•
•
•
•
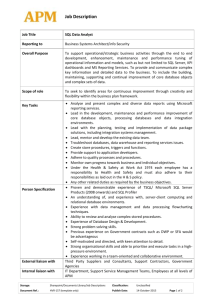
Notes: Update as of 1/13/2010. Vulnerabilities are included for SQL Server 2000 , SQL Server 2005 , SQL Server 2008. Oracle (8i, 9i, 9iR2, 10g, 10gR2,11g), IBM DB2
(8.0, 8.1, 8.2, 9.0, 9.5), Query for Oracle was run with vendor name: ‘Oracle’ , and product name: ‘any’ (all database product name variations were queried) . Query
for IBM DB2 was run with vendor name: ‘IBM’ , and product name: ‘db2.’ Query for MySQL was run with vendor name: ‘MySQL’, and product name: ‘Any.’ Query for
Microsoft was run with vendor name: ‘Microsoft ‘ ; product name: ‘Microsoft SQL Server’; version name: ’Any’
This chart counts NIST CVE – Software Flaws (Each CVE might include more than one Oracle vulnerabilities)
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Common Criteria Certification
Security functions: Access control,
audit, management, identification &
authentication, session handling and
memory management
Assurance components: Functional
specs and high level design plus
independent vulnerability testing
Environment: CC certified OS
(Windows Server) and admin roles
Requirement for many governments,
industries, and enterprise customers
SQL Server 2008 Enterprise achieved Common
Criteria (CC) compliance at EAL1+ (Evaluation
Assurance Level), EAL4+ is in progress and
recognized by the US government
Represents the third time for CC
compliance and the first time for
a 64-bit version of SQL Server
R2 is built on the SQL Server 2008 foundation
and brings forward the security benefits with
minimal changes to the core engine
−
— SQL Server Books Online
SQL Server Support
Health Information Portability and
Accountability Act (HIPAA) governs
health information privacy, security,
organizational identifiers, and overall
administrative practices
HIPAA has 5 major components, SQL
Server can help support the Security
Rule; ensuring protected health
information (PHI)
SQL Server supports HIPAA areas: Access
controls, Data integrity & encryption,
Communications security, and Audit &
compliance
Take advantage of SQL Server 2008
capabilities to help meet database-related
compliance requirements
Technical features can support HIPAA
requirements like role-based access, strong user
authentication, encryption, and event logging
SQL Server features can promote the
consistency of deployed technical controls and
enable effective monitoring over time
Whitepaper: “Supporting HIPAA Compliance with Microsoft SQL Server 2008,”
Authored by Information Security Center of Expertise at Jefferson Wells
International, Inc, a leading Risk Advisory and Security Compliance
services organization.
SQL Server Support
Payment Card Industry (PCI) Data
Security Standard (DSS) is a worldwide
security standard created by the
Payment Card Industry Security Council
SQL Server can be deployed to meet the
database server requirements and
should always be considered by
personnel in cardholder environments
SQL Server supports PCI areas: Vendorsupplied defaults, protect stored data,
encrypt data transmission, restrict access
to data, assign unique IDs to persons with
access, and monitor all access to data
Take advantage of SQL Server 2008
capabilities to help meet database-related
compliance requirements
Technical features can support PCI
requirements like TDE, EKM, SQL Server
Audit, and Policy-Based Management
Automated implementation of key SQL
Server 2008 features help enable customers
to achieve PCI compliance and standardized
security controls
Whitepaper: “Deploying SQL Server 2008 Based on Payment Card Industry Data
Security Standards (PCI DSS),” Authored by certified audit firm, Parente Randolph
(now ParenteBeard).
© 2010 Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved. Microsoft, Windows, Windows Vista and other product names are or may be registered trademarks and/or trademarks in the U.S. and/or other countries.
The information herein is for informational purposes only and represents the current view of Microsoft Corporation as of the date of this presentation. Because Microsoft must respond to changing market
conditions, it should not be interpreted to be a commitment on the part of Microsoft, and Microsoft cannot guarantee the accuracy of any information provided after the date of this presentation. MICROSOFT
MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS, IMPLIED OR STATUTORY, AS TO THE INFORMATION IN THIS PRESENTATION.
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•