The Great War - barren.k12.ky.us
advertisement

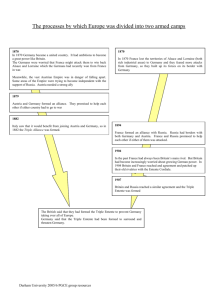
CH 22 Background and Causes The causes of WWI are usually put into four MAIN categories: Militarism Alliances Imperialism Nationalism Militarism “the belief or desire of a government or people that a country should maintain a strong military capability and be prepared to use it aggressively to defend or promote national interests” Governments place a high emphasis on military expansion Militarism • After 1871 alliances lead to an armaments race • • Became increasingly serious between 1900 and 1914. Military expenditures increased dramatically • France 10%, Britain 13%, Russia 39% • Germany being the most militaristic at 73% Militarism Conscription- Compulsory enlistment for state service; typically military ○ Also known as draft All continental powers had enforced conscription system after 1870 ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ ○ France since the Revolutionary Wars A-H by 1868 Germany since 1870 Italy since 1873 Russia since 1874 Great Britain did not have a conscription system France vs. Germany Franco-Prussian War After war Bismarck wanted to keep France isolated and weak Began building a strong army and navy to do so Seeing what Germany was doing France started building a strong military as well Both built massive militaries to protect against one another Britain vs. Germany Germany very critical about the Boer Wars - 1895 Kaiser William II sent telegram to Boer president congratulating them on their stand against the Brits. Naval rivalry top concern among these two countries - In 1897 the Reichstag allocated funds to speed up naval expansion - British response was the Dreadnought Russia Russo-Japanese War After defeat started to rebuild military Wanted strong military to control interest in the Balkans Alliances Agreement made between two or more countries to come to the aid if one needs help. Secret alliances sprouted all over Europe starting in the late 1800’s Alliances Alliances in the late 1800’s hinged on: German and French enmity Competing interests in the Balkans by A-H and Russia Germany’s fear of being attacked from both east and west 1879 The Dual Alliance 1881 Austro-Serbian Alliance Germany and AustriaAustria-Hungary made Hungary made an alliance an alliance with Serbia to protect themselves from to stop Russia gaining Russia control of Serbia 1882 The Triple Alliance Germany and AustriaHungary made an alliance with Italy to stop Italy from taking sides with Russia 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance 1914 Triple Entente (no separate peace) Russia formed an alliance with France to protect herself against Germany and AustriaHungary Britain, Russia and France agreed not to sign for peace separately. 1907 Triple Entente 1907 Anglo-Russian Entente 1904 Entente Cordiale This was made between Russia, France and Britain to counter the increasing threat from Germany. This was an agreement between Britain and Russia This was an agreement, but not a formal alliance, between France and Britain. Germany and A-H vs. Russia Germany enjoyed good relations with Russia 1873 Bismarck forged the Three Emperors’ League Russo-Turkish War (1877-1878) ○ In 1881 Serbia signed the Austro-Serbian Alliance Why would Serbia sign this alliance if it looked to Russia for leadership? Germany and A-H vs. Russia 1879 fearing Russia, Germany and A-H forged the Dual Alliance. ○ This alliance became a central factor of European diplomacy for the next thirty-five years. 1882 Italy joins into an alliance with Germany and A-H ○ Known as The Triple Alliance ○ G and A-H wanted to keep Italy from joining with Russia 1879 The Dual Alliance 1881 Austro-Serbian Alliance Germany and AustriaAustria-Hungary made Hungary made an alliance an alliance with Serbia to protect themselves from to stop Russia gaining Russia control of Serbia 1882 The Triple Alliance Germany and AustriaHungary made an alliance with Italy to stop Italy from taking sides with Russia 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance 1914 Triple Entente (no separate peace) Russia formed an alliance with France to protect herself against Germany and AustriaHungary Britain, Russia and France agreed not to sign for peace separately. 1907 Triple Entente 1907 Anglo-Russian Entente 1904 Entente Cordiale This was made between Russia, France and Britain to counter the increasing threat from Germany. This was an agreement between Britain and Russia This was an agreement, but not a formal alliance, between France and Britain. Germany Encircled The last thing Germany wanted was and alliance between France and Russia. Despite the political differences factors drew Russia and France together. Both faced diplomatic isolation Cultural ties between France and Russian aristocracy was still strong. In 1890, Bismarck dismissed by William II. ○ 1894 France and Russia agree to the Franco- Russian Alliance. Great Britain Great Britain had been diplomatically isolated until around 1901. ○ After the Russo-Japanese War; Britain worried more about Germany than Russia. The Entente Cordiale (1904) was reached between Great Britain and France. ○ Eliminated tension between the two powers The Moroccan Crisis (1905) France had interest in Morocco Germany only had commercial interest William II decided to test the new agreement between F and GB. French gov’t reacted with fury but backed down. Algeciras Conference (1906) ○ Forced Germany to recognize French interest in Morocco ○ Brought Russia and GB closer together 1879 The Dual Alliance 1881 Austro-Serbian Alliance Germany and AustriaAustria-Hungary made Hungary made an alliance an alliance with Serbia to protect themselves from to stop Russia gaining Russia control of Serbia 1882 The Triple Alliance Germany and AustriaHungary made an alliance with Italy to stop Italy from taking sides with Russia 1894 Franco-Russian Alliance 1914 Triple Entente (no separate peace) Russia formed an alliance with France to protect herself against Germany and AustriaHungary Britain, Russia and France agreed not to sign for peace separately. 1907 Triple Entente 1907 Anglo-Russian Entente 1904 Entente Cordiale This was made between Russia, France and Britain to counter the increasing threat from Germany. This was an agreement between Britain and Russia This was an agreement, but not a formal alliance, between France and Britain. The Triple Entente Russia joined with France and GB in 1907 Feared Germany’s expansion of Army as well as, A-H. Unlike the Triple Alliance they were not required to come to the aid if another was attacked. It was a moral obligation to protect each other. Imperialism Scramble for Africa- Push to gain control over parts of Africa. The Balkans Asia Nationalism Nationalism- intense pride in one’s country or culture. East Europe becomes a hot box of nationalism before World War 1. The Balkan Tinderbox The Balkans becomes the key to maintaining peace in Europe. In 1897 Russia and Austria-Hungary agreed informally to respect the status quo in the region. In 1903 a revolution led to the assassination of the king and queen of Serbia. Russia quickly recognized the new king hoping Pan- Slav ideas would dominate. A-H fearing this would drive Serbia closer to Russia, recognized the fait accompli The Balkan Tinderbox Relations between Serbia and A-H deteriorated when Serbia tried to lessen its economic dependence. Signed a commercial treaty with Bulgaria A-H responded by banning the import of Serbian livestock 1906 and economic battle known as the “Pig War” Instability in Turkey Political instability caused Russia and A-H desire for the Balkans to increase. In 1894-1895 the Turkish Sultan had about 200,000 Armenians murdered. ○ Done because of Armenian nationalism encouraged by Russia ○ In 1908 a group known as the “Young Turks” lead a revolt against the Sultan Bosnia Turkish instability lead to the Bosnian Crisis of 1908. ○ At Congress of Berlin 1878 A-H started to occupy Bosnia and Herzegovina. October of 1908 after Bulgaria declared its independence A-H annexed Bosnia and Herzegovina. ○ Feared that the Young Turks would inspire a revolt Bosnia The annexation was a clear violation of the agreement of the Congress of Berlin. ○ Russian and Serbia responded with fury. ○ Strained relations with Italy ○ War was avoided with the help of Archduke Francis Ferdinand. ○ Russia drew closer to Britain. ○ Serbian nationalist groups like the “Black Hand” gained support in the area. The Balkan Wars Italy provided a kindling for another flare up. ○ 1911 they invaded Libya which became known as the Tripoli War ○ France agreed to the invasion if Italy would recognized their influence in Morocco. The Balkan League formed in 1912 ○ First Balkan War lasted less than a month with victory for the League. The Balkan Wars The Balkan Wars Germany didn’t want any Balkan state to become too strong in fear of nationalist uprisings. The Treaty of London of May 1913 The Second Balkan War – fought between Bulgaria, Serbia, and Greece. As a result of the Peace of Bucharest Germany readied its military. The Spark Archduke Francis Ferdinand- heir to the Habsburg throne. More sympathy to South Slavs problems than being pro-Germany. Disliked by the Hungarians On June 28, 1914 Gavrilo Princip shot and killed the Archduke and his wife in Sarajevo. The Ultimatum A-H took this assassination as a chance to crush Serbia. William II urged retaliation blaming Serbia for the assassination Germany offers A-H what is known as the “blank check” A-H sends Serbia an Ultimatum July 23, 1914. Germany’s plan for war 1905 Alfred von Schlieffen creates the “Schlieffen Plan” This was to solve the German fear of fighting on two fronts. Wanted to attack France quickly taking them out. After defeat of the French turn towards fighting Russia in the West. France’s plan for the War France had its version of the Schlieffen Plan Called the “Plan XVII” France would send two different armies to fight Germany. Unlike Germany, France didn’t have to worry about fighting a two front war. Serbia’s Answer With Russian backing Serbia mobilized its military on July 25, 1914. Serbia agreed to all the conditions of A-H ultimatum except for one thing. A-H wanted to be part of the investigation into the “Serb” plot behind the assassination of the Archduke. A-H would not accept anything but total compliance. And so the war begins…. July 28, 1914 exactly one month after the assassination of the Archduke A-H declares war on Serbia. A-H plots a plan to make it look like its Russia’s fault if Europe goes to war. Britain still hesitant to join due to problems at home And so the war begins…. August 1- Germany declares war on Russia. August 3- Germany declares war on France August 4- Great Britain declares war on Germany when they invaded Belguim Opening Stages of the War The Schlieffen Plan was put into effect early in August of 1914. Both sides underestimated each others capabilities. Russia quick mobilization causes Germany to send troops east. Germany gets within 35 miles of Paris France signs a secret treaty with Italy. Opening stages of the war In November 1914, the last open battle on the western front takes place. Ypres, Belgium British forces stop Germany from reaching the French Channel. Neither side could make any advances and a stalemate occurs. The start of Trench Warfare begins at this time. Trench Warfare Spades and barbed wire become more important to the fight than rifles. Over 6,000 miles of trenches were dug by both sides in France. Life in the trenches was not an easy one. Had to deal with rats and lice, as well as, enemy sniper and artillery fire. New weapons introduced during this time presented even bigger obstacles for the troops that would “go over the top” New Weapons New weapons that had never been used on a wide scale during war are introduced. Examples: machine guns, tanks, air planes, gas. New Weapons Machine gun was not useful at the beginning of war. GB rejected the use of it. G seeing its potential employed it for defensive purposes. As accurate as about 80 rifles. New Weapons Start of the war used for recon. Advanced into fighter planes and bombers. Red Baron- German ace. (Confirmed 80 kills) New Weapons Conditions inside the tanks were miserable for the crew. First primarily used for clearing path for infantry in “no man’s land” First tank vs. tank battle took place in 1918 between 3 British tanks and 3 German tanks. New Weapons Poison gas prior to WWI considered uncivilized. Two primary gases used; chlorine, and mustard gas. At the start of the war casualties from poison gases were high by the end it was rare to have a casualty. Home Front Waging a full scale war required full support on the “home front” Propaganda became increasingly popular to get this full support. Political divisions began to be pushed aside. Daylight savings time put into action. Soldiers and Civilians Women begin to take over jobs normally done by men. Received lower wages Working conditions still bad for women. Censorship in news paper about the war comes about in every country. This infuriates the soldiers. Soldiers and Civilians Life in the trenches allowed for close bonds to be made. Soldiers didn’t like their commanding officers. Often felt more sympathy for soldiers in the other trenches than politicians and generals back home. Christmas day 1914, France, Britain, German troops call for one-day truce. The Eastern Front In early stages of the war Russian army advances into eastern Prussia. Russian military equipment. very inadequate in the beginning stages of war. In 1915, a German offensive drove Russia back 100 miles and ended 100 years of Russian control over Poland. Middle East, Africa, and Asia Turkey enters the war in 1914 on the side of the Central Powers. British leaders like Winston Churchill believed strikes on Turkey would undermine German interest in the Balkans. Hoped that this would keep Bulgaria out of the war. This became known as the Gallipoli Campaign. Final Stages of the War The United States remained neutral in first years of the war. Popular sympathy lay with the allies Germany tried to capitalize on American anger over the British blockade. Woodrow Wilson had been re-elected in 1916 on the promise that he would keep America out of the War. Sinking of the Lusitania Unrestricted submarine warfare was Germany’s only way to fight Britain's control of the seas. May 7, 1915 a German U-boat sank the British cruise liner Lusitania. Killed 128 U.S. citizens Despite denial by the U.S. it was carrying ammunition to Britain. Sinking of the Lusitania September 1, Germany accepts U.S. demand to stop unrestricted submarine warfare. After British victory at the Battle of Jutland, Germany announced it would sink any ship in the “war zone” Zimmermann Telegram German foreign secretary, Arthur Zimmerman, made a secret offer to Mexico if they would attack the U.S., then they would be given back the lost territory in TX, AZ, and NM the note was intercepted by the British neither Wilson nor Mexico took the note seriously however, the American public called for war Russia Withdraws By 1916 the Russian army was depleted. The Russian home front was on the verge of collapse. March 15, 1917 Nicolas II, abdicates the throne Amid demands for political reform, strikes, and bread riots. Russia Withdraws November 6, 1917 revolutionary group known as the Bolsheviks take control of the Russian gov’t. With the Germany army in the Ukraine, Russia signed the Treaty of BrestLitovsk which ended Russian participation in the war. Enter the United States April 6, 1917 the U.S. enters the war Wilson promised the war would “make the world safe for democracy” The U.S. focused its industrial strength on producing wartime materials. Produced an army that reached 4 million half was in France by November 1918. The entry of the United States was fatal for Germany. The Fourteen points and peace January 8, 1918 President Wilson gave his “fourteen points” speech to Congress This was a blueprint for permanent peace. Germany appeared willing to agree to Wilson’s plan for peace. After a German U-boat sank a British cruise liner Wilson called off negotiations. On November 11, 1918 an armistice was signed bringing an end to fighting in Europe. Treaty of Versailles Paris Peace Conference (Jan. 1919) – attended by the “Big 4” (leaders of the 4 major Allied powers): Woodrow Wilson (U.S.) David Lloyd George (G.B.) George Clemenceau (France) Vittorio Orlando (Italy) Treaty of Versailles remember: Russia had dropped out of the war in 1917 and Italy joined Allies in 1915 -Goals – Wilson concerned about world peace – brought 14 Points with him – the other 3 leaders wanted to punish Germany (esp. France) Treaty of Versailles Treaty of Versailles – officially ended WWI – compromise – included: War Guilt Clause – forced Germany to take the blame for starting the war (big mistake!) Germany stripped of all colonies and loses some land in Europe Treaty of Versailles -Alsace Lorraine back to France, territory taken from Germany and used to create Poland Germany forced to pay reparations (payment for damages) to Allies - $33 billion total Treaty of Versailles German military restricted -not allowed to have Air Force -navy restricted -army reduced to 100,000 League of Nations created Treaty of Versailles Germany signed it on June 28, 1919 Republicans in Congress were upset that they were not represented in Versailles. they refused to approve the treaty The U.S. never joined League of Nations (very weak without U.S.)