Principles of Ecology
advertisement

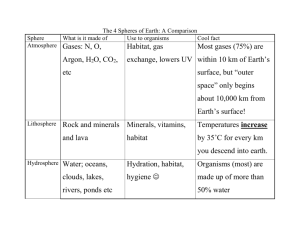
Principles of Ecology Chapters 3, 4, 5, & 6 What is Ecology? • Ecology is the study of interactions between organisms and their environment. Components of the Biosphere 1. Biosphere – portion of the Earth supporting life Within the biosphere you have the following factors: A. Biotic factors 1. All organisms inhabiting the environment 2. The “living” things in the environment! B. Abiotic factors 1. Nonliving parts of the environment 2. Can determine which species will survive examples: rainfall, temperature, light, soil Rain, Rain Go Away… C. Levels of Biological Organization 1. Species: a group of organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring! 2. Populations -A group of organisms of the same species living together -Must compete for resources Levels of Biological Organization 3. Community a. Several populations that interact b. Changes in one population will cause changes in the others 4. Ecosystem a. Interactions between populations and their surroundings b. 2 main types 1. Terrestrial – land 2. Aquatic – fresh or salt water D. Niche vs. Habitat 1. Niche *The role an organism plays in the environment *(Its “job” in the community) 2. Habitat *Place where an organism lives Habitat of the earthworm: SOIL Niche: To aerate (break-up) the soil. Types of Feeding Relationships 1. Autotrophs a. Self-feeders, produce their own food b. Example: plants, algae 2. Heterotrophs a. Depend on other organisms for food Herbivore – eats only plants Carnivore – eats only meat Omnivore – eats both 3. Decomposers a. Break down and absorb nutrients from dead organisms b. Example: mushrooms, bacteria bacteria fungus mushroom earthworms 4. Symbiosis - close, permanent relationship between organisms a. Three major types: 1. Commensalism 2. Mutualism 3. Parasitism 2) Friend alga cell is prepared to greet Mr. Fungus 1) Mr. Fungus is ready to greet our friend the alga 3) The Lichen is created between the fungus and the alga 1. Commensalism a. Relationship in which one species benefits and the other is not affected b. Example: remoras that live on/around a shark’s mouth Remora on a Ray tickbirds 2. Mutualism • a. Both species benefit b. Example: tickbirds eat parasites off of a rhino oxpeckers 3. Parasitism • a. One organism benefits and the other is harmed b. Example: tapeworm living inside a person’s intestine o Energy pyramids: show decreasing amounts of energy, biomass, and number of individuals as you move up the pyramid There is no limit to the number of levels that a food chain can support. Only 10% of the energy from one level is transferred to organisms at the next level. *The remaining energy is released into the environment as heat. Food Chains and Food Webs 1. Food Chains a. Model showing movement of energy through the ecosystem b. Uses arrows to show “what eats what” Food Chain Grass Cow Human 2. Food Web a. More complicated than a food chain b. Shows more than one food source for each organism c. More realistic view of energy transfer Quiz 1 1. Your house is an example of a(n) ___. a. biotic factor b. habitat c. niche 2. Trees, mosses and shrubs are all examples of what type of factor? a. abiotic b. biotic c. commensalism 3. The study of interactions between organisms and their environments is called ? a. botany b. cytology c. ecology 4. If you work at McDonald’s, that is an example of your? a. habitat b. niche c. community 5. A group of deer that live in a forest is an example of a? a. biosphere b. community c. population