ALevelComputing_Session3
advertisement
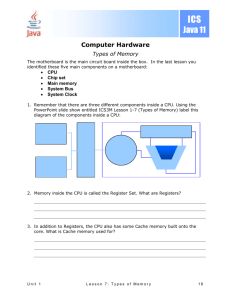
Session Objectives#3 COULD explain the role memory plays in computer processing SHOULD describe the purpose of a CPU and its individual components MUST identify components of a CPU Explore key factors affecting computer performance. A-Level Computing#BristolMet Processing Components Starter... Convert the binary digits denary) 10 1101 to decimal (also known as 32 16 8 4 2 1 X1 x0 x1 x1 x0 x1 =32 =0 =8 =4 =0 =1 = 32+0+8+4+2+1 = 45 All instructions and data are stored in a computer as binary numbers. The organisation and structure of a computers’ processing components is known as computer architecture. A-Level Computing#BristolMet Processing Components The Central Processing Unit (CPU or Processor) This is the core of every computer system and it processes instructions from the various programs that are running. They consist of 2 main components: i)the Control Unit (CU) which uses electrical signals to direct the system to excecute the instructions in stored programs. It controls the order and flow data to be executed ii)The Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU) which carries out all the mathematical and logical operations i.e addition, subtraction and comparisons (relational operations such as =, < and >) In order for a processor to function it also needs to access 2 things; Main Memory or RAM (Random Access Memory) where the programs are stored whilst in operation, and cache memory which is used to store data whilst waiting to be processed. A-Level Computing#BristolMet Processing Components Main Memory (RAM) & Cache Memory are called Primary Storage (or Primary Memory). Knowledge Gap - What is secondary storage...? Cache memory is very fast memory and is located close to the CPU. It also a lot more expensive compared to RAM. Modern computers have Level 1 (L1), L2 and L3 Cache memory with the numbers referring to the distance from the CPU in that order. L1 is built into the chip itself. L3 is further away on the motherboard (Printed Circuit Board PCB) . The closer the cache the faster the CPU can access the data and execute instructions. NB Cache Memory and RAM are both known as volatile memory since they can be erased, which allows them to take on board new data. They also need power to store data. A-Level Computing#BristolMet Processing Components Data BUSES – the processing components are connected on the motherboard via circuits called buses which allow the transfer of data and control signals. The speed of the buses also affect how fast a computer can perform operations. TASK: Attempt to draw a block diagram illustrating the architecture of the given example. A-Level Computing#BristolMet Block diagram of computer architecture Main Memory (RAM) Other devices, Hard disk drives, USB ports, DVD drives Front Side Bus (FSB) CPU (CU, ALU & LI Cache) Back Side Bus (BSB) Southbridge L2 Cache L3 Cache A-Level Computing#BristolMet Northbridge RECAP Learning check – what do we now know??? Name the 2 components of a CPU? What are they used for? What is primary storage and what does it consist of? How data is transferred around a motherboard? A-Level Computing#BristolMet Processing Componets A dual-core processor simply has 2 CPU’s working together. They may both have their own cache memory or may share L2 or L3 cache but since they can fetch, decode and execute instructions at the same time so the computer is able to process more instructions as a whole. What affect will this have on performance? CPU Core & L1 Cache CPU Core & L1 Cache Back Side Bus Interface to bus and L2 Cache TASK: Using sticky notes label as many internal parts of the computer as you can. A-Level Computing#BristolMet Processing Components Consolidate learning: Questions: 1. What is the purpose of the CPU in a computer? 2. What is a dual-core processor? 3. What are the names given for CPUs with 4 cores, 6 cores and 8 cores? 4. Describe how cache memory and RAM are used by the CPU? A-Level Computing#BristolMet