Unit 1 Cell and Molecular Biology
advertisement

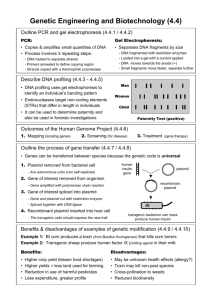
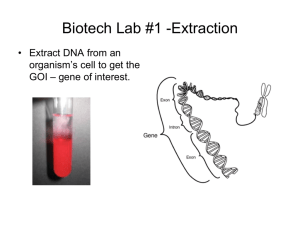
Unit 1 Cell and Molecular Biology Section 10 Agriculture Transgenic Plants A transgenic organism is an organism that is carrying genetic material of another organism in its genome. Producing a transgenic organism requires: A vector used to insert the required DNA into a plant A way of ensuring the gene is carried in all cells Vectors A vector is an agent used to transfer DNA from one organism to another Agrobacterium (tumerfaciens) is a commonly used vector Agrobacterium is a soil bacteria It contains a plasmid (known as Ti) which it can insert into plant DNA causing a tumour (crown gall disease) Procedure for creating a transgenic plant using a Ti-plasmid Ti disease gene is disabled Eg. By removing it with restriction enzymes A target gene containing desired characteristics is identified A target gene is removed from source DNA using a restriction enzyme The plasmid is then cut using the same restriction enzyme The foreign DNA (target gene) is then added to the plasmid and sealed using DNA ligase The modified plasmid is returned to the Agrobacterium (Note the plasmid also has a method for identification e.g antibiotic resistance – later in the process this is used to identify the cells that have the plasmid) Plant cell protoplasts are prepared The protoplasts are incubated with the bacterium containing the modified plasmid Grown in a selective medium that allows only the growth of cells containing the plasmid (and selected gene) E.g the medium may contain an antibiotic Example 1 – insect resistance The bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis produces proteins (known as BT toxins) that have been used for insecticides The toxin is isolated from the bacteria genome and inserted into Ti plasmid of agrobacterium The resulting plant kills insects that eat it Potato, cotton and soybean are all plants were this technique is used Benefits Only insects eating the plant are killed Reduces the use of pesticides The entire plant has protection (not just the leaves and stem, as would be the case if it was sprayed) Example 2 – Tomato plants Tomato ripening is naturally accompanied by softening due to an enzyme – PG (polygalacturonase) Fruit an usually picked while still green and ripened artificially using ethene gas By modifying the PG gene, fruit could be left to ripen longer without softening Fresher, riper tomatoes could be delivered to supermarkets Bovine Somatotrophin (BST) production Bovine somatotrophin is a growth hormone that can be used to increase growth (mainly muscle and bone) and milk production in cattle The gene is isolated from cattle cells using restriction enzymes A restriction enzyme is also used to open a plasmid from an E. coli bacteria The BST gene is inserted into the plasmid using DNA ligase The E.coli bacteria containing the plasmid are then cultured The gene is expressed (i.e. transcribed and translated into protein form) during bacterial growth The protein is then purified and prepared for administration to cattle Use of BST BST is either administered by injection or the protein is included in cattle feed Results in a 10% increase in milk production Disadvantages / concerns Can increase mastitis in cows Lameness later in life – due to enlarged udders BST causes a lack of fat deposits (more of the glucose etc.. is used) therefore hypothermia can develop BST found in milk – supposedly safe as it will be broken down in our stomachs Activities Monograph pg 90 – 94 DART pg 88 – 93 Scholar Make flow diagrams / posters of the process of Creating transgenic plants BST production Look at websites http://www.food.gov.uk/gmfoods/gmtt/gmplant show Moral and Ethical Issues related to transgenic organisms Moral and Ethical codes attempt to establish acceptable human behaviour for the benefit of all society ‘DART’ Transgenic organisms What rights do they have? Farmers What might there opinions towards transgenic be? How might differing views on accompanying farms be dealt with? Consumers The Environment What are the pros and cons? What are the facts vs media hype? Benefits vs problems Biotechnology Industry Motives vs issues