Chapter 25 Section 1: Outline I. Election of 1920 A. Return to
advertisement

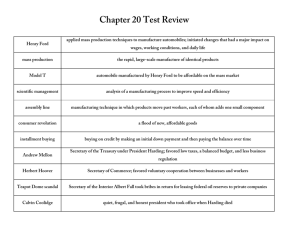
Chapter 25 Section 1: Outline I. Election of 1920 A. Return to Normalcy 1. Warren G. Harding/Calvin Coolidge (Republicans) 2. James Cox/Franklin D. Roosevelt (Democrats) II. Republicans in Office A. Democrats lose the White House 1. Woodrow Wilson was no longer popular 2. A recession followed World War I, and the Democrats were blamed B. Corruption and Scandal 1. Warren Harding hires friends from Ohio, known as the “Ohio Gang” 2. Harding’s ‘friends’ take advantage of the government jobs. C. Teapot Dome Scandal 1. Takes place after Harding’s death (heart attack) 2. Sec. of the Interior (Albert Fall) illegally leased government land to oil Executives 3. Fall, becomes first Cabinet member ever sent to prison. III. Coolidge Prosperity A. Presidency 1923-1929 1. Domestic policy – pro business: his administration cut regulations on businesses 2. Businessmen were put in charge of government agencies B. Industry Booms 1. Government’s pro-business policies made investors more confident 2. This increased confidence led investors to buy more stock. 3. Buying more stock meant a rapid rise in the stock market. 4. Consumers were allowed to buy on credit. (Installment buying) IV. A Limited Role in World Affairs A. Latin America 1. US trade and investment grew with Latin America 2. Potential war with Mexico was resolved diplomatically B. The Soviet Union 1. US was recovering from the Red Scare and Sacco-Vanzetti trial 2. The US refuses to recognize Lenin’s government. (Communism) 3. Communism did away with private property, and attacked religion. C. Washington Conference of 1921 1. The US, Britain, and Japan agreed to limit the size of their navies Chapter 25 Section 2 I. Changes in American Way of Life A. Prohibition 1. It undermined respect for law, and gave rise to organized crime. 2. Manufacture, sale, and transportation of liquor was banned in the US. 3. People began making their own liquor in stills at home. 4. Some smuggled liquor from abroad, or buying it in speak-easies B. 21st Amendment 1. Replaced the 18th Amendment 2. Congress agreed that though alcohol consumption was prohibited it did not stop people from drinking alcohol. II. Women’s Rights A. 19th Amendment 1. Allowed women the right to vote starting in 1920. 2. Women were chosen to elected office. 3. Carrie Chapman Catt led the fight to educate voters and fight for women’s rights (League of Women Voters) B. Notable Changes for Women 1. Ready-made clothing freed women from making their own. 2. Electric appliances meant less time needed for housework. 3. Women began working outside the home pre- and post-WWI. III. Transportation A. Automobile Age 1. A tremendous rise in car sales meant people could live farther away from their workplaces. 2. More and more roads were paved, and more highways built. 3. A great increase in filling (gas) stations 4. Travel became easier and more frequent. Chapter 25 Section 4 - A Nation Divided I. Fear of Radicalism 1. The Red Scare A. U.S. concerned about sabotage by foreigners B. Communist leader Lenin called on workers to unite and overthrow their governments. C. Those who opposed the U.S. government were round up by the thousands (anarchists). D. The result for many “Reds” was deportation. 2. Sacco-Vanzetti 1921 A. Two Italian immigrants arrested for robbery and murder. B. Many believed they were tried based on prejudice, and not evidence. C. They appealed their conviction for 6 yrs. D. In the end, they were executed for their crimes. 3. Quota System A. The Red Scare eventually dies down. B. Nativist pushes for strict policy on immigration C. Congress passes the Emergency Quota Act – 1921 D. Latin America and Canada were excluded from this act. 4. Scopes Trial A. John Scopes, a biology teacher is put on trial for teaching Charles Darwin’s theory of evolution. B. The theory stated that all life had developed from simpler forms over a long period of time. C. Clarence Darrow defended Scopes, he believed that it wasn’t Scopes who was on trial, instead traditional beliefs vs. modern ideas. D. In the end, Scopes was convicted and fined. Laws for teaching evolution remain, but are rarely enforced. II. Racial Unrest 1. The New Klan A. The “old” Klan used terror to keep African Americans from voting after the Civil War. B. As of 1920, the KKK campaigned against immigrants as well as African Americans. C. Members of the KKK strongly supported efforts to limit immigration. D. The Klan gained political influence because of their growing powers. 2. Northern migration A. African American populations grew in the northern cities. B. White Americans felt threatened by the migration. C. Whites would not rent to blacks, and were only offering low-paying jobs to African Americans. D. Less than a year after WWI there were race riots throughout the north. 3. Marcus Garvey A. Led a Black Nationalist movement to cope with racism. B. Garvey, organized the United Negro Improvement Assoc. (UNIA) C. He believed African Americans must rely on each other, and not white people. D. Garvey promoted black pride with a campaign for “Back to Africa”