PC Fundamentals
Presentation 3 – The Motherboard
Copyright © 2007 Heathkit Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved
Objectives
At the end of this presentation,
you will be able to:
2
Explain how power is distributed throughout the
motherboard.
Identify and explain the purpose of several circuits on
the motherboard.
Identify and explain the purpose of the ISA expansion
bus, the PCI expansion bus, and the accelerated graphics
port (AGP).
Identify and explain the purpose of the DIMMs.
Identify and explain the purpose of each of the field
replaceable units (FRUs) on the motherboard.
3
Motherboard Form Factors
AT-Type
Baby
or Mini AT
ATX-Type
LPX
Mini LPX
Proprietary Designs
4
Evolution of the Motherboard
Processors have gone through several
generations.
Busses have evolved
Memory has evolved
5
Evolution of the Pentium Processor
I
II
III
D
6
The AT and ATX Motherboards
AT
ATX
7
AT Motherboard with
Pentium CPU
8
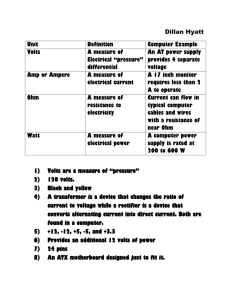
Power Distribution
Black
Wires
AT-Motherboard Power Connectors
10
11
Edge View of Motherboard
Voltages supplied to the
motherboard
+
5 Volts
- 5 Volts
+ 12 Volts
- 12 Volts
13
Voltage Regulator
14
CPU Socket
15
The MPU
16
The Pin Grid Array (PGA) Socket.
17
MPU
Lever
18
18
Fan
Heat Sink
CPU
19
19
Industry Standard Architecture
(ISA) Bus.
8-MHz Speed
Supports 8-bit and 16-bit data transfer
Used for slow speed operations such as
modems and sound cards.
20
ISA BUS
21
16-bit Cards
8-bit Cards
22
22
ISA boards installed.
16-Bit
8-Bit
Motherboard
23
Peripheral Component
Interconnect (PCI) Bus
33 MHz
Handles 32-bit and 64-bit data transfers
Processor independent
Supports Plug and Play
24
PCI BUS
25
SIMMs
26
Single In-line Memory Module (SIMM)
27
Cache
Memory
28
The Chipset
The support chips that make the
microprocessor a microcomputer.
Applications Specific Integrated Circuits
(ASICs) that provide the signals,
controllers, interfaces and buffers that the
system needs to operate.
29
Chipset
30
Main functions of the Chipset
A System Controller handles timing,
interrupt and DMA control, and power
management.
A Memory Controller provides
interconnection and control of memory
systems.
A Peripheral Controller connects the MPU
to internal and external devices such as disk
drives, buses, and peripherals.
31
Super I/O
Controller
32
Super I\O Controller
Interface to the floppy drive.
Interface to serial ports.
Interface to parallel ports.
33
Keyboard
Controller
34
Keyboard Controller
Communicates with the microprocessor in
the keyboard.
Performs a parity check.
Converts serial data from the keyboard into
the parallel data needed by the computer.
Generates an interrupt to alert the system
that a key has been depressed.
35
ROM
BIOS
36
Identifying the ROM BIOS.
Socket
Version #
R3.60
37
Electrically-Erasable
PROM… EEPROM
38
Real Time
Clock
39
The Real Time Clock (RTC)
contains:
Clock
CMOS memory
And in some cases the battery.
40
CMOS is used to hold SETUP
information.
41
The FRUs on the AT
Motherboard include:
The MPU
Any board plugged into the PCI bus.
Any board plugged into the ISA bus.
The SIMMs/DIMMs
The ROM BIOS
42
ATX
Motherboard
43
9.6 ”
Early
ATX
Motherboard
12 ”
44
45
Power Distribution
ATX-Motherboard Power Connector
47
Motherboard Power Connector
48
49
Power Supply Output Voltages
ATX-Type
+5 Volts
+12 Volts
-12 Volts
-5 Volts
+3.3 Volts
50
Pentium 4,
Heat Sink & Fan
51
PCI Bus
52
AGP
53
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP)
Operates at twice the speed of the PCI bus
or at 66MHz.
Even higher speed versions are being
developed.
Mostly used by Video Cards
54
DIMMs
55
Dual In-line Memory Modules (DIMMs)
have components and pin
connections on both sides of board.
56
Chipset
57
Super I/O
Controller
58
ROM BIOS
Battery
59
I/O Ports
60
ATX
Motherboard
Pentium D
Processor
PCI Bus
61
ATX
Motherboard
62
ATX
Motherboard
DDR DIMM
63
I/O Ports
10101
10101
64
The motherboard is the heart and
soul of the computer.
PC Fundamentals
End
Copyright © 2007 Heathkit Company, Inc. All Rights Reserved