CASE Tools
advertisement

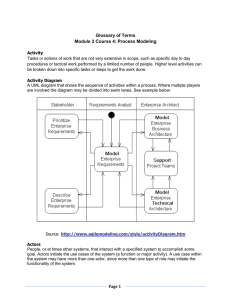
CASE tools 1980s… Upper CASE tools: support for the analysis and design Lower CASE tools: support for construction and maintenance Nowadays… Integrated CASE tools: Offer extensive life cycle coverage CASE tools: Automated Diagram Support Checks for syntactic correctness Data dictionary support Checks for consistency and completeness Navigation to linked diagrams Layering Requirements traceability Automatic report generation System simulation Performance analysis CASE tools: Software construction and maintenance Code generators …Generate code from the design model… Think of the advantages! …may also generate database schemata… Maintenance tools Reverse Engineering Analysis of program code CASE tools: Advantages Help standardization of notations and diagrams Help communication between development team members Automatically check the quality of the A&D models Reduction of time and effort Enhance reuse of models or models’ components CASE tools: Disadvantages • Limitations in flexibility of documentation • May lead to restriction to the tool’s capabilities • Major danger: completeness and syntactic correctness does NOT mean compliance with requirements • Costs associated with the use of the tool: purchase + training UML: History and Brief Summary (1/2) Adoption of the OO paradigm … problematic Emergence of UML as a methods’ unification approach UML: An OMG standard since 1997… Under way to become an ISO standard! UML notation: a melding of graphical notations from various sources. + other concepts… UML: History and Brief Summary (2/2) UML: A method or a notation? Modeling method: techniques + guidelines + notations roadmap for the development of a model Primarily a notation However, there are attempts to describe OO methods or methodological frameworks that would be able to employ UML. 1. The Rational Unified Process 2. The Object-oriented Process, Environment and Notation (OPEN)