Cells Powerpoint
advertisement

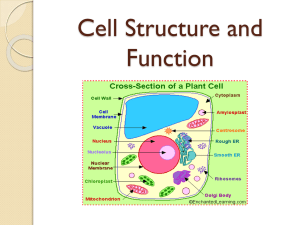
The Discovery of Cells Cells - the basic unit of living organisms; weren’t discovered until the invention of the microscope (Anton van Leewenhoek). The Discovery of Cells The term “cells” was a term coined by Robert Hooke as he studied the first cork cells. In fact, it was Hooke who coined the term "cells": the boxlike cells of cork reminded him of the cells of a monastery. The Discovery of Cells Types of Microscopes: Light Microscope – uses a series of lenses to magnify objects (1500x) Electron Microscope – uses a beam of electrons instead of light to magnify structures VIDEO Here Cells Intro The Discovery of Cells Cell Theory (Schleiden and Schwann contributed to these fundamental ideas) All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. All cells come from preexisting cells. The Discovery of Cells before nucleus true nucleus The Discovery of Cells Two basic types of cells Prokaryotes - cells that do NOT have membrane bound organelles. Eukaryotes – cells that do contain membrane bound organelles like the nucleus, chloroplast, or mitochondria What do cells really look like? Nerve cells Red Blood Cells Cardiac cells Macrophage attacking a bacteria HIV Why are cells so small ????? http://www.cellsalive.com/howbig.htm The Plasma Membrane Survival of a cell depends the cell’s ability to maintain the proper conditions (homeostasis) within itself. The plasma membrane is a flexible boundary between the cell and its environment. The plasma membrane is selectively permeable, which means that only certain molecules can pass through. http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/lipids/membrane%20fluidity.swf http://www.bio.davidson.edu/people/macampbell/111/memb-swf/membranes.swf http://telstar.ote.cmu.edu/biology/downloads/membranes/index.html Hydrophilic head Hydrophobic tails VIDEO Here The Cell Membrane http://telstar.ote.cmu.edu/biology/downloads/membranes/index.html Cool animation http://www.stolaf.edu/people/giannini/flashanimat/lipids/membrane%20fluidity.swf http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm Parts of the Cell Ribosomes – site of protein synthesis, made up of rRNA Golgi apparatus – folded membranes that store and transports enzymes and hormones, also produces the cell wall in plants Cytoplasm – jelly-like material surrounding the nucleus of the cell Nucleus – The control center of the cell Nucleolus – Site of ribosome synthesis Nuclear Membrane – Surrounds the nucleus. Cell Membrane – Membrane surrounding the organelles and the cytoplasm of the cell. Parts of the Cell Mitochondria – The site of cellular respiration or energy production. Membrane bound. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – forms a link between the nuclear membrane and the cell. Ribosomes are attached to the surface. Proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes and enclosed in vessicles and sent to the Golgi. Vacuole – Site of storage of glucose, water, salts, and toxic substances. Larger in plants cells than in animal cells. Parts of the Cell Cell Wall – Plant, fungal, and bacteria have a cell wall that us used for support and protection. It is composed of cellulose. Chloroplast – Site of photosynthesis in the plant and algal cell. They are generally lens shaped and bound by a double membrane. Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum – It forms a link between the nuclear membrane and the cell. Site of many metabolic reactions and synthesis of phospholipids and fatty acids. Parts of the Cell Lysosome – Contain enzymes needed for digesting food, viruses, bacteria and old cells. Centrioles – Not normally found in plant cells. They are found in animal cells in pairs and are necessary for cell division.