Topic
advertisement

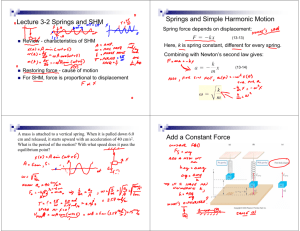
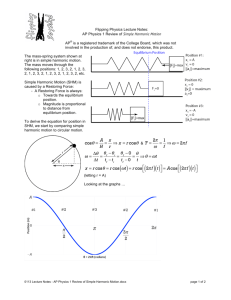
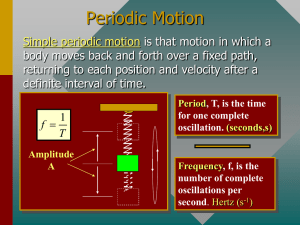
12.1 Simple Harmonic Motion Date, Section, Pages, etc. Mr. Richter Agenda Warm Up Any paper stragglers? Intro to Simple Harmonic Motion Notes: Simple Harmonic Motion Springs and Hooke’s Law Simple Pendulums Motion and Energy in SHM Objectives: We Will Be Able To… Identify the conditions of simple harmonic motion (SHM) Explain how force, velocity, and acceleration change as an object vibrates with simple harmonic motion. Calculate the spring force using Hooke’s Law. Warm Up A metronome keeps a ticking count of 90 beats per minute. 1. What is its period of oscillation? 2. What is its frequency of oscillation? Introduction to Simple Harmonic Motion What keeps an object bouncing up and down on a spring? What would cause this to stop? Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) Vibrations and Waves Vibration: any repeated motion of an object moving back and forth, or oscillating Fans Mass at the end of a spring. Pendulums. Waves are formed when a stationary substance vibrates. Ripples in water. Vibrating air with sound waves. Whipping a rope. Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM) “any periodic motion that is the result of a restoring force that is proportional to displacement” Basically: back-and-forth motion over the same path. Restoring Force: Object tends to want to return to original position. (Location is “restored”). Hooke’s Law (Springs!) Most mass-spring systems obey a simple (proportional) relationship between force and displacement. This is also true of systems that can be modeled by a mass and spring. This relationship is called Hooke’s Law k = spring constant [N/m] Force (F) always in opposite direction of displacement (restoring!) The Simple Pendulum Mass is called “bob”. Assume string is weightless. Restoring force is a component of the weight of the bob. Fg = mgsinθ For small angles, the pendulum’s motion is simple harmonic. Energy During SHM Total mechanical energy stays the same. Trade off between potential and kinetic energy. Motion during Simple Harmonic Motion Wrap-Up: Did we meet our objectives? Identify the conditions of simple harmonic motion (SHM) Explain how force, velocity, and acceleration change as an object vibrates with simple harmonic motion. Calculate the spring force using Hooke’s Law. Homework p. 441 #e,4 p. 445 #1, 2, 4