Notes - Godley ISD

Force, Work, and
Simple Machines
7
th
Grade Science Homework
Name: ____________________________________
Date: _________________ Period: __________
Part I: Force
In 7 th grade, we will learn about how the skeletal and muscular systems work together to generate movement.
More importantly, we will learn how they work together to generate force. A force is anything that causes an object to change speed, change direction, or change shape. When you lift a cell phone to your ear, your muscles create the force needed to move the phone. When you throw a ball or kick a box on the floor, again your muscles are generating a force that causes the ball or box to change direction, speed, or shape.
1) What is force? A force is _____________________________________________________________________________________
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
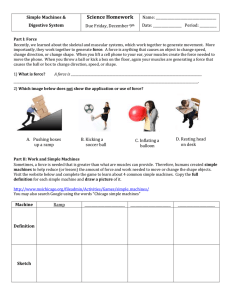
2) Which image below does not show the application or use of force?
A.
Pushing boxes
up a ramp
B. Kicking a
soccer ball
C. Inflating a
balloon
D. Resting head
on desk
Part II: Work and Simple Machines
Sometimes, a force is needed that is greater than what our muscles can provide. Therefore, humans created
simple machines to help reduce (or lessen) the amount of force and work needed to move or change the shape of objects. Visit the website below and play the game to learn about four common simple machines. Copy the
definition for each simple machine and draw a picture of it. http://www.msichicago.org/fileadmin/Activities/Games/simple_machines/
(You may also search Google using the words “Chicago simple machines” )
Machine Inclined Plane (ramp) ________________________ ________________________ ______________________
Definition
Sketch
PART III: Energy, Work, and Force
Work happens when an object moves a certain distance when a force is applied. This releases mechanical energy, and it is measured in units called joules. Work is calculated by multiplying force by distance.
Sometimes, force can be applied, but the object does not move. In this case, no work is done.
What is work?
What unit is used to measure work?
If an object does not move, how much work is done on the object?
There are different ways to accomplish work, such as making use of inclined planes, pulleys or other simple machines. Simple machines allow you to decrease the force you need to do work by increasing the total distance that the force is exerted. Thus, the total amount of energy or work is the same, it just seems easier.
Using the formula and units chart, complete the problems below.
Formula and Units Chart
Type of Measurement
Force
Distance
Work (Force x Distance)
Units Used
Newton (N)
Meters (m)
Joules (J)
1.
A frog uses a force of 3 N to leap 2 meters. How much work did the frog do?
2.
An elephant traveled 50 meters and exerted a total force of 100 N during its trip. How much work did the elephant do?
3.
Joe Jonas bet Justin Bieber that he could move Miley Cyrus’s Mercedes farther than Justin. Joe moved the car 5 meters and exerted 50 N of force. Justin Bieber exerted 75 N of force but did not move the car. How much work did Joe and Justin do? Who did more work?