File - Religious Education 4 U
advertisement
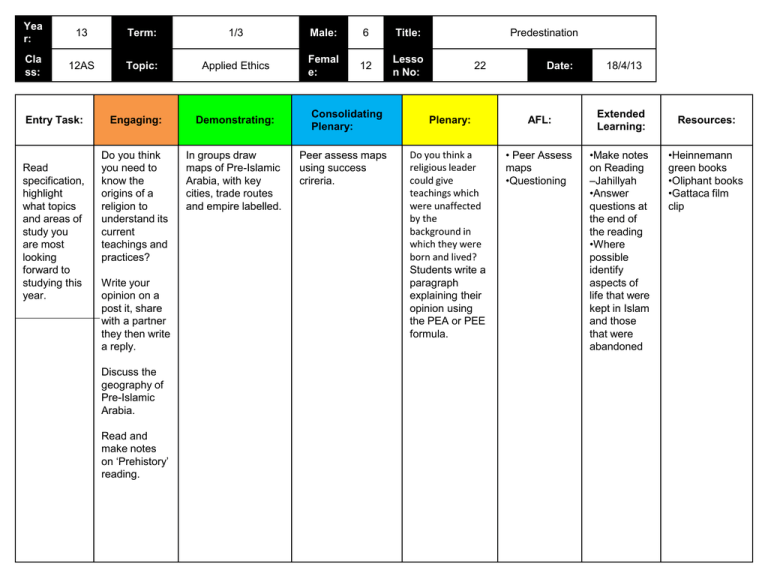
Yea r: 13 Term: 1/3 Male: 6 Title: Cla ss: 12AS Topic: Applied Ethics Femal e: 12 Lesso n No: Entry Task: Read specification, highlight what topics and areas of study you are most looking forward to studying this year. Engaging: Demonstrating: Do you think you need to know the origins of a religion to understand its current teachings and practices? In groups draw maps of Pre-Islamic Arabia, with key cities, trade routes and empire labelled. Write your opinion on a post it, share with a partner they then write a reply. Discuss the geography of Pre-Islamic Arabia. Read and make notes on ‘Prehistory’ reading. Consolidating Plenary: Peer assess maps using success crireria. Predestination 22 Date: Plenary: AFL: Do you think a religious leader could give teachings which were unaffected by the background in which they were born and lived? Students write a paragraph explaining their opinion using the PEA or PEE formula. • Peer Assess maps •Questioning 18/4/13 Extended Learning: •Make notes on Reading –Jahillyah •Answer questions at the end of the reading •Where possible identify aspects of life that were kept in Islam and those that were abandoned Resources: •Heinnemann green books •Oliphant books •Gattaca film clip Entry Task: • Read the specification, and highlight what topics and areas of study you are most looking forward to studying this year. Today's Date: 23 March 2016 Year: 12 Today’ s Title: Term: 1/3 Topic: AS: Islam The Geography of Pre-Islamic Arabia Learning Outcomes: To explain the geographical background from which Islam emerged (AO1) To evaluate the extent to which the geographical background of PreIslamic Arabia effected the emergence of Islam (AO2) A01 – Knowledge & Understanding Evaluation A02 – Analysis & What do you think? • Do you think you need to know the origins of a religion to understand its current teachings and practices? Pre-Islamic Arabia • What was life like in Arabia? • How did the geography of the land effect how people lived? • What trade links were established in Pre-Islamic Arabia? • How much did this influence the life of Muhammad (pbuh) and the rise of Islam? Pre-Islamic Arabia History • Stone Age settlements from c.3000 BCE have been found in Arabia. There are no written records until after 1000 BCE. The earliest records have been found in modern-day Yemen and are in the form of inscriptions on stone and bronze tablets. These are written in many languages including Old North and Old South Arabian, Aramaic, Greek and Latin. • A Greek, Eratosthenes, writing in the 3rd century said that four tribal peoples lived in the edge of the Yemen desert controlling most of the trading routes through the area. These people were nomads and Bedouins who spent their lives in the desert. They relied on their animals and on trade with other groups. There were frequent battles between tribes. Geography The Arabian peninsula was a very arid a dry place, neighboured by three seas. The Red sea, Arabian sea and the Persian Gulf The area can be largely split into three sections. The southern peninsula of Yemen, the western coast of Hijaz and the central and eastern area, Najd. In the southern lands towns and villages prospered as the landscape was more hospitable and agriculture was able to prosper Agriculture This difference between the regions, as far as vegetation is concerned, can also be observed in the regional produce. In the inner regions, date trees thrive in the arid climate, and being hardy with little need of water, dominate, whereas Yemen is renowned for the sweetgum (liquidambar styrax), which is a symbol of productivity and luxury. Dates are the main food source for people in the oases. There are a few areas where wheat, barley, millet, onions, sesame, various vegetables, tobacco, apricots, almonds, grapes and citrus fruits can be grown. In the southern regions it is possible to grow such a variety of crops as bananas, cotton, coffee and even rice and sugar cane. Trade The increased trans-Arabian trade produced two important results. One was the rise of cities that could service the trains of camels moving across the desert. The most prosperous of these- -Petra in Jordan and Palmyra in Syria, for example--were relatively close to markets in the Mediterranean region, but small caravan cities developed within the Arabian Peninsula as well. The most important of these was Mecca, which also owed its prosperity to certain shrines in the area visited by Arabs from all over the peninsula. • Some Arabs, particularly in the Hijaz, held some religious beliefs that recognized a number of gods as well as a number of rituals for worshiping them. The most important beliefs involved the sense that certain places and times of year were sacred and must be respected. At those times and in those places, warfare, in particular, was forbidden, and various rituals were required. Foremost of these was the pilgrimage, and the best known pilgrimage site was Mecca. • By the 4th century Makkah was ruled by the Jurhum tribe. The Bedouins around Makkah formed an alliance c.400 CE and settled in Makkah. This was brought together by the Quraysh tribe, who wanted to take on a residential style of life rather than their traditional nomadic existence. • Through family links the Quraysh turned Makkah into an important trading centre standing on the junction of the north-south and east-west routes. Makkah had water for camels but not enough for agriculture and depended for its existence on the merchants passing through the city. • Although there was fighting all around the area, Makkah provided a safe place in the country. Large trading fairs were set up there and pilgrimage to the shrine of the Ka’bah became increasingly important. The Ka’bah contained statues of the many gods of the tribes who travelled through Makkah on their trading routes. • Changes in Makkah produced a settled and established community which then moved towards adopting a common language. The city, with its established trading community, produced a social structure which was based on trade and wealth. Empires Byzantine The Byzantine Empire, the successor of the Roman Empire, reigned over the Balkan Peninsula, Anatolia, Syria, Palestine and Egypt from 330 to 1450. Before the emergence of Islam in the Arabian Peninsula and its sovereignty over a huge region, Byzantium was one of two significant forces in the region, holding territory over three continents. The era between 610-641, which corresponds to the birth of Islam in Arabia, was one of the harshest eras in Byzantine history. The state was going through severe hardships during this period, when there were dynastic struggles, corruption in civil and military administration, and economic decline. Economic and religious embargos laid upon the members of different sects led to serious problems between the state and the people. Byzantine In addition to all these domestic threats, as the expansion policy of the Byzantines targeted the lands of the Sassanid Empire, they were faced with serious threats from the Avars and Slavs, bringing the state to the edge of collapse. The invasion by the Sassanid Empire into the eastern provinces in 611 led to the loss of Antioch, Damascus, Jerusalem and Egypt; The Persian army then targeted Istanbul, moving along the coast of the Bosphorus. This predicament forced the Byzantine emperor Herakleios to sign a treaty, the terms of which were considerably detrimental. The fact that the Sassanid Empire had defeated the Byzantines, who were considered to be people of the Book (of an Abrahamic, monotheist religion), delighted the polytheist Arabs to whom Prophet Muhammad was conveying Islam. This defeat also led the polytheists to think that the end of the Muslims would be the same as that of the Byzantines. Pre-Islamic Arabia Use the maps to create your own map of Pre-Islamic Arabia. You should include: Mecca Medina Yemen Jerusalem Damascus Byzantine Empire Sassanid Empire Red sea, Persian Gulf, Arabian Sea Discuss • Do you think a religious leader could give teachings which were unaffected by the background in which they were born and lived? • Write a paragraph explaining your opinion using PEE (Point, Evidence, Explain) or PEA (Point, Evidence, Analysis) Homework • Make notes on Reading –Jahillyah • Answer questions at the end of the reading • Where possible identify aspects of life that were kept in Islam and those that were abandoned








