Exam 1, Fall 2013
advertisement
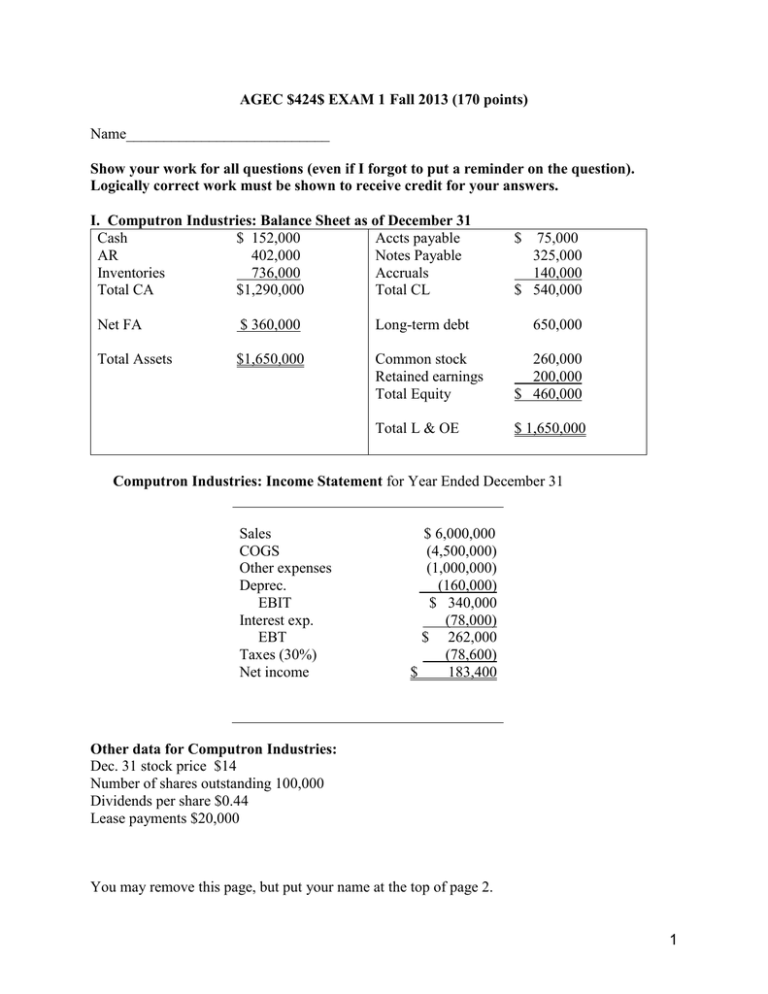
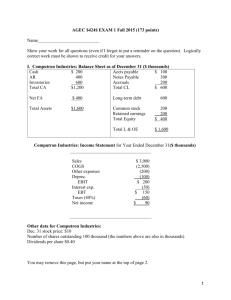
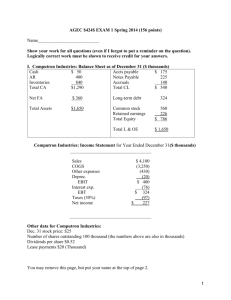
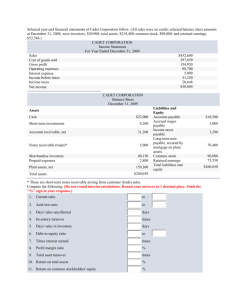
AGEC $424$ EXAM 1 Fall 2013 (170 points) Name___________________________ Show your work for all questions (even if I forgot to put a reminder on the question). Logically correct work must be shown to receive credit for your answers. I. Computron Industries: Balance Sheet as of December 31 Cash $ 152,000 Accts payable AR 402,000 Notes Payable Inventories 736,000 Accruals Total CA $1,290,000 Total CL $ 75,000 325,000 140,000 $ 540,000 Net FA $ 360,000 Long-term debt 650,000 Total Assets $1,650,000 Common stock Retained earnings Total Equity 260,000 200,000 $ 460,000 Total L & OE $ 1,650,000 Computron Industries: Income Statement for Year Ended December 31 Sales COGS Other expenses Deprec. EBIT Interest exp. EBT Taxes (30%) Net income $ 6,000,000 (4,500,000) (1,000,000) (160,000) $ 340,000 (78,000) $ 262,000 (78,600) $ 183,400 Other data for Computron Industries: Dec. 31 stock price $14 Number of shares outstanding 100,000 Dividends per share $0.44 Lease payments $20,000 You may remove this page, but put your name at the top of page 2. 1 Name_______________________ 1. (45 points) Calculate ratios for Computron Industries for use in comparison to the following industry averages. Show your work in the Computron Industries box. Ratio Industry Computron Industries Evaluate briefly and then support If you don’t show your work in this average your statement of by comparing to column you don’t get the points. the industry average. Current Ratio 2.7x Evaluate liquidity: Quick Ratio 1.0x Debt ratio (TL/TA) 70% Times Interest Earned 2.5x Inventory turnover 5x Days sales outstanding 40 days Fixed Asset turnover 4.5x Total assets turnover 2.0x Profit margin (Return on Sales) 3.0% Return on total assets (ROA) 6% Return on equity (ROE) 20% Price-Earnings 15x Market to Book 2.2x Evaluate debt level: Evaluate asset management Evaluate profitability: Evaluate market ratios: 2 Accounts pay. 20 da. Don’t evaluate. deferral Inventory 72 da. Conv. Period Use the above data for questions 2 through 5. 2. (10 points) Construct the extended Du Pont equation for both Computron and for the industry. Then analyze the component breakdown of the company's ROE in comparison to the industry (say something about each component). 3. (4 points) Which is most responsible for the deviation of Computron’s ROE from the industry average: cost control, asset management, or debt management? Explain. 4. (8 points) Show a side by side comparison of the cash conversion cycle for Computron with the industry. Use the CCC to analyze each component of working capital management for Computron in comparison to the industry. Indicate if deviations from the industry are good or not. 5. (4 points) Based on the ratios and information in questions 1-4, point out any red flags or major successes that you see for Computron. 3 6. (10 points). A firm has the following balance sheet: Last Factor Next Last Cash $ 10 Accounts receivable 10 Inventories 10 Fixed assets 90 Total assets Accounts payable Notes payable Long-term debt Common stock Retained earnings Total liab.& equity $120 Factor Next__ $ 10 20 40 40 10 $120 Fixed assets are being used at 80 percent of capacity; sales for the year just ended were $200; sales will increase $20 per year for each of the next 4 years; the profit margin is 5 percent; and the dividend payout ratio is 60 percent. Assume that fixed assets cannot be sold. Show the projected balance sheet above and other calculations below. What are the total external financing requirements for the entire 4 years, i.e., the total AFN for the 4-year period? 7. (14 points) The following question(s) refer to the year-end account balances for UBUS Inc. The accounts are listed in alphabetical order, NOT in the order they appear on the financial statements. Show your work. UBUS Income Statement Cost of Goods Sold 330 Depreciation Expense 35 Interest Expense 20 Operating Expense (excl. Dep.) 115 c) What is UBUS Inc.’s tax liability? Sales 600 Tax rate 40% UBUS Balance Sheet Accounts Payable Accounts Receivable Accruals Accumulated Depreciation Cash Common Stock Fixed Assets (gross) Inventory Long-Term Debt Retained Earnings 35 65 30 (175) 35 120 390 135 200 65 a) What was UBUS Inc.’s earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT)? d) What was UBUS Inc.’s Net Income? e) What is UBUS Inc.’s Total Assets? f) What is UBUS Inc.’s Total Equity? g) What is UBUS Inc.”s Net Working Capital? b) What is UBUS Inc.’s EBT? 4 8. (30 points) Forecast AFN with a 40 % sales increase; at 90% of capacity last year; any additiona funds will come from Notes payable, or a surplus will reduce notes payable. The interest rate is 10%. Round to the nearest whole dollar. Show Sales factor _______ And capacity calculation ___________ Last Sales -VC -FC EBIT -interest EBT -Taxes (40%) NI -Div (45%) Add. RE Cash AR Inv CA NFA TA AP Accr. Notes CL Bonds Stock RE TL+E Factor 1st Pass Feedback 2nd Pass 40,000 -20,000 -15,000 5,000 -600 4,400 -1,760 2,640 -1188 1452 1,000 6,000 9,000 16,000 13,000 29,000 5,000 2,000 2,000 9,000 4,000 4,000 12,000 29,000 Below show calculations and label: AFN for each pass, total AFN after two passes and additional interest expense calculation. 5 (4 points) You have been assigned to estimate the interest rates that your company may have to pay when borrowing money in the near future. The following information is available. kPR = 2% MR = .1% for a 1 year loan increasing by .1% for each additional year LR = .05% for a 1 year loan increasing by .05% for each additional year DR = 0 for a 1 year loan, .2% for a 2-year loan, increasing.1% for each additional year Expected Inflation Rates Year 1 = 7% Year 2 = 5% Year 3 and thereafter = 3% a. Calculate the inflation adjustment (INFL) for a 5-year loan. b. Calculate the appropriate interest rate for a 5-year loan. 9. Show work here: 10. (3 points). Adams Inc. recently borrowed money for one year at 9%. The pure rate is 3%, and Adams’ financial condition warrants a default risk premium of 2% and a liquidity risk premium of 1%. There is little or no maturity risk in one-year loans. What inflation rate do lenders expect next year? Show work here: 11. (3 points) Gowen Inc. began the year with equity of $1,000,000 and 100,000 shares of stock outstanding. During the year the firm paid a dividend of $1.50 per share. Year-end equity was $1,100,000. Assuming no other factors impacted equity, what was Gowen Inc.’s net income for the year? a. $100,000 Show work here: b. $150,000 c. $200,000 d. $250,000 e. $300,000 12. (3 points) During the last year, Alpha Co had Net Income of $150, paid $20 in dividends, and sold new stock for $40. Beginning equity for the year was $700. Ending equity was a. $830 b. $840 Show work here: c. $850 d. $870 6 13. (3 points) Grass Enterprises just closed a good year. It had Sales of $10 million, EBIT of $1 million, and Net Income of $500,000. The firm also paid dividends of $150,000 during the year. If Grass started the year with equity of $900,000, what will its year ending equity be? a. $1,900,000 Show work here: b. $1,400,000 c. $1,250,000 d. $850,000 14. (3 points) A firm had a piece of machinery that cost $7,000 when new and has accumulated $4,500 in depreciation. If the machine is sold for $4,000, which of the following is true? a. The firm has a taxable gain of $4,000 on the sale of the machine Show work here: b. The firm has a taxable gain of $1,500 on the sale of the machine c. The firm has a deductible loss of $3,000 on the sale of the machine d. The firm has a taxable gain of $7,000 on the sale of the machine 15. (3 points) CVD, Inc. has an equity multiplier of 2. What is CVD’s stockholders’ equity if total liabilities are $100,000? a. $100,000 Show work here: b. $150,000 c. $200,000 d. $50,000 16. (3 points) What is the market price per share of Whopie, Inc. if the firm had net income of $200,000, earnings per share of $2.70, total equity of $800,000, and a market to book value ratio of 1.5? a. $16.20 Show work here: b. $10.80 c. $7.20 d. None of the above 17. (2 points) The initial public offerings, or IPOs: a. do not require the SEC’s final approval of the prospectus. b. always result in immediate wealth for the executives of the company who have divested most of their ownership through the offering. c. represent a very risky subdivision of the general stock market. d. all of the above 18. a. b. c. d. (2 points) Which organization typically helps a company market new securities? Commercial bank Insurance company Investment bank Mutual fund 19. a. b. c. d. (2 points) The ________ has traditionally been called the “over-the-counter” market. American Stock Exchange NASDAQ New York Stock Exchange money 7 20. a. b. c. d. (2 points) Interest rates and stock prices move: randomly exhibiting no causal relationship. in opposite directions. up and down together. none of the above 21. (2 points) The increased volatility of longer term bonds in response to interest rate movements is reflected in the: a. pure interest rate. b. default risk premium. c. liquidity risk premium. d. maturity risk premium. 22. (3 points) Marshall Manufacturing has an ACP of 60 days, an inventory turnover of 6, and turns its payables over once a month. How long is Marshall’s cash conversion cycle? (Assume a 360-day year) a. 30 days Show work here: b. 60 days c. 90 days d. 120 days 23. a. b. c. d. (2 points) The cash conversion cycle measures the time: between the creation of receivables and their collection. it takes for inventory to be turned into product and sold. between payment for inventory and collection of cash for its subsequent sale as product. for a check to clear the banking system. 24. (2 points)Which of the following factors does not directly affect the firm’s investment in working capital? a. The firm’s inventory and credit policies b. The age of the firm’s plant and equipment c. The firm’s sales level d. The length of the firm’s operating cycle 25. (3 points) J&J Production Inc. has annual sales of $30 million and accounts receivables of $1.5 million. They have an inventory turnover of 4. How long is J &J's operating cycle? (Assume a 360day year) a. 18 days Show work here: b. 90 days c. 108 days d. 72 days 8