Survey of the Phyla-ProtistsPart ION
advertisement

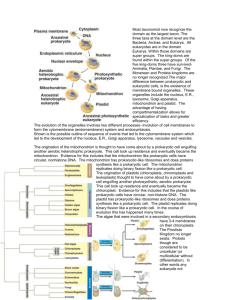
` Domain EukaryaThe Protists Most taxonomists now recognize the domain as the largest taxon. The three taxa at the domain level are the Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. All eukaryotes are in the domain Eukarya. Within those domains are super groups. The kingdoms are found within the super groups. Of the five kingdoms three are still used-Animalia, Plantae, and Fungi. The Moneran and Protista kingdoms are no longer recognized. The major difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, is the existence of membrane bound organelles. These organelles include the nucleus, E.R., lysosome, Golgi apparatus, mitochondrion and plastid. The advantage of having compartmentalization allows for specialization of tasks and greater efficiency. The evolution of the organelles involves two different processes- involution of cell membranes to form the cytomembrane (endomembrane) system and endosymbiosis. Shown is the possible sequence of events that led to the cytomembrane system which led to the development of the nucleus, E.R., Golgi apparatus, lysosome, vacoules and vesicles. Which of the following is not considered to be a domain? A) Eukarya B) Archaea C) Protista D) Bacteria ANS: C There are three domains (super-kingdoms) based on the sequencing of the ribsomal RNA. These include the Eukarya (all eukaryotic cells), Archaea (prokaryotic cells more closely related to eukaryotic cells), and Bacteria (prokaryotic cells not in the domain Archaea). The kingdoms that no longer exists are the Monera kingdom and the Protista kingdom The origination of the mitochondrion is thought to have come about by endosymbiosis, meaning a prokaryotic cell engulfing another aerobic heterotrophic prokaryote. This cell took up residence and eventually became the mitochondrion. Evidence for this includes that the mitochondrion like prokaryotic cells have circular, nonhistone DNA. The mitochondrion has prokaryotic-like ribosomes and does protein synthesis like a prokaryotic cell. The mitochondrion also replicates by undergoing binary fission like a prokaryotic cell. Which of the following is not considered to be part of the endomembrane and cytomembrane system? A) Golgi apparatus B) flagellum C) nucleus D) lysosome ANS: B The endomembrane system includes all of the following-nucleus, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, E.R., vacuoles, and vesicles. These are membranes that are connected to one another or originate from one another. The flagellum is made from microtubule proteins. The origination of plastids (chloroplasts, chromoplasts and leukoplasts) is also thought to have come about by endosymbiosis when a prokaryotic cell engulfing another photosynthetic, aerobic prokaryote. This cell took up residence and eventually became the chlroroplast. Evidence for this includes that plastids, like prokaryotic cells, have circular, non-histone DNA. A plastid has prokaryotic-like ribosomes and does protein synthesis like a prokaryotic cell. The plastid replicates doing binary fission like a prokaryotic cell. In the course of evolution this has happened many times. Which of the following is NOT evidence that supports the endosymbiosis hypothesis for the origin of mitochondria? A) Mitochondria have a membrane like a prokaryotic cell. B) Mitochondria have non-histone, circular DNA like a prokaryotic cell. C) Mitochondria have smaller prokaryotic like ribosomes. D) Mitochondria replicate like a prokaryotic cell ANS: A Both eukaryotic cells, the mitochondria, and the prokaryotic cell have a membrane, so this NOT a piece of evidence to support the endosymbiosis hypothesis, the other three statements are true. They do support the endosymbiosis hypothesis. The algae that were involved in a secondary endosymbiosis have 3-4 membranes on their chloroplasts. The Prostista Kingdom is no longer used by taxonomists. The term Protist refers to eukaryotic organisms that are unicellular (or multicellular without differentiation). In other words any eukaryote not considered to be a plant, animal or fungus is a protist. Remember, protists, animals, fungi, and plants are all in the same domain, Eukarya. There are five recognized super groups in the domain Eukarya 1. Excavata 2. Chromalveolata 3. Rhizaria 4. Archaeplastida (plant kingdom found in this group) 5. Unikonta (Animal and Fungi Kingdom found in this group) All the tan boxes represent groups that used to be in the Protista Kingdom. Which considered to be the correct sequence from largest grouping to smaller grouping? A) super group -> domain -> kingdom B) kingdom -> domain -> super group C) domain -> super group -> kingdom D) domain -> kingdom -> super group ANS: C The correct sequence is domain -> super group -> kingdom The super group Excavata (relationship in the Eukarya is not clear) a. Oral Groove on one side of the cell body b. Diplomonads and Parabasalids have reduced mitochondria c. Euglenozoans have flagella with unique spiral rod i. Kinetoplastids-have large mitochondrion with large mass of DNA-feed on prokaryotes ii. Euglenid- Mixotrophs: in light do photosynthesis in the dark become heterotrophic. Have protein pellicle under the cell membrane. Giradia intestinalis (shown) can cause intestinal distress and diarrhea. Trichomonas vaginalis is a sexually transmitted parasite that can infect both males and females causing tissue damage. Has the ability to change surface proteins to evade recognition by the immune system. (tricky little suckers!) Some taxonomists argue that Diplomonads and Parabasalids are closely related to prokaryotes. The best reasoning for this is A) like prokaryotic cells, they do not have nucleus. B) they contain smaller ribosomes like prokaryotic cells. C) like prokaryotic cells, they have circular DNA. D) they contain reduced, nonfunctioning mitochondrion. ANS: D Diplomonads and Parabasalids contain reduced, nonfunctioning mitochondrion. Diplomonads and Parabasalids have linear DNA, normal eukaryotic ribosomes and do have nucleus. The super group- Chromalveolata I. Alvelolates-have membrane bags under cell membrane A. Dinoflagellates-cellulose plates with perpendicular grooves with flagella. Cause of red tide. Some autotrophs, heterotrophs and mixotrophs. B. Apicomplexan-parasites (Plasmodium) causes malaria. Complex life cycle C. Ciliates-Covered with cilia (Paramecium caudatum) has large and small nuclei II. Stramenopiles-covered with numerous fine “hairy”flagella which is paired with regular shorter flagellum The life cycle of Plasmodium, the cause of malaria Ciliates to include stentor and paramecium Dinoflagellate causes red tide Which of the following is true? A) Malaria is a rare disease B) Malaria is treated by common antibiotics C) Malaria uses leeches as vector to infect human D) Malaria is caused by the protist Plasmodium ANS: D Malaria is caused by a protistPlasmodium. It uses a mosquito as a vector to infect humans. It is a common disease in the tropics, infecting 300,000,000 and killing approximately 2,000,000 people annually. Scientists are trying to find an antibiotic that will be treatment but so far nothing has been developed.