Interference Of Waves
advertisement

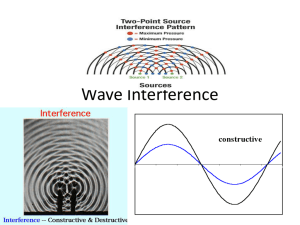
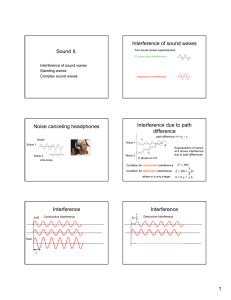
Interference Of Waves Interference When two or more waves act simultaneously on the same particle in a medium Resultant displacement is equal to the sum of the individual displacements Principle of Superposition – sum of two waves Types of Interference Constructive – 2 waves interfere to produce a resultant displacement greater than the displacement of one Destructive – 2 waves interfere and produce a wave smaller than one wave Phase When the crests and troughs of two waves are aligned for constructive interference – In Phase When crest of one wave repeatedly meet troughs of another wave and destructive interference occurs – Out of Phase Standing Wave Two interfering waves have the same amplitude and wavelength but opposite directions Wave produced remains relatively stationary Definitions Node – points of standing wave that remain at rest – where destructive interference is occurring Loop or Antinode – double crest or double trough – where constructive interference occurs ½λ Natural Frequency Only certain frequencies of waves produce standing wave patterns Frequencies that produce standing wave patterns are called Natural Frequencies First Harmonic Lowest frequency of standing wave Also called fundamental freq. One loop and two nodes L=½ Overtones Other natural frequencies of vibration Multiples of the fundamental First Overtone/ nd 2 Harmonic Two loops and three nodes L= Second Overtone/ rd 3 Harmonic Three loops and five nodes L = 3/2 Frequency of given harmonic is a multiple of the fundamental frequency Fn = n F1 Example A piano string is 1.10m long and has a mass of 9.00g a) how much tension must the string be under if it is to vibrate at 131Hz? B) what are the frequencies of the first four harmonics?