Unit 1B Class Notes - Boone County Schools
advertisement

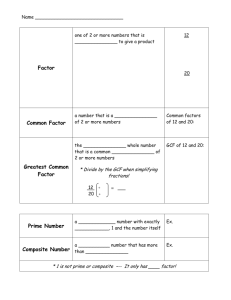
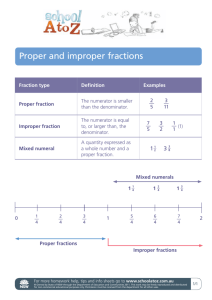
Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Simplify Fractions and Equivalent Fractions Common Core Standard: 3.NF.A.3 Understand that two fractions are equivalent id they are the same size. Recognize and generate equivalent fractions. Learning Targets 1. I can simplify fractions. 2. I can create equivalent fractions. Important Terms Simplify: To write a fraction or expression in simplest form. To reduce or put in lowest terms. Equivalent Fraction: Fractions that name the same amount or part, they are equal. Examples: Part A: Simplify Fractions 18 Write the fraction 24 in simplest form. - Method 1: Use a ladder diagram. - Method 2: Use the GCF (Greatest Common Factor). Part B: Equivalent Fractions - Create two equivalent fractions for each given faction. To do this, multiply or divide both the numerator (top number) and denominator (bottom number) by the same number. - Fill in for the missing number. For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 1 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Try This: Write each fraction in simplest form. 6 4 1) 8 2) 20 3) Find two equivalent fractions for each fraction. 2 1) 3 2) 3) 4 10 4) 10 35 4) 12 72 6 8 1 4 Find the missing numbers that make the fractions equivalent. 4 𝑥 2 40 1) 36 = 18 2) 7 = 𝑥 3) 70 100 7 =𝑥 4) 56 8 𝑥 =2 For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 2 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions Common Core Standard: Learning Targets 1. I can convert improper fractions into mixed numbers. 2. I can convert mixed numbers into improper fractions. Important Terms: 1. Numerator: The top number of a fraction and tells how many parts are being used. 2. Denominator: The bottom number of a fraction and tells how many parts make up the whole. 3. Improper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is greater than or equal to the denominator. Example: 3 4 1 32 9 7 4. Proper Fraction: A fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator. Example: 5. Mixed Number: A number made up of a whole number and a fractional part. Example: Examples: Converting Improper Fractions to Mixed Numbers 15 Write 2 as a mixed number. Converting Mixed Numbers to Improper Fractions 1 Write 2 5 as an improper fraction. Try This: Write each improper fraction as a mixed number. 19 43 1) 5 2) 5 3) Write each mixed number as an improper fraction. 1 9 5) 9 6) 4 7) 18 4 11 For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org 108 9 3 5 4) 98 11 8) 11 4 9 Page 3 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Factors and Multiples Common Core Standard: 6.NS.B.4 Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Learning Targets 1. I can list all factor pairs for whole numbers between 1 and 100. 2. I can list the first 10 multiples of a given number between 1 and 12. Important Terms: 1. Factor: A number that is multiplied by another number to get a product. Example: the factor pairs of 6 are 1 and 6, 2 and 3. 2. Multiple: The product of any number and a whole number is a multiple of that number. Example: the first 10 multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60 Examples: Factor pairs: List all the factor pairs of 48. Answer in pairs: 1 and 48, 2 and 24, 3 and 16, 4 and 12, 6 and 8 Answer in numerical order: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 16, 24, 48 Multiples: List the first 10 multiples of 11. Answer: 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 110 Try This: List all factors of the following numbers. You can list as pairs or in numerical order. 1) 35 2) 12 3) 54 4) 88 List the first 10 multiples of the following numbers. 5) 4 6) 6 For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org 7) 8 8) 9 Page 4 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Prime Factorization Common Core Standard: 4.OA.B.4 Determine whether a given whole number is prime or composite. 5.NBT.A.3 Read and write numbers in expanded form. Learning Targets 1. I can find the prime factorization of a given number. 2. I can write numbers in expanded and exponential form. Important Terms: 1. Prime Number: A whole number greater than 1 that has exactly two factors, 1 and itself. 2. Prime Factorization: A number written as the product of its prime factors. 3. Expanded Form: A number written as the sum of the values of its digits. 4. Exponential Form: A number is in its exponential form when it is written with a base and an exponent. Examples: Prime Numbers: List the first 10 prime numbers. Answer: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29 Prime Factorization: Expanded Form: Write 236,536 in expanded form. Answer: 200,000 + 30,000 + 6000 + 500 + 30 + 6 Exponential Form: Write the following in exponential form. a. 2 × 2 × 2 answer: 2³ For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org b. 2 × 2 × 3 × 4 × 4 × 4 answer: 2² × 3 × 4³ Page 5 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Try This: Write the following numbers using expanded form. 1) 6587 2) 587,506 3) 4,485,123 4) 98,742 Find the prime factorization of the following numbers. Write your answer in exponential form when possible. 5) 99 6) 150 7) 840 8) 402 For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org 9) 249 10) 284 Page 6 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Greatest Common Factor (GCF) Common Core Standard: 6.NS.B.4 Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Learning Target: I can find the greatest common factor of two numbers. Key Terms Factor: A number that is multiplied by a number to get a product. For example, the factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6. Greatest Common Factor: The largest common factor of two or more numbers. This is sometimes referred to as the GCF. Methods 1. List the factors. 2. Use a Ladder Diagram Examples 1) Find the GFC of 16 and 24. Method 1: List the factors 2) Find the GFC of 12 and 18. Method 2: Use a Ladder Diagram 3) There are 12 boys and 18 girls in Mr. Smith’s science class. The students must form lab groups. Each group must have the same number of boys and the same number of girls. What is the greatest number of groups Mr. Smith can make it every student must be in a group? Factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 Factors of 18: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18 The GCF of 12 and 18 is 6, so Mr. Smith students can create 6 lab groups. Try This Write the GCF of each set of numbers using Method 1. 1) 10 and 35 2) 28 and 70 For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org 3) 36 and 72 Page 7 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Write the GCF of each set of numbers using Method 2. 4) 60 and 84 5) 45 and 75 6) 42 and 56 Write the GCF of each set of numbers using either method. 7) 66 and 88 8) 14 and 17 9) 28 and 42 Solve the following word problems. 10) The local recreation center held a scavenger hunt. There were 15 boys and 9 girls at the event. The group was divided into the greatest number of teams possible with the same number of boys and each team and the same number of girls on each team. How many teams were made if each person was on a team? 11) Ms. Kline makes balloon arrangements. She has 32 blue balloons and 24 yellow balloons. Each arrangement must have the same number of each color. What is the greatest number of arrangements that Ms. Kline can make if every balloon is used? 12) Peter has 18 oranges and 27 pears. He wants to make fruit baskets with the same number of each fruit in each basket. What is the greatest number of fruit baskets he can make? For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 8 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Least Common Multiple (LCM) Common Core Standard: 6.NS.B.4 Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Learning Target: I can find the least common multiple of two numbers. Key Terms Least Common Multiple: The smallest number, other than zero, that is a multiple of two or more numbers. Also referred to as the LCM. Multiple: The product of any number and a whole number is a multiple of that number. For example, multiples of 2 include 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20…. Methods 1. List the Multiples. 2. Use a Ladder Diagram Examples Find the LCM of 5 and 6. Method 1: List the multiples Find the LCM of 8 and 12 Method 2: Use a ladder diagram. 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45… 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54… LCM: 30 Try This Write the LCM of each set of numbers using Method 1. 1) 6 and 20 2) 5 and 8 3) 10 and 15 Write the LCM of each set of numbers using Method 2. 4) 6 and 7 5) 22 and 55 6) 14 and 6 For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 9 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Write the LCM of each set of numbers using either method. 7) 21 and 63 8) 6 and 16 9) 28 and 10 Solve the following word problems. 10) Two students are stacking blocks, one on top of the other. Reece’s blocks are 5 cm high and Maddy’s blocks are 8 cm high. How tall will their stacks be when they are the same height for the first time? 11) During a promotion, a music store gives a free CD to every fifteenth customer and a free DVD to every fortieth customer. Which customer will be the first to get both gifts? 12) Pencils are sold in packs of 12 and erasers are sold in packs of 9. Mr. Jones wants to give each of 36 students a pencil and an eraser. What is the least number of packs he should buy so that there are no left overs? 13) Tony wants to make 36 party bags. Glitter pens come in packs of 6. Stickers come in sheets of 4, and balls come in packs of 3. What is the least number of each package he should buy to have 1 of each item in every party bag, and no supplies left over? For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 10 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Dividing Fractions by Fractions Common Core Standard: 6.NS.A.1 Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions. Learning Target: I can divide fractions. Important Term: Reciprocal: One of two numbers whose product is one. For example, 2/3 and 3/2 are reciprocals. Important Information You DO NOT need common denominators. To find the reciprocal of a fraction, flip it. 4 2 9 1 10 Ex. ¾ is 3 = = 1 9 2 10 Steps 1. Multiply by the reciprocal. a. Change the division sign to a multiplication sign. b. “Flip” the fraction that comes after it. 2. Look to see if you can simplify before multiplying. Remember you can simplify any numerator with any denominator as long as they have a common factor. 3. Multiply numerators. 4. Multiply denominators. 5. Make sure your answer is in simplest form. Don’t forget to ask yourself the following questions before moving on to the next problem. If you answer YES to either of these questions you MUST fix that before moving on!!! o Is this an improper fraction? o Can it be reduced? Example: For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 11 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Try This: 2 1 1) 3 ÷ 6 5 3 2) 8 ÷ 4 4) 9 7 ÷ 12 16 5) 12 ÷ 6 7) 7 8 8) 3 ÷4 11 5 5 6 ÷9 3 4 2 3) 9 2 ÷5 10 6) 11 3 ÷5 15 9) 7 8 1 ÷6 1 4 10) Julia has of a yard of felt. How many puppets can she make if she uses of a yard of felt for each puppet? For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 12 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Date Dividing Fractions by Whole Numbers & Mixed Numbers Common Core Standard: 6.NS.A.1 Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions Learning Targets: I can divide fractions by whole numbers. I can divide fractions by mixed numbers. Important Information You DO NOT need common denominators. To find the reciprocal of a fraction, flip it. The reciprocal of… 3 4 2 9 1 10 Ex. 4 is 3 is 2 is 1 9 10 To find the reciprocal of a whole number or mixed number, make it a fraction first then flip it. 8 1 1 5 2 Ex. 8 = 1 is 8 2 2= 2 is 5 Steps 1. Look for any whole number of mixed numbers and make them fractions. 2. Multiply by the reciprocal. a. Change the division sign to a multiplication sign. b. “Flip” the fraction that comes after it. 3. Look to see if you can simplify before multiplying. Remember you can simplify any numerator with any denominator as long as they have a common factor. 4. Multiply numerators. 5. Multiply denominators. 6. Make sure your answer is in simplest form. Don’t forget to ask yourself the following questions before moving on to the next problem. If you answer YES to either of these questions you MUST fix that before moving on!!! o Is this an improper fraction? o Can it be reduced? Examples: 1) 2) For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 13 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions Try This: 9 1) 16 ÷ 6 3 1 2) 12 ÷ 2 4 7 15 4) 1 7 ÷ 12 7) 1 1 2 ÷ 3 4 3) 7 ÷ 1 ¾ 5 3 5) 16 ÷ 1 6 ∙ 2 5 8) 2 3 4 ÷1 2 3 4 6) 3 11 ÷ 1 5 ÷5 9) 11 12 ÷ 9 10 ÷1 1 4 2 10) A washing machine holds 36 gallons of water. It fills at a rate of 8 gallons a minute. How long does the machine 5 take to fill with water? 1 5 11) A roll contains 80 2 feet of ribbon. It takes 3 6 feet of ribbon to make a bow. How many bows can be made? For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 14 Unit 1B – The Number System – Factors, Multiples and Fractions For more help, go to www.khanacademy.org Page 15