Simple Harmonic Motion and Springs
advertisement
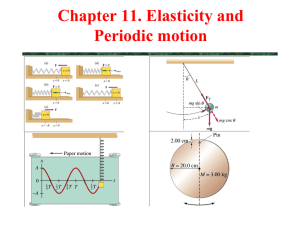
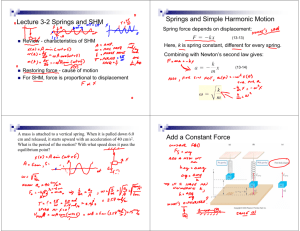
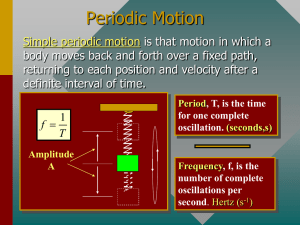
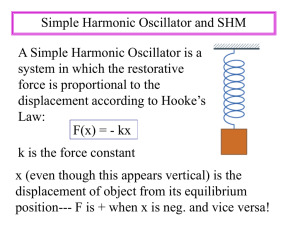
SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION AND SPRINGS SIMPLE HARMONIC MOTION Starts from a stable point or a rest point When an object is disturbed, it has a restorative force which tries to restore the object to its rest position Generally, the force (and therefore) acceleration is proportional to displacement This results in a back and forth motion that continues indefinitely SPRING MOTION When a spring is stretched and let go, it undergoes a longitudinal motion that is one type of simple harmonic motion. Restorative Force Fspring kx k – spring constant (N/m) x – displacement (m) Why would the negative sign be present? FOR THE PURPOSES OF SHM… We consider an ideal spring… An ideal spring has no internal or external friction acting upon it In a practical (unrealistic) sense, this means that spring keeps oscillating forever IF WE WERE TO EXAMINE THE MOTION WRT TIME What does this look like? Hint: The answer is not fun. As much fun as it is, that’s not what I’m looking for. What is a sine or cosine function based on? LET’S SEE HOW A UNIT CIRCLE RELATES TO SHM https://www.geogebratube.org/student/m87292 How does SHM relate to the unit circle? Observe! Maximum speed through the rest point Stopped at the amplitude f of motion on a point of the circle = f of vibration in SHM They two motions are in phase Radius of the circle = amplitude HOW CAN WE RELATE UCM TO SHM? What do we know about things moving in a circle? Derive 1 f 2 k m m T 2 k SHM ISN’T REAL LIFE SO LET’S LOOK AT DHM Damped Harmonic Motion Periodic or repeated motion where amplitude decreases with time There are no perfect springs!!! DAMPING OF CAR SHOCKS Damping for a car’s shocks: - 0.7 is ideal in this case -Overdamping is preferable to underdamping - Why is this so? TOTAL ENERGY IN SHM Energy is conserved! Therefore, total energy remains constant What is types of energy are being exchanged? - Kinetic for Elastic potential and back Therefore, 𝐸𝑇 = 𝐸𝑘 + 𝐸𝑒 𝐸𝑇 = 1 𝑚𝑣 2 2 1 2 + 𝑘𝑥 2 EXAMPLE A pendulum is disturbed from rest and is released from an amplitude of 15cm. If the pendulum has a mass of 45g and a spring constant of 26N/m, what will the period of the oscillation be? EXAMPLE A spring (k=20N/m) is compressed 30cm by a ball (m= 100g) and fired upwards. How fast will the object be moving after it has a vertical displacement of 20cm after it leaves the spring? 26. A 0.20 kg mass is hung from a vertical spring of force constant 55N/m. When the spring is released from its unstretched equilibrium position, the mass is allowed to fall. Use the conservation of energy to determine: a) the speed of the mass after it falls 1.5cm. b) the distance the mass will fall before reversing direction EXAMPLE A 35kg child is bouncing on a pogo stick, if the spring constant is 4945N/m and it is compressed by 25cm, how high will the child bounce? QUESTION # 16 #18-20 Q # 13 REVIEW VIDEO https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VnGkoMoUkgI 4.5 Pg 217 Q 23 -26 Pg 219 Q12-14 P9 218 Q3-10 Review Pg 225 Q1-9,16 Pg 226 Q1,2,4,9-15,17,19 22, 24,25