The nature of leadership
advertisement

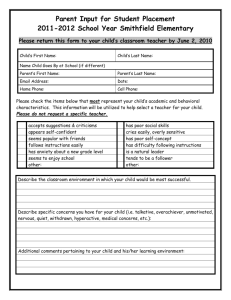
Introduction: The Nature of Leadership 領導與競爭優勢 Instructor:曾燦燈老師 第一組 陳立賢、董俊宏、葉明川、張榮元 張世偉、王素英、方真祥 1 Learning Objective of Chapter 1 • Why leadership has been defined so many different way. • The controversy about different between leadership and management • How leadership will be defined in this book. • Why it is so difficult to assess leadership effectiveness. • The different indicators used to assess leadership effectiveness. • What aspect of leadership had been studied the most during the past 50 years. • How leadership can be described as individual, dyadic, group, or organizational process. • The organization of this book 2 Why leadership has been defined so many different way (1/2) • Additional confusion by imprecise term: power, authority, management, administration, control & supervision. • Specialized role or shared influence process. – Role: the person expected to perform the specialized leadership role is designed as the leader. (個人表現?) – Process: various leadership functions may be carried out by different people who influence what the group does, how it is done, and the way people in the group related to each other. (群體程序?) 3 Why leadership has been defined so many different way (2/2) Claim of definition Description Dispute The type of influence Who exercise influence. process What type of influence is exercised and the outcome. too restrictive because it excludes why a manager is effective or ineffective in a given situation. Purpose influence attempts Leadership occurs only when people are influenced to do what is ethical & beneficial for the organization & themselves. It does not include influence attempts that are irrelevant or detrimental to follower. Influence based on reason or emotion Before 1980, it was defined by rational, cognitive process. Only the emotional value-based aspect of leadership influence can account for exceptional achievement of group. Rational and emotional are combined. Direct vs. indirect leadership Directly influence the follower Indirect influence the follower They are not mutually exclusive. 4 Leadership vs. Management Leadership Management Value flexibility, innovation Value stability, order, & & adaptation efficiency Value Concern what things mean to people and try to get people to agree about the most important things to be done. Concern Concern how things get done & get people perform better People do the right things. People do the things right Manager is occupational title. 5 Remark The Definition of Leadership • Leadership is the process of influencing others to understand and agree about what needs to be done and how to do it, and the process of facilitating individual and collective effort to accomplish shared objective. • Leader, manager and boss are interchangeable. • Subordinate, direct report, staff are interchangeable. • Follower > direct report. 6 Evaluate Leadership Effectiveness • The extent to which the leader’s organizational unit perform its task successfully and attains it’s goal, like net profit, profit margin. • Attitude of follower toward the leader – How well does the leader satisfy follower’s need and expectation? – Does follower like, respect & admire the leader? • Leader’s contribution to the quality of the group process, as perceived by follower or by outside observers. • Immediate and delayed outcomes • No simple criteria to evaluate leadership effectiveness – Objective and value of the person making the evaluation. 7 Overview of Major Research Approaches (1/2) • Key variables in leadership theories – Characteristics of the leader – Characteristics of the followers – Characteristics of the situation • Causal relationships among the primary types of leadership processes Leader traits & skills Leader behavior Influence processes Situational variables 8 Follower Attitudes & behavior Performance outcomes Overview of Major Research Approaches (2/2) • Trait approach – Emphasize leader’s attribute such as personality, motives, values & skills. • Behavior approach – How managers spend their time and the typical pattern of activities, responsibilities, and function for managerial jobs. – Identify the effective leadership behavior. • Power-influence approach – Influence processes between leaders and other people. • Situational approach – Emphasize contextual factors that influence leadership processes. • Integrative approach 9 – Involve more than one type of leadership variables. Level of Conceptualization for Leadership Organization (process that occurs in a larger open system) Group (group process) Dyadic (Relation btw a leader & another individual) Individual (Behavior on individual leader) 10 Other Bases for Comparing Leadership Theories • Leader- vs. follower-centered theory – Characteristic and action of leader – Characteristic of followers • Descriptive vs. prescriptive theory – Descriptive, 描述性的 • Explain leadership processes • Describe the typical activities of leaders • Explain why certain behaviors occur in particular situation – Prescriptive, 指示性的 • Specify what leader must to do to become effective • Identify any necessary condition for using a particular type of behavior effectively • Universal vs. contingency (偶發的) theory 11 – Some aspect of leadership that applies to all types situation. – An aspect of leadership that applies to some situation but not to others. Summary • Most leadership definitions share the assumption that it involves an influence process concerned with facilitating the performance of a collective task. • No single “correct” definition of leadership cover all situations. • To evaluate leadership effectiveness: followers + stakeholders multiple criteria • Research coverage for leadership: narrow aspect cut across and integrate approach. 12 Thank You! and Please Comment! 13