Exam 1 Review New
advertisement

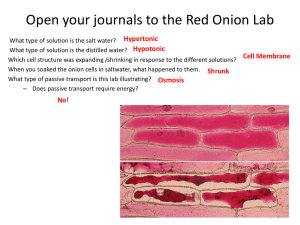
Ashmore Biology 1510 Exam 1 Review Ch. 1- Science of Biology Kingdoms of life include Animalia, Plantae, Protista, Fungi, Bacteria & Archaea What is homeostasis? Why is it essential to all living things? What are the underlying themes of biology Evolution by cooperation; In many cases, organisms have changed (evolved) in response to one another. Distinguish between hypothesis and theory Deductive vs Inductive reasoning; Scientists use inductive reasoning when performing scientific processes. Review the proper order of the Scientific Process Review the properties shared among living organisms CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) act as a catalyst to destroy the ozone which increases UV passage to Earth Definition of Heredity Definition of Theory Symbiosis and the origin of eukaryotic cells; Be able to describe the process by which eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes Ch. 2- Chemistry of Life Be able to distinguish between the atomic number and atomic mass. What do these numbers indicate? Subatomic Particles o Protons- found in the nucleus; positively charged (+1) o Neutrons- found in the nucleus; no charge (0) o Electrons- found in orbitals; negatively charged (-1) Ions- atoms with a positive or a negative charge o Cations- positively charged ion o Anions- negatively charged ion Orbitals pH (acids vs bases); What is the pH scale. Recall that acids have a pH that is less than 7 (<7) and bases have a pH that is greater than 7 (>7). Ionic bonds have a tendency to break when dissolved in water. Ionic bonds form when two atoms are bonded together due to a transfer of electrons. Covalent bonds are formed when to atoms are bonded together due to the sharing of electrons. Review electrons and how they distinguish the properties of atoms o If you change the number of electrons of an atom, the properties of the atom change!! electrons with a filled outer energy level are stable; electrons without a filled outer energy level are reactive. o 2 electrons fill the first energy level o 8 electrons fill the second and third energy level Ashmore Biology 1510 Ch. 3- Molecules of Life The four essential macromolecules are o Carbohydrates- composed of monosaccharides. When many monosaccharides join together a polysaccharide is formed. o Lipids- include fats, phospholipids, and steroids; composed of a glycerol and fatty acids o Proteins- built out of amino acids. Amino acids are joined together by a peptide bond to build a polypeptide chain. o Nucleic Acids- build out of nucleotides; examples of nucleic acid include DNA and RNA Dehydration synthesis is the process by which organic macromolecules such as polysaccharides are made by joining individual monosaccharides. Dehydration synthesis involves the removal of water. Basic structure of proteins Levels of protein structure o Primary- sequence of amino acids o Secondary- formation of alpha helix or beta-pleated sheets o Tertiary- three-dimensional shape of a protein o Quaternary- combining of two polypeptide chains DNA vs RNA o DNA- double stranded molecule containing the sugar deoxyribose. DNA has the four bases Adendine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine o RNA- single stranded molecule containing the sugar ribose. RNA has the four bases Adendine, Uracil, Guanine, and Cytosine Properties of phospholipids- composed of a polar region with two nonpolar fatty acid tails Ch. 4- Cells Cell size (surface area to volume ratio); Why are cell small? Nuclear Envelope; What is its function? Where is it found? Active Transport (low to high concentration); Are molecules moving with the concentration gradient or against it? Prokaryotic cells vs Eukaryotic- Prokaryotes appeared on Earth first and are believed to have given rise to Eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells are the simplest cells. Hypotonic vs Hypertonic o A hypertonic solution such as salt water will cause a cell to shrivel because there is net movement of water out of the cell. o A hypotonic solution such as pure water will cause a cell to swell and possibly burst because there is a net movement of water into the cell. Cell theory o All organisms are composed of cells o Cells are the basic unit of structure and function (smallest living things) o All cells come from pre-existing cells Know the function of ribosomes in protein synthesis. Carbohydrates and lipids are manufactured in the smooth Endoplasmic reticulum Why are chloroplasts and mitochondria believed to have been free-living bacterial cells? The golgi body transports proteins out of the cell. Ashmore Biology 1510 Endocytosis vs exocytosis Active transport vs passive transport o Active transport involves a transmembrane protein and energy to pump molecules from low to high concentration. o Passive transport may occur through the membrane or membrane proteins and does not require energy because molecules are moving from high to low concentration. Chemiosmosis Bacterial cells do not have membrane bound organelles. Osmosis is the diffusion of water Diffusion Transmembrane channel proteins help polar molecule and ions move into and out of the cell. Different kinds of microscopes o Compound light microscope o Electron microscope o Phase-Contrast microscope What is involved in exocytosis? Lab Review Lab 1 and 2 Be able to measure the mass of an object with the triple beam balance. (*the base unit for mass is grams(g)). Be able to convert grams to pounds using the following conversion: 2.2 pounds= 1 kilogram (this will be given to you). Be able to measure the temperature of a solution in degrees Celsius with the use of a thermometer Be able to convert degree Celsius to Fahrenheit using the following conversion: Fahrenheit degrees = (Celsius degrees x 1.8) +32 (this will be given to you) Be able to measure the length of an object in centimeters (cm) Be able to convert centimeters to inches using the following conversion: 1 inch = 2.54 centimeters (this will be given to you) Be able to measure the volume of a liquid in milliliters (ml)** Remember to measure from the bottom line (meniscus) Be able to convert milliliters to quarts using the following conversion: 1.06 quarts = 1 liter (this will be given to you). Be able to rank the metric units in the order of their magnitude from the largest to the smallest. Ex. Meter-decimeter-centimeter-millimeter-micrometer Ashmore Biology 1510 Lab 3 Know the role of the cell membrane. What is the function? How does temperature affect the rate of osmosis? How do you know when a cell (dialysis bag) has reached equilibrium? What would happen to a human cell if it were placed in a salt solution (hypertonic)? Why? What would happen to a human cell if it were placed in a pure water solution (hypotonic)? Why? What cell part keeps a plant cell from rupturing in a pure water solution? What happens to a plant cell that is placed in a salt solution? Explain what happens to the cell membrane. What is the relationship between molasses concentration, rate of osmosis, and mass change? Define solute and solvent. If a solution is 35% solute, what percent is solvent? In what direction does water flow? High to low or low to high? Why does a cook wait until the last minute to put the salad dressing on? Explain in terms of osmosis and diffusion!! Lab 5 Be able to identify the location of the ocular lenses, objective lenses, coarse adjustment knob, fine adjustment knob, and stage What happens to the field of view as the magnification increases? Is the depth of field greater of lesser when the magnification increases?