds the resistance . For your legs or any other body part to move the appropriate muscles and bones must work together as levers Chaitali prabhudesai Examples Common Examples: Class I lever Scissors: The fulcrum lies at the center, we apply force at the handles of the scissor, the resistance is at the other end Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Our head is connected to the spine at the atlanto- occipital joint(fulcrum). A coronal plane passing through the body divides the head into a greater anterior part and a smaller posterior part, such the weight of the anterior part is greater than the posterior part Thus the anterior part of the head tends to fall (bend)forwards(Load) This bending action is prevented by weight of the posterior part of the head and occipital muscles (effort) Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Class I lever: Chaitali prabhudesai Coronal plane Examples Common Examples: Class II lever: The fulcrum lies at one end ,the load is present at the center, and the effort force is applied at the other end Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Class II Lever: When we raise our body on the toes ,the toes act as the fulcrum, the weight of the body acts as the resistance force and the calf muscles act as the effort force Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Class II lever: Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Common Examples: Class III lever: Forceps:The fulcrum lies at one end, the effort force lies at the center ,the resistance force lies at the other end Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Class III Lever: When we hold a object in our hand the object acts the load, the elbow joint acts as the fulcrum and the muscles in the arm(Biceps) act as the effort force. Generally most of the levers in the human body are class III levers Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples Class III lever: Chaitali prabhudesai Anatomical Examples