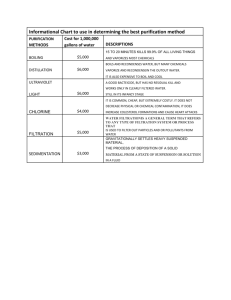
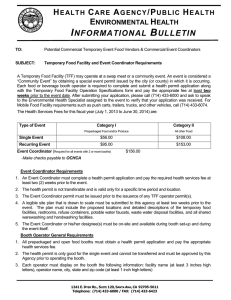
Dock to Stock at Skyline Biotech
advertisement

Dock to Stock at Skyline Biotech A brief Outline of how we make our product at Skyline Biotech What is a Tech expected to do? • Focus on – – – – Quality Your training The facilities around you The Utilities that you use • Operational Excellence Dock to STock • A process overview • How exactly do we go from our raw materials to a finished product Alpha Amylase From Bacillus subtilis Training Goals • Describe the main functions of the manufacturing process • Explain how these processes come together to make a product Master cell Bank • Large volume of the original Strain or construct is held under cryogenic preservation. – Usually in 1ml ampoules – Usually in liquid Nitrogen • Access is limited to ensure integrity of product. Working Cell bank • Created from the master cell bank for producing batches of product • Do not need to continually go to Master cell bank • A culture of the strain that makes your product – Continuously checked for efficiency and purity – When parameters are not met then another WCB is made from MCB Raw Materials • Media for the cells • A list of accepted • Quarantined and tested suppliers is kept for quality before • A list of accepted being used in substitutes is kept manufacturing • Many positions exist to ensure the consistency and quality of the Raw Materials chain Process Paperwork • Forms, Formulas and SOP are kept current and up to date • Small changes may be made but must be proved to not change the process • All completed paperwork is kept • Typically people with experience in writing or the process are involved Small Scale Cell culture • A sample from the WCB is transferred to successively larger culture tubes • Selective Media used to keep strain • Check for – – – – Cell density pH Temperature Nutrient concentration • Aa, sugar, oxygen, carbon dioxide Continuously check for • Quality • Quantity • consistency Large cell Culture • Typically a culture is not diluted more than 10x between each fermentation exchange • Fermentation process is Batch – Cells are grown until they reach a certain density then transferred en mass to a new vessel with new media How important is sterile technique? Product Recovery • Harvest. This depends on where the product is – In cells • Separate the cells out, break open cells and start product purification – In media • Separate the cells out, start product purification from the spent media Types of Harvest • TFF Tangential Flow Filtration • Continuous Flow Centrifugation Purification, Isolation and Viral inactivation • TFF or column chromatography is used to separate proteins by size, charge, affinity or hydrophobic. • The product will be separated by a complex mixture • The product may not be absolutely pure – However if the process is the same the contaminants are validated with the final product Viral Inactivation Formulation and pool bulks • Formulation – Concentrated protein is formulated to become tolerable to the patients – Ensures that the product is compatible in blood pH 7.1 – Bulk is frozen and stored in freeze/thaw tanks to await filling Filling • Final vials are filled under as sterile conditions as possible Freeze drying • Process increases shelf life and product stability Product inspection • Empty vials and stoppers are checked • Filled are checked • Also perform a container integrity test Label Final Product Final Product is packaged. Alpha Amylase is ready to use