The stages of the writing process approach
advertisement

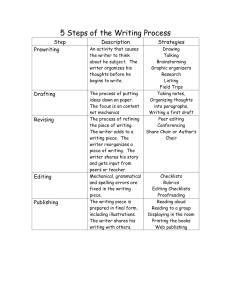
Process writing means that the writer should move away from the view that written texts are a collection of grammatically correct sentences. Process writing is connected with the different subskills (stages) that the language writers use when they write. Process writing refers to a broad range of strategies that include pre-writing activities, such as defining audience, using a variety of resources, planning the writing, as well as drafting and revising. These activities, collectively referred to as processoriented instruction, approach writing as problem-solving. The process of how ideas are developed and formulated in writing. “Good writing does not just happen. The best writers spend a great deal of time thinking, planning, rewriting, and editing.” The teacher’s role in the process model is to facilitate the writing process rather than to provide direct instruction (Teacher as the facilitator). Students are given considerable freedom within the task. Encourages students to communicate their own written ideas. It focuses more on the fluency of producing ideas than on the linguistic and grammatical accuracy of these ideas. Inaccurate attempts at handwriting, spelling, and grammar are accepted in this time and dealt with later on in individual and small group conference interviews. Writing moves naturally from invention to convention. Classmates and others, including the teacher, respond to drafts (Freeman and Freeman 2004). Prewriting: Selecting a topic and planning what to say. While Writing: ◦ Drafting: Putting a draft on paper. ◦ Revising: Making changes to improve writing. ◦ Editing: Correcting grammar, spelling, punctuation marks and mechanics of writing. Post writing: ◦ Evaluation: Assessment of the written work. ◦ Publishing: Publishing the final written work. PRE-WRITING: Students work cooperatively and write down all the ideas that come to mind in connection with a topic. Students have to do the following: Group Brainstorming Group research on a writing topic Questioning (Journalist Questions) Discussion and Debate Mapping / Clustering. The preferred prewriting technique for writers who are visually oriented because it allows them to generate and organize ideas in a visual context. Writing the thesis statement: The writer (s) should write a comprehensive statement that gives a complete and brief idea concerning what the writer will talk about in the rest of the essay. Individual writing. Collaborative writing. Students work together to write a previously agreed text. Peer Revision: students exchange their first drafts of a text and point out changes in the macro aspects of writing which are needed to help the reader. Peer editing (students exchange their first drafts of a text and point out changes in the micro aspects of writing which are needed to help the reader. Whole class discussion of how a particular text might need adjustment according to the audience it is addressed to. Self-editing. Conferencing. Reformulation. EVALUATION Negotiated feedback in which the learner decides the focus of the given evaluation. PUBLISHING Publishing the final product and sharing it with an appropriate audience. It may be oral, visual, or written. Thank you so much for your attention