Unit 1 Notes
advertisement

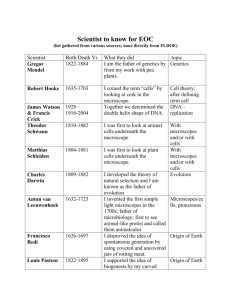
Unit 1 Introduction to Biology Warm Up: Vocabulary Work in groups at your table to come up with basic scientific method vocabulary. Discuss and define these words in your groups. Defining Key Terms Science- an organized way of using evidence to learn about the natural world. Biology- the study of life. Observation- the process of gathering information Defining Key Terms Data- the information gathered from observation. Quantitative- expressed as numbers Qualitative- descriptive, involves characteristics or qualities (no numbers) Defining Key Terms (continued) Inference- a logical interpretation based on prior knowledge or experiences. Hypothesis- a proposed scientific explanation for a set of observations. Hypotheses must be testable!! Typically written in an If….then format. (If… independent variable, then…dependent variable) Think About It You see a plant that is starting to wilt. It does not appear dead, but clearly needs some love. Is this an observation or an inference? In your table groups, come up with as many inferences as you can. Scientific Process Asking a Question Forming a Hypothesis Setting Up a Controlled Experiment Collecting Data Analyzing Results Drawing Conclusions Science As A Way Of Understanding Truths About Science It is an ongoing process Scientific understanding is always changing. Science explores the universe and way many systems and processes interact. Qualities of a Good Scientist Skeptical Open-Minded Come up with one on your own! Exit Slip In KY, all individuals are required to wear seatbelts in moving vehicles. How could scientific research have had an impact on this decision? Warm-Up Exercise Is a scientific hypothesis acceptable if there is no way to demonstrate that the hypothesis is wrong? Explain. Designing an Experiment Independent Variable- the variable that is changed. When graphing, the independent variable is placed on the X axis. Dependent Variable (responding)the variable that is measured. When graphing, the dependent variable is placed on the Y axis. Designing an Experiment Controlled Variables (Constants)factors that remain the same between experimental groups. Control Group- used to compare with the experimental groups. Theories Theory- a well tested explanation that unifies a broad range of observations. To be valid a theory must pass several tests: It must explain observations clearly and consistently. Experiments that illustrate the theory must be repeatable. You must be able to predict results from the theory. Modeling Models- a representation of an object or event that can be studied to understand the real object or event. Types of Models Drawings on paper Real objects used to help us picture things we cannot see A mental picture A set of rules or mathematical relationships that describe how something works Warm Up Calvin is conducting a study on the effects of exercise on personal happiness. He plans on having one group run/walk 6 miles per week and lift weights 3 times a week. He plans to have the other group maintain their normal daily routines, which does not include any exercise whatsoever. Come up with a hypothesis, independent and dependent variables, identify the experimental group and the control group. Evaluate this study. What are some of the problems, and how could it be better? Where Do Living Things Come From? Spontaneous Generation- living things can arise spontaneously from non-living things. While this was the common belief for many years, we now know that it is not true and scientists all over the world prescribe to the idea of biogenesis. Biogenesis- all living things come from other living things. Redi’s Experiment on Spontaneous Generation Repeating Investigations John Needham Claimed that spontaneous generation could occur under the right conditions. Heated sealed flask of gravy and found microorganisms (thought heat would kill any living things in gravy) Found gravy swarming with activity. Repeating Investigations Lazzaro Spallanzani Boiled 2 flasks of gravy, sealed 1 immediately and left the other open (thought boiling would definitely kill microorganisms). Open jar was full of life. Sealed jar was uncontaminated. Spallanzani’s Test of Redi’s Findings Pasteur’s Test of Spontaneous Generation Pasteur showed that all living things come from other living things. (biogenesis) Exit Slip What does the term “spontaneous generation” mean? How does a scientific theory compare with a scientific hypothesis? Warm-Up There are several things that are similar between my fish and the second hand of a clock. Name some of the similarities as well as some of the differences and think about what makes the fish living but the clock not. Characteristics of Living Things Living things are made up of units called cells. Living things reproduce. Sexual Reproduction- 2 parents are united to form a genetically unique offspring. Asexual Reproduction- a single parent produces offspring that are identical to itself. Living things are based on a universal genetic code. A cell is the smallest unit of an organism that can be considered alive. This information is needed to live, grow, and reproduce. Living things grow and develop. Cells undergo differentiation to perform different functions. Characteristics of Living Things Living things obtain and use materials and energy. Living things respond to their environment. Organisms detect and respond to stimuli from their environment. Living things maintain a stable environment. All organisms must take in materials and energy to grow, develop, and reproduce. Metabolism- the sum of all chemical reactions in the body. Although conditions outside an organism may change dramatically, most organisms need to keep conditions inside their bodies constant. (Homeostasis) Taken as a group, living things change over time. Individuals do not change, but groups of organisms tend to evolve over time. Branches of Biology Biosphere- all living things Biome- group of similar ecosystems Ecosystem- living things and their nonliving surroundings Community- populations that live together in a defined area Population- group of organisms of one type that live in the same area Organism- individual living thing Groups of cells- tissues, organs, and organ systems Cells- smallest functional unit of life Molecules- groups of atoms; smallest unit of most compounds Microscopes Microscopes- produce magnified images of structures that are too small to see with the unaided eye. Light Microscopes Produce magnified images by focusing visible light rays. Uses 2 lenses to form an image. The only microscope that can be used to study living things. Electron Microscope Use beams of electrons to produce images. Can produce images up to 1,000x more detailed than light microscopes. Cannot view living cells. 2 Types: Transmission Electron Microscopes (TEMs)Has the most magnification. Used to view the fine structures inside a cell. (organelles) Scanning Electron Microscopes (SEMs)- used to view the detailed surface of a specimen. Early Microbiologists Anton Van Leeuwenhoek Viewed “animalcules” or microorganisms, in pond water, rain water, and dust. Credited for advances in the microscope. Robert Hooke First to describe and coin the word “cell.” Exit Slip What is homeostasis? Give an example of how it is maintained. What biological processes includes chemical reactions that break down materials? List some observations that could be made to determine whether an object that is not moving is living or nonliving. Warm Up List at least two differences between sexual and asexual reproduction. What does it mean/why is is necessary for cells to differentiate? Making Measurements Length- a measure of the straight-line distance between two points. Mass- a measure of the amount of matter in an object. Weight- a measure of the gravitational force exerted on an object. (weight = mass x gravity) Volume- a measure of the size of the body or region in three-dimensional space. Units of Measurement SI System- the standard units of measurements used by scientists. Quantity Unit Abbreviation Length Meter m Mass Gram g Time Second s Temperature Celsius C Volume Liter L SI Prefixes SI prefixes are used for very large and small measurements. SI prefixes are all based in multiples of 10. Ex: 5,000 kilometers = 500,000,000 centimeters Kentucky Has Dark base unit K – kilo H – hecta Da – deca Deep Coal Mines De – deci C – centi M – milli Class Practice Convert 486 milliliters to centiliters. Convert 312 kilometers to meters. Convert 0.32 hectagrams to decigrams. You Try It! Convert 1.85 meters to centimeters. Write 55 decimeters as meters. Change 1.6 kilograms to grams. Warm Up Exercise How many milliliters are on 0.45 liters? How many grams are in 500,000 kilograms? Scientific Notation Scientific Notation- a method of expressing a quantity as a number multiplied by 10 to the appropriate power. (10x) When you multiply in scientific notation, you ADD the exponents. When you divide in scientific notation, you SUBTRACT the exponents. Class Practice Write the following measurements in scientific notation. • • • 800,000,000 meters 0.0015 kg 67,453 L You Try It! Write the following measurements in scientific notation. • • • 0.00046 mL 42,000,000,000 km 89,265 g Class Practice Write these measurements in long form. • • • 4.5 x 103 g 1.99 x 10-8 cm 0.422 x 104 m You Try It! Write these measurements in long form. • • • 9.53 x 105 dm 0.1223 x 103 cg 6.04 x 10-4 mL Class Practice Perform the following calculations • (5.5 x 104 cm) x (1.4 x 104 cm) Perform the following calculations • 5.2 x 108 cm3 9.5 x 102 cm3 You Try It! Perform the following calculations • • (4.34 g/mL) x (8.22 x 106 g/mL) (3.8 x 10-2 cm) x (4.4 x 10-2 cm) x (7.5 x 10-2 cm) Perform the following calculations • 6.05 x 107 g 8.8 x 106 cm3 Graphing Scientific Data Line Graphs- show continuous changes Bar Graphs- compare the values of items Pie Graphs- show the parts of a whole