MASS AND BALANCE

MASS AND BALANCE
LECTURE 4
BALANCE, STABILITY AND
CENTRE OF GRAVITY
INTRODUCTION : RELATIONSHIP
STABILITY BALANCE
WEIGHT
CENTRE OF
GRAVITY
INTRODUCTION
As weight change, it affect the aircraft stability and balance.
Stability is the condition of being stable.
Balance refer to the location of centre of gravity (CG).
If we can’t guarantee the aircraft stability and balance, we’ll have trouble to operate the aircraft.
THEORY OF LEVER
To balance the lever, the weight must be distributed so that the turning effect is the same on one side of the fulcrum.
Important for
Aircraft Stability
Balance
Ensure Flight safety
Refer to CG
4H 1W CREATION
1. What is CG?
2. How important CG is?
3. Where is CG location?
4. When aircraft CG move away?
5. Who can control CG?
WHAT IS CG?
The center of gravity is a point at which an airplane would balance if it were suspended at that point.
How to Balance Aircraft?
CG Location
Longitudinal
(From A/c side view)
Lateral
(From A/c front view)
Figure:
Aircraft
Axis
CG Location
The prime concern of airplane balancing is the fore and aft location of the CG along the longitudinal axis.
1. Where is Fore?
2. Where is aft?
Draw on note!
CG Location
Location of the CG with reference to the lateral axis is also important.
Center of gravity
CG Location Shifted
Lateral balance is relatively easy to control and longitudinal balance is more critical .
The center of gravity is not necessarily a fixed point.
a) Location depends on the distribution of weight.
b) As variable load items are shifted or expended, there is a resultant shift in CG location.
EXAMPLE
• As we move, CG also move.
• Still remember what is CG?
• How can you relate with aircraft situation?
INDIVIDUAL TASK : CLASS
IN 5 MINUTES, I WANT EACH OF YOU TO GIVE
EXAMPLE OF CG WHICH CAN BE RELATED WITH
AIRCRAFT SITIUATION / CONDITION.
What are the variables that can affect weight and CG?
Luggage
Passenger
& Crew
Instrument Fuel
Affect Lateral CG
Affect Longitudinal CG
CG Importance
• As the results, CG location shifted (move).
• Thus, thus the A/C have will pitch up.
• Can cause the A/C stall.
CG Importance
• This cause the A/c lose lateral balance.
• One side of the wing is much more heavy.
• This cause difficulties for pilot to control.
• This unbalance create aircraft instability
Continue. . .
The pilot should realize that if the CG of an airplane is displaced too far forward on the longitudinal axis, a nose-heavy condition will result.
Conversely, if the CG is displaced too far aft on the longitudinal axis, a tail-heavy condition will result.
It is possible that an unfavorable location of the CG could produce such an unstable condition that the pilot could not control the airplane.
Forward Center of Gravity
Nose become Heavy
– Problems controlling and raising the nose
– Inability to flare for landing
Acts as more weight
– More stable ( base on basic principle. The more the weight, the more stable an object)
– Decreased Performance
Higher stall speeds
Aft Center of Gravity
Tail become Heavy
– Light control forces
– Easy to over-control and overstress
Reduced capability to recover from stalls and spins
– Can not lower nose
– Flat spin: nearly impossible to recover
Decreased stability
– Difficult to right itself after maneuvering/turbulence
WHO CAN CONTROL
CG?
PILOT
• Ensure Luggage weight
• Calculate Luggage loading
• Monitor fuel weight
GROUND
TECHNICIAN
• Ensure Luggage weight
• Communicate with Pilot
Terminology & Definition
Terminology & Definition
Datum
Imaginary vertical plane or line from which all measurements of arm are taken. Established by
manufacturer. Everything (moment arms, CG range) measured from this point.
Arm
The distance from the datum to any component part of the airplane, or any object loaded on the airplane. (+) denotes aft of datum, (-) denotes forward of datum
Terminology & Definition
Station
Location in the airplane identified by a number designating its distance in inches from the datum.
Moment
Product of the weight of an item multiplied by its arm.
Moment = Weight (Load) x Arm Distance
Exercise 1 : Calculate Moments
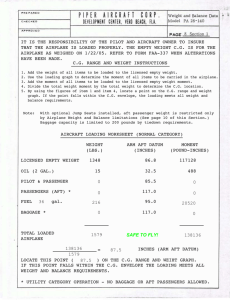
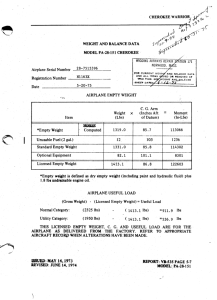
Exercise 2 : Calculate Moments
Exercise 3 : Calculate moments
After receiving your Private Pilot Certificate, you decide to take your family on sight-seeing flight around Grand Forks.
If your mom weighs 150 lbs and sits it the co-pilot seat, your dad is 200 lbs, your sister is 115lbs and you weigh 130 lbs:
How much fuel can you bring? Calculate moments.
Given:
MZFW = 800lbs
MTOW = 775lbs
MLW = 1090 lbs