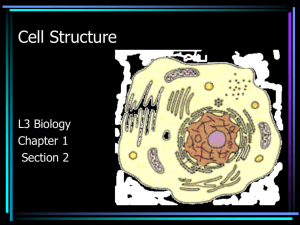
The Parts of A Cell
advertisement

Goal #1: Cell Theory Anton Van Leeuwenhoek • Dutch fabric merchant. • Amateur Scientist. • Made the first microscope. Leeuwenhoek looked at: Blood Pond Water Plaque Results: He discovered microorganisms He was the first person to see a living cell Before the microscope people believed diseases were caused by curses or supernatural spirits. Robert Hooke • English Scientist • Museum Caretaker He looked at: • Thin slices of cork. • Results: • Observed nonliving cells. • Came up with the name “cells”. Matthias Schleiden German Botanist Schleiden Looked at Plant Cells & Parts Results: He made the statement… “All plants are made up of cells”. Memory Trick: ”Matt Shleiden to a tree!” Theodor Schwann German Zoologist Schwann looked at animal cells & parts Results: He made the statement… “All animals are made up of cells”. Memory Trick: ”The Schwann is an animal!” Rudolph Virchow German Doctor What he Looked at: Used the microscope to look at all kinds of cells. Results: Stated that all cells come from other cells Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of cells. 2. Cells are the basic (smallest) units of structure of living things. 3. All cells come from other cells. Goal #2: Prokaryotes pro = before kary = nut/kernel (nucleus) ote = type Two Types of Cells • Prokaryotic Cells – Do not contain a nucleus or any membrane bound organelles • Eukaryotic Cells – Contain a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles The first cells… • Prokaryotic cells are believed to be the first cells that existed. • It is believed that this occurred when genetic material (DNA) became lumped together and sealed into tiny packages – called cells. • Later on, prokaryotes would be “swallowed” by larger cells and would form the nucleus of the larger cells, known as eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotic cells are 1 to 100 times bigger than prokaryotic cells. The genetic material (DNA or RNA) floats around loose in the jelly-like cytoplasm The cell is held together by the cell membrane (like a water balloon) Genetic material Cytoplasm Cell Membrane Ribosomes ROUND ROD SPIRAL • Prokaryotes are very small organisms made of 1 prokaryotic cell. –Ex) Bacteria • They are microscopic! (cannot be seen without the aid of a microscope) Escheria coli Food poisoning Streptoccus aureus Strep Throat Staphylococcus aureus Staph Infection Neisseria meningitidis Meningitis Goal #3: Eukaryotes eu = true kary = nut/kernel (nucleus) ote = type • Eukaryotic cells – cells that have a nucleus and other membrane bound organelles – Plants – Animals – Fungi – Protists Eukaryotic cells have… Organelles • Structures in eukaryotic cells that perform certain functions for the cell Cell Membrane • Flexible outer covering of the cell. • Has tiny holes & gates to control what goes in or out of the cell. • Clear thick, jelly-like fluid. • Supports cell’s organelles • Fills up the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus. • It is constantly flowing. Cytoplasm Nucleus • Largest organelle in the cell. • The control center of the cell. • Contains the directions for making proteins. • Contains the genetic material Chromatin • Stringy material spread throughout nucleus – uncoiled chromosomes • Consists of DNA bound to protein • Contains instructions for making protein Chromosome • Wound up chromatin structures that contain DNA • Only present in cell during cell division Protein Transport Chain • A cell’s job is to make protein • That protein is produced in the nucleus and shipped out to other cells Nucleolus • Small round object found in the nucleus • Place where ribosomes are made. • Small round structures found on ER and scattered throughout the cytoplasm • Place where protein is made. Nuclear Envelope (Membrane) • Doublemembrane layer around nucleus • Contains tiny pores • Allows materials to move in and out of the nucleus Endoplasmic Reticulum • Two types: – Smooth ER (no proteins on surface) – Rough ER (proteins on surface – like sprinkles!) • Tunnels in the cytoplasm. • The transport system used to get protein from one part of the cell to another. Golgi Apparatus • Smooth, stacklike membranes. • Protein is sent here from the ER and is packaged for shipment out of the cell. Other Organelles • Much more happens in a cell besides protein production and transport • Many other organelles are present and have their own function within the cell! Mitochondria • Bean shaped. • Has 2 membranes • Place where sugar is broken down. • Supplies energy to the cell. • The “powerhouse ” of the cell. Centrioles • Tube made of many smaller “microtubules” • Assist during cell division – only present during division Cilia & Flagella Cilia short hairlike projections from cell surface Cilia & Flagella Flagella Long whiplike projections Both help the cell to move Lysosomes • Small round structures filled with enzymes – found only in animal cells. • The “clean up crew”. • Dissolves old cell parts. Cell Wall • Rigid, Strong outer covering of a plant cell. • Helps protect and support the cell. • Made of cellulose (fiber). Vacuoles • Liquid Storage Tanks • Plants cells have one large vacuole. • Animals cells have a few small vacuoles. • Holds waste, water, enzymes. Chloroplast • Large green structures found only in plant cells • Contains chlorophyll that captures sunlight. • Place where food is made. Diversity of Life Overview This presentation highlights the specialized organelles that each type of living thing has in order to survive in its conditions. This information can be written anywhere on your note page – if you cannot fit it in the slide, write in the margins around the slide! BACTERIA Cell Wall – in some – cell membrane in ALL Pilli – Sex/Communication Organs Flagella – For Movement Cilia – for movement and engulfing prey Flagella – whips for moving themeslves Many different organelles Cell wall, but no chloroplasts Cell Wall – Rigid covering – for protection Chloroplasts – for absorbing sun Chlorophyll – makes plant appear green Vacuole – Stores water – makes plant strong http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm Centrioles – used in cell division Homework • Cell Choice #2 P R O K A R Y O T E A N I M A L C E L L P L A N T C E L L Monday September 27th 1.What type of eukaryotic cell is shown? 2.What are the things inside of the cell called? 3.What is the function of the nucleus? Goal #4: Focus magnification on a specimen using a microscope Parts of Microscope http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=4584444570497215104&ei=M3zSOCPKofA-wHW4WKBA&q=microscope&hl=en Parts of Microscope http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=4584444570497215104&ei=M3zSOCPKofA-wHW4WKBA&q=microscope&hl=en Pond Water http://video.google.com/videoplay?docid=4573224209896349246&hl=en Key Terms Specimen – the object that you are looking at Clean slide – a glass slide that does not have a specimen on it Field of View – the area that you see when looking through the microscope Things You Never Do Touch the lenses Place slide on table Place scope towards edge of table Turn large knob when using the high power Touch the specimen on a slide Things You Always Do Carry scope with two hands Use lens paper to clean lens Keep slides in slide box Turn small knob when using high power How to Focus 1. 2. 3. 4. With low power Turn large knob to focus Turn diaphragm to adjust light Slowly turn to medium/high power 5. Focus by turning small knob ONLY Magnification Ocular lens X Objective lens = Total magnification Low Power _____ Medium Power _____ High Power _____ x x x _____ _____ _____ = ______ = ______ = ______ Making a Wet Mount Slide 1. Place 1 drop of water on glass slide using pipet. 2. Place specimen on glass slide. 3. Place cover slip on specimen. (Do not push down on cover slip!) How to Store a Microscope 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Turn off light Turn to low-power objective Lower stage Remove slide Cover the microscope Goal #5 Cell Membrane I. The Plasma Membrane Function (Cell Membrane) Selectively permeable •Permeable – things can go in and out •Selective – some things can, some can’t Provides •Protection •support What is the plasma membrane’s job? • To allow nutrients to come into the cell when amounts become low. • To remove excess nutrients when levels get too high. • To allow waste products to leave the cell. The Fluid Mosaic Model • Fluid – phospholipids and proteins are always moving • Mosaic – the proteins are scattered with no pattern Phospholipid bilayer: 2 layers of phospholipids arranged back-to-back Phospholipid Cholesterol – prevents fatty acids chains from sticking together Protein Function Passageways for molecules to pass through using transport proteins Communication with other cells using carbohydrates 2 types of Proteins • Channel – small molecules (ions) diffuse (pass through) • Carrier – binds specific molecule and changes shape to allow molecule through