Pancreas: Anatomy & Physiology
advertisement
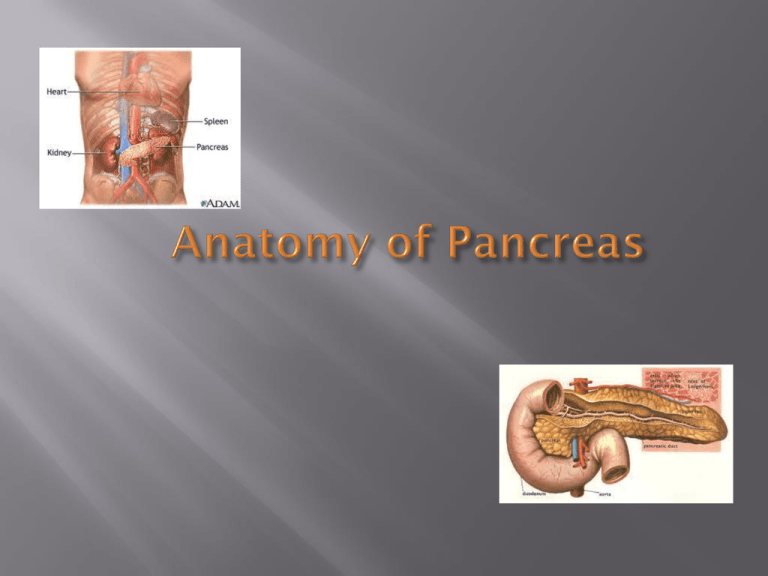
Identify location of the Pancreas Recognize important anatomical relations to the pancreas Identify different parts of the pancreas Recognize main and accessory pancreatic ducts Identify blood supply of the pancreas Discuss lymphatic drainage, and nerve supply of the pancreas Pancreas is an elongated accessory digestive gland It is a retro peritoneal organ that lies transversely crossing the bodies of L1-L2 vertebra “ trans pyloric plane” It is both an endocrine and exocrine organ Location: Retro-peritoneum, 2nd lumbar vertebral level Has an oblique, transverse position Parts of pancreas: head, neck, body and tail Anatomical relations & Parts Parts: Body Head, Neck, Tail Uncinate process Includes uncinate process Flattened, 2 – 3 cm thick Right border: related to the 2nd and 3rd portions of duodenum Superior Pancreatico Duodenal Artery(SPDA) and Inferior Pancreatico Duodenal Artery (IPDA) anastamose between the rt. lateral border & the duodenum 2.5 cm in length Straddles SMV and PV Superior border relates to the pylorus Superior mesenteric vessels emerge from the inferior border Posteriorly, SMV and splenic vein confluence to form portal vein Posteriorly, most often no branches to pancreas Elongated, long structure Anterior surface, separated from stomach by lesser sac Posterior surface, related to aorta, Lt. adrenal gland, Lt. renal vessels and upper 1/3rd of Lt. kidney Splenic vein runs embedded in the post. surface closer to the superior border Inferior surface is covered by transverse mesocolon Posterior relations Narrow, short segment Lies at the level of the 12th thoracic vertebra Ends within the splenic hilum Lies in the splenophrenic ligament Anteriorly, related to splenic flexure of colon May be injured during splenectomy (fistula) Main duct (Wirsung) runs the entire length of pancreas Joins CBD at the ampulla of Vater Variety of major arterial sources (Celiac, SMA and Splenic) Celiac Common Hepatic Artery Gastroduodenal Artery Superior pancreaticoduodenal artery which divides into anterior and posterior branches SMA Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery which divides into anterior and posterior branches Arterial Supply of Pancreas Follows arterial supply Ultimately, into portal vein Rich periacinar network that drain into 5 nodal groups Superior nodes Anterior nodes Inferior nodes Posterior PD nodes Splenic nodes Sympathetic fibers from the splanchnic nerves Parasympathetic fibers from the vagus Rich afferent sensory fiber network Ganglionectomy or celiac ganglion blockade interrupt these somatic fibers (pancreatic pain) However the origin of pancreatic pain is difficult to explain anatomically Keith L. Moore Clinically Oriented Anatomy Sixth edition pages 265-268 Keith L. Moore Clinically Oriented Anatomy Sixth edition pages 265-268 www.medicalstudent.com www.netteranatomy.com http://www.bartleby.com/107/