Project Management Fundamentals
advertisement

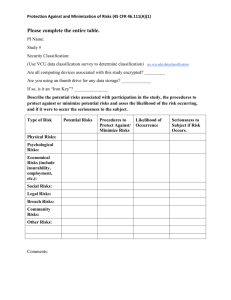
Project Management Information and Tracking Basics Technology Services Project Management Office Course Outline Background VCU Project Management Methodology Project Management Information and Tracking System Requirements Analysis Project Classification PMIT System Demo Lab Discussion/Questions Background VCU signs Tier III Management Agreement with COVA in mid-2007 Project Management Office created in early 2008 to meet COVA requirements TS Task Force determines PM methodology and system requirements 2008-2009 Project Management Information and Tracking System goes live in July 2009 VCU Project Management Methodology Combination of best practices from Project Management Institute (PMI) VITA Other colleges/universities Projects are classified and managed according to four criteria 1. 2. 3. 4. Cost Resources Time Risk VCU Project Management Methodology The more complex a project: the greater the planning requirements the more involved the execution and control the more advanced skills and greater experience the PM must have All projects have a single identified Project Manager and a Project Sponsor Anyone in Technology Services is eligible to become a Project Manager by meeting the education and experience qualifications VCU Project Management Methodology PMs are responsible for all aspects of their projects – planning, monitoring, control, budget, change management, etc., etc. VCU’s PM Methodology is subject to both internal and State audit JLARC did perform an audit in 2010 and found VCU in compliance with all COVA requirements VCU Project Information System Lack of funding meant a COTS system was not feasible Evaluated freeware Limited shareability Linear communications Task and schedule focused Weak analysis and reporting capabilities Decision was made to design and build one ourselves (within limited resources & time) VCU Project Information System System Requirements Web-accessible w/ CAS authentication Relational database Data input workflows with status indicators Lean and agile with minimal overhead on Project Managers The amount of documentation and required project management activities scales with the level of the project Reporting and data analysis capabilities for operational, managerial, and strategic purposes Project Management Information and Tracking System PMIT system consists of two components 1. Data entry 2. Reporting and analysis Modified version of the Change Management System application’s Web-based architecture SQL/Server database, ASP.Net application SAS Enterprise Business Intelligence tool Both use CAS/eID to authenticate Project Management Information and Tracking System PMIT’s internal role-based security authorizes users Project Managers can enter and update data for their projects only TS projects accessible by TS staff only School/department projects accessible by their staff only All TS staff can view any and all project information and access all strategic, managerial, and operational reports Project Management Information and Tracking System Purpose of PMIT is to punish you for being a Project Manager - NOT PMIT is designed to serve TS needs for: 1. 2. 3. 4. Capturing project information for tracking and analysis Sharing best practices and lessons learned Enhancing planning skills Improving on-time and within-budget deliverables Requirements Analysis Critical step in any project is a complete a thorough Requirements Analysis Document and obtain agreement from the sponsor & primary stakeholders on the project’s Mission, goals and objectives Deliverables and how measured Contribution to unit and University strategic goals Required budget Begin-to-end time to complete Impact on resource base Project risk and strategies Requirements Analysis Requirements Analyses templates are available on the PMO Web site Initially, the RA may be done by a more senior PM in your area (or by PMO) The more accurate the analysis the greater the project’s chances of success! Resist the temptation to skip or shorten this crucial effort! Requirements Analysis Key goal is to evaluate the project’s Return On Investment (ROI) and cost/benefit ratio Focus on deliverables in business context: Improve service Reduce cost Mitigate risk A project can be worthwhile but not be worth doing! Requirements Analysis “We know our business and don’t need anyone to tell us how to do it” New user technology almost always requires changes to existing business processes A Business Process Analysis (BPA) will help insure those changes are identified and made BPAs are the responsibility of the business owner but can be critical to TS project success 1. Requirements Analysis 2. Classification Worksheet 3. Planning Templates 4. PMIT Data Entry Requirements Analysis Guides 1. 2. Short Form – simple projects Long Form – more complex projects Classification Worksheet Using information from the RA, the PM completes the Classification Worksheet to arrive at the project’s complexity level The classification is a guideline. If, for any reason, the PM feels the project to be higher in complexity than calculated, the project can always be managed at the next level Projects are not to be managed at a lower level than calculated Project Classification Criteria Projects are classified by: Budget Time Resources Risk Project Classification Fast Track 80 hours or less Two or less personnel from within one TS unit Below $10,000 total cost Low Complexity Greater than 80 and less than 240 hours Greater than two and less than 10 personnel Greater than $10,000 and less than $100,000 Project Classification Medium Complexity Greater than six weeks and less than one year Greater than 10 and less than 25 personnel Greater than $100,000 and less than $500,000 High Complexity Greater than one year Greater than 25 personnel Greater than $500,000 Project Classification Complexity determines what project plan components are required Fast Track Fast Track Project Worksheet Low Complexity 1. Project Information 2. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) 3. Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) 4. Schedule 5. Communications Plan 6. Quality Management Test Plan Project Classification Medium Complexity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Project Information Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) Schedule Communications Plan Quality Management Test Plan Quality Management IV&V Plan Budget Plan Spending Plan Risk Plan Project Classification High Complexity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Project Information Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS) Schedule Communications Plan Quality Management Test Plan Quality Management IV&V Plan Budget Plan Spending Plan Risk Plan Procurement Plan Change and Configuration Management Plan Performance Plan Classification Worksheet Review PMO Web Site Classification Worksheet PMIT System Once you authenticate with your eID and password, PMIT home page displays You have two options: 1. 2. Data Review Data Management In Data Review, you can review previously entered project data In Data Management, you can enter a new project or update an existing one PMIT System For existing projects, you can Assign to another project manager Suspend a project Previous PM can no longer update Retains all data entered Removes from management reports Can be made Active again later Delete a project Removes it from the database No longer available for any future action PMIT System PMIT has workflows for each project complexity level to automatically guide you through the entry of required plans If interrupted, PMIT records where the workflow stopped and upon signing in again displays the completion status of all forms Once all forms are completed, the status of the project is automatically set to Active PMIT System All project information can be edited/deleted until the project is Closed Three aspects of active project performance will be monitored by the management dashboard 1. 2. 3. Scope Budget Schedule PM must update status of all three at least every two weeks! PMIT Demos 1. Create a new Fast Track project 2. Create a new Low Complexity project 3. 4. Update the LC project’s budget, scope and schedule status Close the LC project LAB #1 http://wrc2003-test.vcu.edu/WSS/ITPros/default.aspx 1. 2. 3. Classify example projects #1 and #2 Identify the project plan templates needed for each Enter the plan data into PMIT for #1 VCU Project Workflow Review Project proposal 1. Builds the business case Requirements analysis 2. Budget, Time, Resources, Risk, Alternative Solutions, Recommendation Review, approve, prioritize according to: 3. Contribution to department, unit, and University goals and objectives Return On Investment (ROI) VCU Project Workflow Review Assign Project Manager 4. TS Management with sponsor input Develop Project Plan, enter and update project information in PMIT 5. Plans, reports and analyses Monitor project performance 6. Update plans, record issues Closeout 7. Obtain user acceptance of all deliverables Close project in PMIT Course Take-Aways VCU’s management agreement with COVA requires a project management methodology be followed for University IT projects TS Task Force developed VCU’s Project Management policy, standards, best practices and established requirements for PMIT system Project manager skills and experience and PMIT requirements scale up with project complexity Course Take-Aways As a PM you may use any other project management tools you like, but you must enter and update data in PMIT CIO says “If it’s not in PMIT it’s not a project…” Anyone in TS is eligible to become a PM by meeting the education and experience qualifications Anything that doesn’t work as designed, we can change for the better PMIT Basics Questions/Discussion James C. Thomas Project Management Office 8-9954 jcthomas@vcu.edu