Chapter 7 - Choteau Schools
advertisement

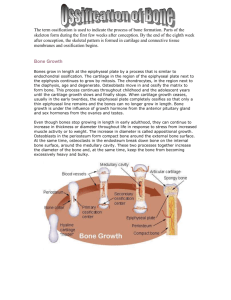
Chapter 7 Bone Development and Growth Types of Bone Development • Intramembraneous Bones – Form by replacing existing connective tissue – Originate within sheetlike layers of connective tissues – Ex. – Skull bones • Endochondral Bones – Form by replacing existing connective tissue – Begin as masses of hyaline cartilage that are later replaced by bone tissue – Ex. – most skeletal bones The process of forming bones is called osteogenesis Intramembraneous Bones • Development (intramembranous ossification) 1. Membrane-like layers of relatively undifferentiated connective tissues appear • 2. 3. Tissue cells enlarge and differentiate into osteoblasts (bone-forming cells) Osteoblasts deposit bony matrix around themselves, forming spongy bone in all directions along the blood vessels within the layers of connective tissues • 4. Spongy bone may later become compact bone through spaces being filled with bone matrix As development continues: 1. 2. 5. These tissue layers are supplied by dense networks of blood vessels Osteoblasts may become completely surrounded by extracellular matrix and secluded within lacunae (and are now called osteocytes) Extracellular matrix encloses cellular processes of the osteoblasts to form canaliculi Cells of the connective tissue that are outside the developing bone give rise to the periosteum. 6. Osteoblasts on the inside of the periosteum form a layer of compact bones over the surface of the newly formed spongy bone Endochondral Bones • Development (endochondral ossification) – Masses of hyaline cartilage shaped like future bones develops – Cartilage cells enlarge, lacunae grow, and surrounding matrix breaks down, leading to the death and degeneration of cartilage cells – As cartilage decomposes, a periosteum forms from connective tissue surrounding the structure – Blood vessels and partially differentiated connective tissue cells invade the disintegrating cartilage tissue – Some of the invading cells further differentiate into osteoblasts and begin to form spongy bone in the spaces previously occupied by cartilage – Osteoblasts beneath the periosteum deposit compact bones around the spongy bone Osteogenesis in Long Bones • Bony tissue begins to replace hyaline cartilage in the center of the diaphysis (called the primary ossification center) – Bone then develops from the center out while osteoblasts in the periosteum deposit a thin layer of compact bone around the primary ossification center • The epiphyses remain cartilage until secondary ossification centers form in the epiphyses and spongy bone begins to be deposited in all directions – As this secondary process occurs, a band of cartilage called the epiphyseal plate separates the two ossification centers Osteogenesis in Long Bones Osteogenesis in Long Bones • Growth at the epiphyseal plate: – The cartilage cells of the epiphyseal plate form four layers: • 1st layer – Closest to the end of the epiphysis – Composed of resting cells that do not actively participate in growth – Anchors the epiphyseal plate to the bpny tissue of the epiphysis • 2nd layer – Include rows of young cells going through mitosis – As new cells and extracellular matrix forms, the cartilage plate thickens • 3rd Layer – Consists of older cells that are left behind when new cells appear – This enlarges and thicken the epiphyseal plate causing the whole bone to lengthen – Invading osteoblasts (which secrete calcium salts) accumulate in the extracellular matrix of this layer adjacent to the oldest cartilage cells, causing the matrix to calcify and cells to die • 4th layer – Consists of dead cells and calcified extracellular matrix – Very thin Osteogenesis in Long Bones Growth at the epiphyseal plate: Osteogenesis in Long Bones Growth at the epiphyseal plate: Osteogenesis in Long Bones • Growth at the epiphyseal plate: – After calcification, large, multi-nucleated cells called osteoclasts break down the calcified matrix by: • Secreting an acid that dissolves the inorganic component of the calcified matrix • Digestion of organic components of the calcified matrix by lysosomal enzymes • Phagocytosis Osteoclasts originate from the fusion of single-nucleated white blood cells called monocytes – After osteoclasts remove the extracellular matrix, osteoblasts invade the region and deposit bone tissue in place of the calcified cartilage Osteogenesis in Long Bones • Growth at the epiphyseal plate: – As long as the cartilaginous cells of the epiphyseal plate are active, a long bone will continue to lengthen – However, once the ossification centers of the diaphysis and epiphysis meet and the epiphysial plates ossify, the bone can no longer lengthen on that end – Bones will thicken as compact bone is deposited on the outside , just beneath the periosteum • As this happens, osteoclasts erode bone tissue on the inside of the bone, forming the medullary cavity Homeostasis of Bone Tissue • Bone remodeling – Occurs throughout life as osteoclasts resorb bone tissue and osteoblasts replace bone tissue • 3% to 5% of bone calcium is exchanged each year in adult skeletons • However, total mass of bone tissue remains nearly constant Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Vitamin D – Necessary for proper absorption of calcium in the small intestine – Lack of proper absorption leads to a lack of calcium in bone matrix resulting in softening of the bone (called rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults) – Vitamin D is uncommon in foods but is present in fortified dairy products – Vitamin D also forms from dehydrocholesterol (which is produced by cells in the digestive tract or obtained from food) that is carried by blood to the skin where exposure to UV light converts it to Vitamin D Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Vitamin A – Necessary for osteoblast and osteoclast activity during normal development – Deficiency of Vitamin A may impede growth development Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Vitamin C – Required for collagen synthesis – When Vitamin C is lacking, osteoblasts cannot produce enough collagen in the extracellular matrix of the bone tissue, resulting in abnormally slender and fragile bones Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Growth hormone – Secreted by the pituitary gland – Stimulates the division of cartilage cells in the epiphyseal plates – In the absence of growth hormone, the long bones of the limbs fail to develop normally, a condition called pituitary dwarfism (resulting in a child who is very short but with normal body proportions) – If excess growth hormone is released prior to the ossification of the epiphyseal plates, pituitary gigantism results (height in these individuals may exceed 8 feet) – In adults, secretion of excess growth hormone results in the enlargement of the hands, feet, and jaw (called acromegaly) Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Thyroxine – Hormone produced by the thyroid – Stimulates replacement of cartilage in the epiphyseal plate of long bones – Can halt bone growth by causing premature ossification of the epiphyseal plate or by not stimulating the pituitary gland to produce enough growth hormone Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Parathyroid – Hormone that stimulated an increase in the number and activity level of osteoclasts, which break down bone Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Estrogens and Testosterone – Promote the formation of bone tissue • More abundant during puberty – Stimulate ossification of the epiphyseal plates which stops bone lengthening – The effect of estrogens is stronger than the effect of testosterone, causing girls to reach maximum heights at an earlier age than boys Factors Affecting Bone Development, Growth, and Repair • Physical Stress – Stimulates bone growth • Stress applied to bones by contracting muscles causes bone to thicken and strengthen (hyperatrophy) at attachment sites – Lack of exercise causes bones to atrophy (become thinner and weaker)