AP 2 Unit 7 Power Point Refraction and Physical Optics
advertisement

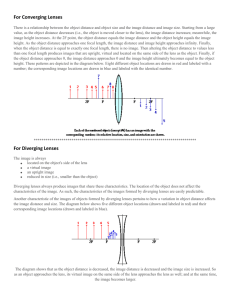
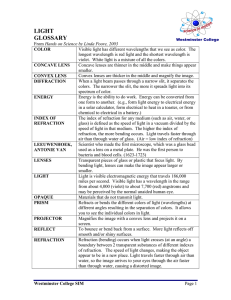
AP Physics 2 Unit 7 Refraction and Physical Optics Refraction and Lenses Refraction – the bending of light as it passes between two media with different optical densities The index of refraction 𝑐 𝑛= 𝑣𝑚 Ex. The index of refraction for a diamond is 2.42. What is the wavelength of green light in a diamond if the frequency of light in air is 5.45 x 1014 Hz? Snell’s Law – “Proof Ahoy” Ex. Light is incident in air (nair = 1.00) upon an equilateral crown glass prism (ng = 1.52) at an angle of 45.0⁰ to one face. Calculate the angle at which the light emerges from the opposite face. Total Internal Reflection Ex. A ray of light in a diamond (n = 2.42) strikes an interface at 28⁰. Will the beam of light enter the air or will it be reflected internally? Will the beam of light be reflected internally if the diamond is surrounded by water (nw = 1.33)? Applications of total internal reflection Dispersion of Light Lenses Two types of lenses Images formed by converging lenses Image formed by a diverging lens A familiar friend Sign conventions for lenses: • f is positive for converging lenses and negative for diverging lenses • so is positive when light is reflected from the object (a real object) • si is positive when it is behind the lens (real image) and negative when it is in front of the lens (virtual image) Physical Optics First, what is diffraction of light? The trumpet and the spotlight outside of the door. Huygen’s Principle Linear Superposition Young’s Double Slit Experiment and Wave Properties of light Bright and dark fringes, also known as maxima and minima also known as bright and dark bands Position of the maxima and minima “Order in the fringe!” Intensity of the maxima and minima Two equations for double-slit interference 𝑚λ = 𝑑 sin 𝜃 and 𝑚λ𝐿 𝑥𝑚 = 𝑑 Ex. The distance between two slits is 1.20 x 10 –4 m. An interference pattern is projected onto a screen 2.75 m away. Find the distance on the screen between the central maximum and and the third order maximum. Single slit interference Diffraction grating The electromagnetic Spectrum All wave of e-m spectrum travel at the speed of light c (2.99 x 108 m/s, like really, really fast). Note the relationship between wavelength, frequency and energy. E-m spectrum • Radio (AM, FM, TV) > 30 cm • Microwaves (radar, atomic-molecular research, microwave ovens) between 30 cm and 1 mm • Infrared between 1 mm and 700 nm • Visible light between 400 nm and 700 nm • Ultraviolet between 400 nm and 60 nm • X-rays between 60 nm and 10-4 nm • Gamma rays between 0.1 nm and 10-5 nm Polarization of Light Let’s look at unpolarized light first The fence and the rope