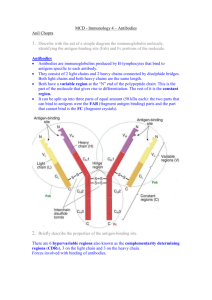
The Prototype Immunoglobulin Molecule
advertisement

Lecture 2 Antigens, Receptors and Immunoglobulins Antigenic Determinants (Epitopes) What is an antibody? Product of adaptive immunity Made specifically to bind a unique antigenic epitope (also called an antigenic determinant) Possesses an antigen binding site A product of the Plasma cell Members of the class of proteins called immunoglobulins Receptor-Epitope Interactions and Affinity Most biological systems can be viewed in terms of interactions between receptors and epitopes (“hand and glove”). Specificity of the interaction between the receptor and epitope is determined by the amino acid sequence of the receptor (“tailoring the glove”). If the glove is too big, the glove falls off. If the glove is too small, you can’t get your hand into it. If the glove is missing fingers… Binding of the epitope in the antigen binding site GOOD FIT POOR FIT antibody combining site antigen determinant high attraction low repulsion high repulsion low attraction Basic Immunoglobulin Structure The Prototype Immunoglobulin Molecule Fab VH VL CH1 CL CH2 Fc CH3 Heavy Chains (five types: Light Chains (two types: and Fab fragment Fc fragment Constant and variable regions Carbohydrate Disulfide linkages Immunoglobulin G (IgG) Fab VH VL CH1 CL CH2 Fc CH3 2 Heavy and 2 Light chains 2 Fab and 1 Fc fragment 4 Subclasses (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4) Mol. Wt. 150,000 ~70-75% of serum immunoglobulin. The major antibody of the secondary immune response Change in affinity with time Immunoglobulin M (IgM) J-Chain 10 Heavy and 10 Light chains 10 Fab and 5 Fc fragments Mol. Wt. ~900,000 <10% of serum immunoglobulin. Single J Chain (15 kDA) The predominant "early" antibody Most primitive immunoglobulin No change in affinity with time Immunoglobulin A (IgA) Monomeric- Serum IgA ~15-20% of serum immunoglobulins 2 Heavy and 2 Light 2 Subclasses (IgA1 and IgA2) Found in serum Secretory Immunoglobulin A (sIgA) J-Chain Secretory Component 4 heavy chains and 4 light chains (dimeric) J-Chain and secretory component The major immunoglobulin of secretions Not found in serum Immunoglobulin E (IgE) CH4 2 Heavy and 2 Light chains Mol. Wt. ~190,000 Trace serum protein Note CH4 region on H chain Associated with atopic or anaphylactic hypersensitivity May play role in immunity to helminthic parasites Immunoglobulin D (IgD) 2 heavy and 2 light chains <1% of serum immunoglobulins Serves as a membrane receptor on B lymphocytes May play role in antigenstimulated lymphocyte differentiation Take Home Lessons What is the basic immunoglobulin structure? What are the characteristics or features of the various fragments of the immunoglobulin molecule? How is the specificity of an antibody “defined” by the amino acid sequence of the immunoglobulin molecule? What features distinguish each immunoglobulin class?