Presentation
advertisement

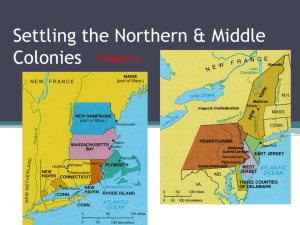
Colonizing the Chesapeake and New England Colonies APUSH Unit One English Colonization 1497- John Cabot commissioned to find a Northern route to reach the Indies (America). Cabot claims land in New England, Nova Scotia and Newfoundland for the English. For about 100 years the English chose to pirate Spanish and Portuguese ships on the seas. Most famous “pirate” was Sir Francis Drake. 1607-Jamestown established in Virginia. 1621-colony of Massachusetts established! English colonization had begun! Joint Stock Companies formed English decided to make the “process” of colonization less dangerous for them. Two companies are formed to colonize the Americas. – Plymouth Company. – London Co. Of Virginia. They are going to set up a colony in territory claimed by Raleigh. Territory was named Virginia. Takes three years to raise money, supplies for trip. Joint Stock Companies Designed to make investors money! Controlled by a Board of Directors. Pay Employees to work for them! Shareholders make money when products are brought back from Colony and sold for a profit. Main Goal is to Make Money! London Company of Virginia Organized by Business investors. June of 1606, King James grants them a Charter to form colony of Jamestown! December of 1606money secured in England for 3 ships and 144 men. Hired No Farmers! All City Folk! April 1607 • Rough Atlantic Crossing during Hurricane season! • Many have never been on board of a ship before! • 39 men die during the Voyage! • Reach the Chesapeake in July of 1607! Weather is warm and Muggy! • Orders opened upon arrival dictate John Smith as one of the leaders. July / August 1607 • Settlers build a trading post in the Middle of a River Delta / swamp. • People start to die off immediately! • No Sanitation! • Pit dug near the river to be used as a toilet/waste disposal…below the water line! • Colonists contract “Bloody Flux” January of 1608 • Things are at their worst! • A Supply ship arrives with 120 new men! • They found a large Graveyard with only 38 survivors! • 5 Days after arrival, supplies and shelter burn to the ground! Spring of 1608 • 158 people are able to survive through the Winter! • Aided by the local Indian tribes. Chief Opeshcancanough believes that is what he should do! • English start digging up the surrounding countryside looking for Gold! • Indian people are amazed! Smith’s Mission • Survival is his Number One priority! • Motto: “you don’t work…you don’t eat!” • Daily life becomes like a boot camp! • Up at Dawn, in bed before dark! • Saved the citizens of Jamestown! Captain John Smith • By Spring of 1608 He has had enough! • He has a military background! • Seized control of settlement in January of 1608. • He reorganizes the settlement in a military fashion! • Moved settlement of Jamestown up River to higher ground! Pocahontas • She was the daughter of the chief of the Powhatan. • She married John Rolfe, a tobacco farmer and went to England. • She died there and is buried in a London graveyard. • She never married John Smith! Three types of colonies in New World • Plantation Colonies: A society based on the cultivation of a cash crop. (tobacco, rice, indigo) • Trading Colonies: A society based on trade with the native peoples of a region. (beaver fur, pelts, fish) • Settlement Colonies: A society based on subsistence farming. (lumber, shipbuilding, trade with Europe) Jamestown after Smith • Smith had moved the settlement upstream & it was moved again after he left. • Eventually became a trading port for English tobacco farmers. • English never found any Gold of significance. • Original settlement was excavated recently and artifacts are being catalogued. New England Colonies Middle Colonies Chesapeake Colonies Southern Colonies Prison Colony Mercantilism Economic Theory of most European Nations between 1500 and 1700. Basically means “the more gold / money you have, then the more powerful you are.” Most European nations wanted to collect as much bullion (raw gold or silver) as possible. •Difficult winter (44 out of 102 survived)…. •First year went through a “starving time” •Developed friendly relations with Indian tribes •Squanto befriended settlement •Plymouth settlement survived under the leadership of Gov. William Bradford •First Thanksgiving Contrast with Virginia: Different environment & key role of religion for Puritans Congregationalists & Separatists Pilgrims (the latter) found Plymouth (1620) – Fled Religious and Political Persecution •41 Male passengers on the Mayflower formed into a “civil body politic”, signed a compact promising to write and obey "just and equal laws ... for the general good of the colony." •The compact brought an element of democracy to America and was an example of the practice of selfgovernment in the colonies. •All the colonies practiced some form of selfgovernment………… James I (1603 - 1625) •James I was the son of Mary, Queen of Scots. He had become James VI of Scotland after Mary lost her head, and he became James I when he took over England. •He was the first to call himself "King of Great Britain." James struggled with Parliament - he thought he ruled by divine right. •There was a new English translation of Bible - the "King James Bible.“ •He persecuted Pilgrims because they would not recognize him as the religious leader of the Church of England. •So, they became a political risk as well. Pilgrims merge with the Puritans to form Massachusetts Bay Colony •John Winthrop, founder of the Massachusetts Bay Colony •Middle class settlers, educated and organized •Successful as fur traders, fishermen and shipbuilders •Ruled as “Bible Commonwealth” or theocracy •New England Way = Puritan covenant with God •To establish holy society----”city upon a hill” Pilgrims merge with the Puritans to form Massachusetts Bay Colony Communities well organized Established towns Protestant Work Ethic Family values New England Massachusetts New Hampshire Rhode Island Connecticut Building the Bay Colony Franchise (right to vote) extended to “freemen” – adult Puritan men of Congregational church (about 40% of men in the colony ~ higher percentage than in England) However, in town government, all propertyowning males could vote in town meetings – Direct democracy----self government Since idea of government was to enforce God’s laws, religious leaders (e.g. John Cotton) were very influential Building the Bay Colony Clergy were barred from formal political office – early “church/state separation” Puritan ideas: “calling” to God’s work, Protestant work ethic, limited worldly pleasures, fear of hell Trouble in Bible Colony (Puritan Rebels) Social harmony when only Puritans, but that didn’t last Quakers: fines, floggings, banishments, executions Anne Hutchinson: truly saved don’t need to obey (“antinomianism” the theological doctrine that by faith and God's grace a Christian is freed from all laws (including the moral standards of the culture) – Banished from Mass. Bay – Travels to Rhode Island with her children and helps organize this settlement Trouble in Bible Colony (Puritan Rebels) Roger Williams Roger Williams: extreme Separatist, denied right of civil government to govern religious behavior, challenged charter for illegally taking land from Indians Avoided exile to England by fleeing to Rhode Island where in 1636, aided by Indians, he started a colony in the Providence area Started the first Baptist church Allowed complete freedom of religion New England Spreads Out 1635: Hartford (Conn.) founded by Dutch/English settlers. Some Puritans moved westward to Connecticut with Rev. Thomas Hooker 1639: Fundamental Orders – modern constitution established democratic government 1641: New Hampshire taken over by overly aggressive Bay Colony 1679: Annoyed by greed of Bay Colony, king arbitrarily separates it, becomes royal colony Half-Way Covenant 1st generation’s Puritan zeal diluted over time Problem of declining church membership 1662: Half-Way Covenant – partial membership to those not yet converted (usually children/ grandchildren of members) Eventually all welcomed to church, erased distinction of “elect” Middle Colonies New York Pennsylvania New Jersey Delaware New Netherland (New York) 1609: Henry Hudson sailing for Dutch East India Company sails into Hudson river looking for passage through continent ~ claims area for Dutch 1623-24: Dutch West India Company establishes New Netherland Goal: quick-profit fur trade “Bought” Manhattan from Indians Company town: no religious tolerance or free speech, harsh governors New York Harbor, 1639 New Amsterdam Dutch Conflicts Dutch cruelties to Indians brought retaliatory massacres – Dutch built wall (Wall Street) Connecticut rejected Dutch settlers Dutch in New York An Angry Peter Stuyvesant Duke of York English immigration to New Netherland resulted in 1/2 total population English regarded Dutch as intruders Charles II brazenly granted area to his brother (Duke of York) English squadron comes, New Netherland leader, Peter Stuyvesant, governor of New York had no defense; surrendered, renamed New York New Jersey Lord John Berkeley James gave 2 friends, Lord John Berkeley and Sir George Carteret, the section of New York located between the Hudson River and Delaware Bay in 1664 – He felt the territory of New York was too large to administer Both proprietors allowed religious freedom and an assembly in addition to giving generous land offers to attract settlers Mid-1600s: religious dissenters named Quakers arose in England Hated by authorities because they refused to pay taxes to Church of England, refused to take oaths, refused military service Penn’s family owed a large debt from the British Crown. Given a land grant in 1681. Pennsylvania Penn governs the colony, unusual for a proprietor Advertised in Europe, promising land & freedoms Frame of Government (guaranteed elected assembly), Charter of Liberties (freedom of worship, open immigration), fair treatment of Native Americans •This was known as the "Glorious Revolution." (Revolution because they overthrew the last Catholic monarch, Glorious because no one died.) • Parliament put more restrictions on the monarch. •The king couldn't make or suspend laws, have an army during peacetime, and the king couldn't interfere with freedom of speech in Parliament. •English Bill of Rights •Charles II was the son of Charles I. •Because his father had been killed, Charles II had the ravens caged so they couldn't leave. •He was a "Merry Monarch," a very popular king. •Charles II encouraged religious toleration. Charles II (1660 - 1685) •The “Restoration Colonies” were settled during his reign.