Slides
advertisement

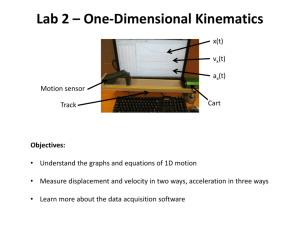
Lessons Learned from Transient Remission Cases: Clues to Biomarkers of HIV Rebound Katherine Luzuriaga, MD University of Massachusetts Medical School Worcester, MA USA www.ias2015.org Global Eradication of Pediatric HIV-1 Infection • New pediatric infections (MTCT) cut by 50% between 2001 and 2012: 900,000 new infections prevented since 2009 • 3.2 million children < 15 yrs living with HIV • 1.5 million HIV-1+ women give birth each year; only ~68% receive ART for PMTCT • 240, 000 children acquire HIV-1: one new infection every 2 minutes UNAIDS, 2014 www.ias2015.org Rationale for Early cART • Rapid tempo of disease progression in HIV infected infants • Median viral loads > 105 copies/ml over first 2 years of life • High rates of viral production • Less robust adaptive HIV-specific immunity • Ready identification of infants at risk and ability to make early nucleic acid-based rapid diagnosis • Early cART reduces HIV-related morbidity and mortality (Violari et al, NEJM, 2008) • Early HIV diagnosis and cART are globally recommended as standard of care www.ias2015.org Early cART restricts the latent reservoir Restricted latent reservoir if treated < 6 wk (red circles) vs. > 6 wk (blue circles) Reservoir decays over the first 2 yrs in early-treated infants (half-life 11 months [95% CI: 6 to 30 months] Remains detectable in most (60%) at two years of age Persaud et al. AIDS, 2012 www.ias2015.org Lower PBMC DNA Levels In Children With Younger Age at Virologic Control 2-LTR DNA circles detectable in 20% of youth: Proviral DNA copy number higher in those with detectable (median = 191) than in those with undetectable (median = 23) 2-LTR circles Median 4.2 19 71 Persaud et al, JAMA Pediatr, 2014 www.ias2015.org Clearance of HIV-specific Antibodies is a Hallmark of Early Effective cART in Infants EIA negative at 15 months: A. Durable HIV RNA suppression to < 400: 11 (73%) of 15 infants B. Early tx, incomplete /transient suppression: None (0%) of 5 C. HIV-uninfected infants born to HIV-infected women: 5 (100%) of 5 D. HIV- infected infants first treated > 12 mo: None (0%) of 4 Luzuriaga et al, J Virol, 2000 www.ias2015.org Low Proviral DNA Loads in Children with HIV-1 Negative or Indeterminate Wb Persaud et al, JAMA Pediatr, 2014. www.ias2015.org Early and Very Early Therapy Restrict the Size and Modify the Persistence of HIV-1 Reservoirs Contribution to the proviral reservoir: TTM > TCM, EM Luzuriaga, CROI, 2014; Persaud, CROI, 2015; Luzuriaga, JID, 2014; Persaud, JAMA Peds, 2014; Ananworanich, www.ias2015.org AIDS, 2014; van Zyl, JID, 2015; Bitnun, CID, 2014 HIV Remission Following Very Early cART ARV administered 31 hours - 18 months Remission 28 months off cART • • • • No detectable HIV-1 in routine or scRNA assay No replication-competent virus recovered No detectable HIV-1 specific antibodies or CD4/CD8+ T cells Absence of host factors associated with elite control Viral Rebound at age 46 months SC RNA: 9 copies/ml AZT/ 3TC/ NVP AZT/ 3TC/ LPV/r AZT/ 3TC/ +RAL EFV Persaud et al, NEJM, 2013; Luzuriaga, NEJM, 2015 www.ias2015.org HIV-1 rebound despite limited proviral and latent reservoirs MS Baby Canadian Milan 1 Milan 2 Timing of infection Time to rebound IU IU IU IU 27 mo < 1 mo 1 mo < 1 mo Pre-ART RNA 19,812 808 15,300 152, 560 Time to RNA< 400 Time on ART Cell-associated DNA Viral outgrowth < 1 mo 18 mo 6 mo 3 yr 1 mo 2 yr 3 mo 3 yr +/- - - - - - ND - culture HIV Ab HIV-sp T cells No T cell activation - + + + T cell activation Other + CAR Bitnun, CID, 2014; Giacomet, PIDJ, 2014; Persaud, NEJM, 2014; Luzuriaga, NEJM, 2015; Vigano, J Peds, 2006 www.ias2015.org Summary: Early/Very Early cART Alters HIV1 Persistence in Children • Limits proviral and replication competent reservoirs • Size correlated with the rapidity of control of HIV replication • Decay rapidly over first year of therapy • Slower decay with prolonged suppression of HIV replication • Decay in HIV proviral reservoirs over time in absence of HIV-specific immune responses suggests that early cART limits infection of long-lived cells • Contribution to the proviral reservoir: TTM > TCM, EM www.ias2015.org Markers for low-level proviral and latent reservoirs • Plasma RNA below detection limits of single copy assays • Lack of detectable 2 LTR DNA circles • Absence of T cell activation • Lack of HIV-specific antibodies, and CD4 and CD8+ T cell responses Luzuriaga et al, J Virol, 2000; Persaud et al, JAMA Peds, 2014; Ananworanich et al, AIDS, 2014 www.ias2015.org Pathways to Remission: Post-Treatment Controllers Adults: 5-15% treated during PHI • On cART 12-192 mo (median 36 mo) • Remission off cART: 48-115 mo (median 89 mo) • Low level T cell activation and HIV-specific T cell responses • Low circulating HIV-1 DNA levels (median 52 c/106 PBMC), with progressive decline over time in some Pediatric case • Infected despite infant ARV prophylaxis • Received cART ~3 mo – 6 years • Plasma HIV-1 RNA < 50 for 12 years, except for blips at 1, 2, 11, and 14 years; now < 4-9 c/ml • HIV-1 DNA 125-136 copies per million PBMC Saez-Cirion, PLoS Pathogens, 2013 Saez-Cirion, IAS, 2015 www.ias2015.org Current Protocols IMPAACT P1115: Very Early Intensive Treatment of HIV-Infected infants to achieve HIV remission: A proof of concept study IMPAACT P1107: Cord Blood Transplantation with CCR5Δ32 Donor Cells in HIV-Infected Subjects who Require Bone Marrow Transplantation for any Indication and its Observed Effects on HIV-1 Persistence www.ias2015.org Early/Very cART and HIV Persistence in Children HIV positive infants and children with persistent suppression of HIV on cART are excellent candidates for additional strategies aimed at remission, particularly therapeutic vaccines: • Normal immune responses • Absent HIV-specific immunity • Limited viral diversity www.ias2015.org Acknowledgements Children and Families Hannah Gay and Deborah Persaud Persaud Lab: Carrie Ziemniak, Ya Hui Chen Luzuriaga Lab: Margaret McManus, Linda Lambrecht, Joyce Pepe, Robin Brody, Keri Sanborn, Jim Coderre, Mohan Somasundaran Collaborators: Matthew Strain, Danielle Murray, Douglas Richman, Tae-Wook Chun Manuel Garber, Barbara Tabak Funding: NIAID, NICHD, AmFAR, JHU CFAR, UMMS CFAR, UMass Center for Clinical and Translational Science www.ias2015.org