Lingzhi mushroom - Gano Cafe Townsville
advertisement
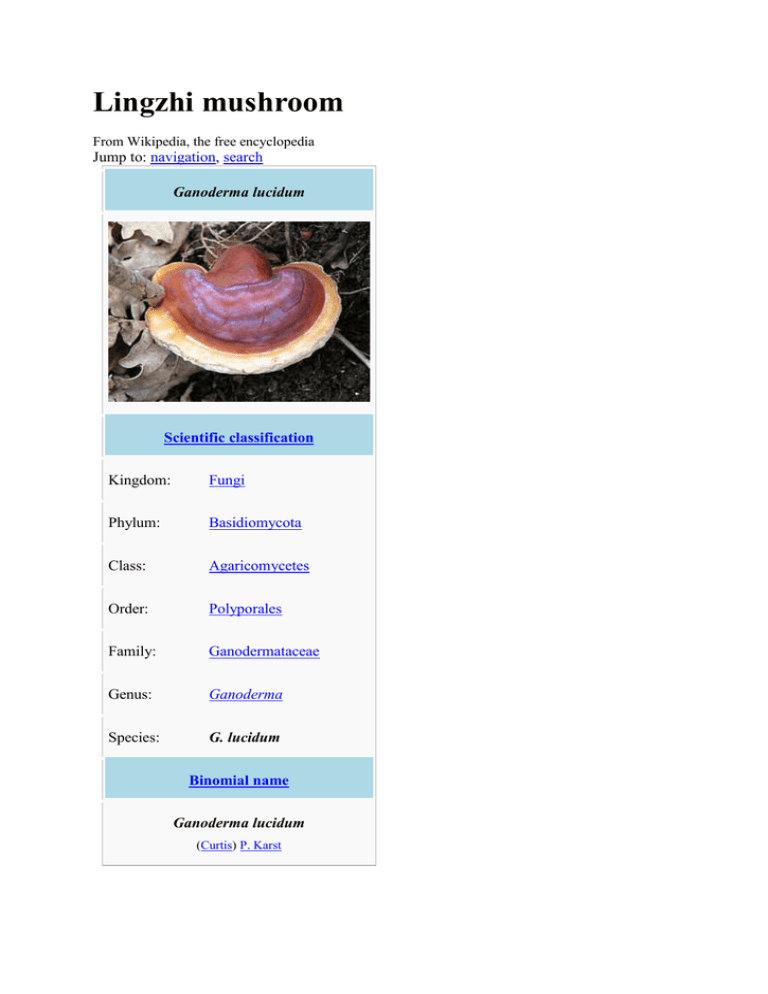
Lingzhi mushroom From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Jump to: navigation, search Ganoderma lucidum Scientific classification Kingdom: Fungi Phylum: Basidiomycota Class: Agaricomycetes Order: Polyporales Family: Ganodermataceae Genus: Ganoderma Species: G. lucidum Binomial name Ganoderma lucidum (Curtis) P. Karst The lingzhi mushroom or reishi mushroom (traditional Chinese: 靈芝; pinyin: língzhī; Japanese: reishi; Vietnamese: linh chi; literally: "supernatural mushroom") encompasses several fungal species of the genus Ganoderma, and most commonly refers to the closely related species, Ganoderma lucidum and Ganoderma tsugae. G. lucidum enjoys special veneration in East Asia, where it has been used as a medicinal mushroom in traditional Chinese medicine for more than 2,000 years,[1] making it one of the oldest mushrooms known to have been used medicinally. Lingzhi is listed in the American Herbal Pharmacopoeia and Therapeutic Compendium. Ganoderma lucidum Mycological characteristics pores on hymenium cap is offset or indistinct hymenium attachment is irregular or not applicable stipe is bare or lacks a stipe spore print is brown ecology is saprotrophic or parasitic edibility: edible Lingzhi mushroom Chinese name Traditional Chinese 靈芝 Simplified Chinese 灵芝 Literal meaning supernatural mushroom [show]Transcriptions Korean name 영지 Hangul [show]Transcriptions Japanese name Kana レイシ Kyūjitai 靈芝 Shinjitai 霊芝 [show]Transcriptions Contents [hide] 1 Taxonomy and naming o 1.1 Botanical names o 1.2 Chinese names o 1.3 Japanese names o 1.4 Korean names o 1.5 Vietnamese names o 1.6 English names 2 Description o 2.1 Varieties 3 Biochemistry 4 Habitat 5 History 6 Research and therapeutic usage o 6.1 Preparation 7 See also 8 References 9 Further reading 10 External links Taxonomy and naming[edit] Names for the lingzhi fungus have a two thousand year history. The Chinese term lingzhi 靈 芝 was first recorded in the Eastern Han Dynasty (25–220 CE). Petter Adolf Karsten named the genus Ganoderma in 1881.[2] Botanical names[edit] The lingzhi's botanical names have Greek and Latin roots. The generic name Ganoderma derives from the Greek ganos γανος "brightness; sheen", hence "shining" and derma δερμα "skin".[3] The specific epithet Lucidum is Latin for "shining" and tsugae for "hemlock" (from Japanese tsuga 栂). There are multiple species of Lingzhi, scientifically known to be within the Ganoderma lucidum species complex and mycologists are still researching the differences among species within this complex.[4] Chinese names[edit] In the Chinese language, lingzhi compounds ling 靈 "spirit, spiritual; soul; miraculous; sacred; divine; mysterious; efficacious; effective" (cf. Lingyan Temple) and zhi 芝 "(traditional) plant of longevity; fungus; seed; branch; mushroom; excrescence". Fabrizio Pregadio explains, "The term zhi, which has no equivalent in Western languages, refers to a variety of supermundane substances often described as plants, fungi, or "excresences"."[5] Zhi occurs in other Chinese plant names such as zhima 芝麻 "sesame" or "seed", and was anciently used a phonetic loan character for zhi 芷 "Angelica iris". Chinese differentiates Ganoderma species between chizhi 赤芝 "red mushroom" G. lucidum and zizhi 紫芝 "purple mushroom" G. japonicum. Lingzhi 靈芝has several synonyms. Ruicao 瑞草 "auspicious plant" (with rui 瑞 "auspicious; felicitous omen" and the suffix cao "plant; herb") is the oldest; the (ca. 3rd century BCE) Erya dictionary defines qiu 苬 (interpreted as a miscopy of jun 菌 "mushroom") as zhi 芝 "mushroom" and the commentary of Guo Pu (276–324) says, "The [zhi] flowers three times in one year. It is a [ruicao] felicitous plant."[6] Other Chinese names for Ganoderma include ruizhi 瑞芝 "auspicious mushroom", shenzhi 神芝 "divine mushroom" (with shen "spirit; god' supernatural; divine"), mulingzhi 木靈芝 (with "tree; wood"), xiancao 仙草 "immortality plant" (with xian "(Daoism) transcendent; immortal; wizard"), and lingzhicao 靈芝草 or zhicao 芝草 "mushroom plant". Since both Chinese Ling and Zhi have multiple meanings, Lingzhi has diverse English translations. Renditions include "[zhi] possessed of soul power",[7] "Herb of Spiritual Potency" or "Mushroom of Immortality",[8] "Numinous Mushroom",[9] "divine mushroom",[10] "divine fungus",[11] "Magic Fungus",[12] and "Marvelous Fungus".[13] Japanese names[edit] Japanese language Reishi 霊芝 is a Sino-Japanese loan word from l=Lingzhi. This modern Japanese kanji 霊 is the shinjitai "new character form" for the kyūjitai "old character form" 靈. Reishi synonyms divide between Sino-Japanese borrowings and native Japanese coinages. Sinitic loanwords include literary terms such as zuisō 瑞草 (from ruicao) "Auspicious Plant" and sensō 仙草 (from xiaocao) "Immortality Plant". A common native Japanese name is mannentake 万年茸 "10,000 year mushroom". The Japanese writing system uses shi or shiba 芝 for "grass; lawn; turf" and take or kinoko 茸 for "mushroom" (e.g., shiitake). Other Japanese terms for Reishi include kadodetake 門出茸 "Departure Mushroom", hijiridake 聖 茸 "Sage Mushroom", and magoshakushi 孫杓子 "grandchild ladle". Korean names[edit] Korean language Yeong Ji or Yung Gee (영지,靈芝) is a word from hanja of lingzhi. It is also called Seon-cho (선초,仙草), Gil-sang-beo-seot (길상버섯,吉祥茸), Yeong ji cho (영지초, 靈芝草) or Jeok ji (적지,赤芝). It can be classified by its color such as Ja-ji (자지,紫芝) for purple one, Heuk-ji (흑지,黑芝) for black, Cheong-ji (청지,靑芝) for blue or green, Baek-ji (백지,白芝) for white, Hwang-ji (황지,黃芝) for yellow. Vietnamese names[edit] Vietnamese language linh chi is a word from tiếng Việt. It is often used with (nấm Linh Chi) which is the equivalent of Ganoderma Lucidum or Reishi Mushroom. English names[edit] English Lingzhi or ling chih (sometimes misspelled "ling chi" from French EFEO Chinese transcription) is a Chinese loanword. The Oxford English Dictionary gives Chinese "líng divine + zhī fungus" as the origin of ling chih or Lingzhi, and defines, "The fungus Ganoderma lucidum, believed in China to confer longevity and used as a symbol of this on Chinese ceramic ware."[14] The OED notes the earliest recorded usage of the Wade-Giles romanization ling chih in 1904,[15] and of the Pinyin lingzhi in 1980. In addition to the transliterated loanword, English names include "Glossy Ganoderma" and "shiny polyporus".[16] Description[edit] Lingzhi is a polypore mushroom that is soft (when fresh), corky, and flat, with a conspicuous red-varnished, kidney-shaped cap and, depending on specimen age, white to dull brown pores underneath.[8] It lacks gills on its underside and releases its spores through fine pores, leading to its morphological classification as a polypore. young Sporocarp Varieties[edit] Ganoderma lucidum generally occurs in two growth forms, one, found in North America, is sessile and rather large with only a small or no stalk, while the other is smaller and has a long, narrow stalk, and is found mainly in the tropics. However, many growth forms exist that are intermediate to the two types, or even exhibit very unusual morphologies,[8] raising the possibility that they are separate species. Environmental conditions also play a substantial role in the different morphological characteristics Lingzhi can exhibit. For example, elevated carbon dioxide levels result in stem elongation in Lingzhi. Other forms show "antlers', without a cap and these may be affected by carbon dioxide levels as well. The species can also be differentiated by their colors in which the red reishi is the most researched kind. Biochemistry[edit] Ganoderic acid A, a compound isolated from Lingzhi. Ganoderma lucidum produces a group of triterpenes, called ganoderic acids, which have a molecular structure similar to steroid hormones.[17] It also contains other compounds often found in fungal materials, including polysaccharides (such as beta-glucan), coumarin,[18] mannitol, and alkaloids.[17] Habitat[edit] Ganoderma lucidum, and its close relative Ganoderma tsugae, grow in the northern Eastern Hemlock forests. These two species of bracket fungus have a worldwide distribution in both tropical and temperate geographical regions, growing as a parasite or saprotroph on a wide variety of trees.[8] Similar species of Ganoderma have been found growing in the Amazon.[19] In nature, Lingzhi grows at the base and stumps of deciduous trees, especially maple.[20] Only two or three out of 10,000 such aged trees will have Lingzhi growth, and therefore its wild form is extremely rare. Today, Lingzhi is effectively cultivated both indoors under sterile conditions and outdoors on either logs or woodchip beds. History[edit] Man holding ganoderma by Chen Hongshou The Chinese classics first used zhi during the Warring States Period (475–221 BCE) and lingzhi during the Han Dynasty (206 BCE-220 CE). The word zhi 芝 occurs approximately 100 times in classical texts.[21] Occurrences in early Chinese histories, such as the (91 BCE) Shiji "Records of the Grand Historian" and (82 CE) Hanshu "Book of Han", predominantly refer to the "Mushroom of Immortality; elixir of life". They record that fangshi "masters of esoterica; alchemists; magicians", supposedly followers of Zou Yan (305–240 BCE), claimed to know secret locations like Mount Penglai where the magic zhi mushroom grew. Some sinologists propose that the mythical zhi 芝 derived from Indian legends about soma that reached China around the 3rd century BCE.[22] Fangshi courtiers convinced Qin and Han emperors, most notably Qin Shi Huang (r. 221–210 BCE) and Emperor Wu of Han (r. 141–87 BCE), to dispatch large expeditions (e.g., Xu Fu in 219 BCE) seeking the zhi Plant of Immortality, but none produced tangible results. Zhi occurrences in other classical texts often refer to an edible fungi. The Liji "Record of Ritual" lists zhi "lichens" as a type of condiment.[23] The Chuci "Song of the South" metaphorically mentions, "The holy herb is weeded out".[24] The Huainanzi "Philosophers of Huainan" records a zizhi 紫芝 "Purple Mushroom" Aphorism, "The zhi fungus grows on mountains, but it cannot grow on barren boulders."[25] The word lingzhi 靈芝 was first recorded in a fu 賦 "rhapsody; prose-poem" by the Han dynasty polymath Zhang Heng (CE 78–139). His Xijing fu 西京賦 "Western Metropolis Rhapsody" description of Emperor Wu of Han's (104 BCE) Jianzhang Palace parallels lingzhi with shijun 石菌 "Rock Mushroom": "Raising huge breakers, lifting waves, That drenched the stone mushrooms on the high bank, And soaked the magic fungus on vermeil boughs."[26] The commentary by Xue Zong (d. 237) notes these fungi were eaten as drugs of immortality. The (ca. 1st–2nd century CE) Shennong bencao jing "Divine Farmer's Classic of Pharmaceutics" classifies zhi into six color categories, each of which is believed to benefit the qi "Life Force" in a different part of the body: qingzhi 青芝 "Green Mushroom" for Liver, chizhi 赤芝 "Red Mushroom" for heart, huangzhi 黃芝 "Yellow Mushroom" for spleen, baizhi 白芝 "White Mushroom" for Lung, heizhi "Black Mushroom" 黑芝 for kidney, and zizhi 紫芝 "Purple Mushroom" for Essence. Commentators identify this red chizhi (or danzhi 丹芝 "cinnabar mushroom") as the lingzhi. Chi Zhi (Ganoderma rubra) is bitter and balanced. It mainly treats binding in the chest, boosts the heart qi, supplements the center, sharpens the wits, and [causes people] not to forget [i.e., improves the memory]. Protracted taking may make the body light, prevent senility, and prolong life so as to make one an immortal. Its other name is Dan Zhi (Cinnabar Ganoderma). It grows in mountains and valleys.[27][28] While Chinese texts have recorded medicinal uses of lingzhi for more than 2,000 years, a few sources erroneously claim more than 4,000 years.[29] Modern scholarship neither accepts the historicity of Shennong "Divine Farmer" (legendary inventor of agriculture, traditionally r. 2737–2697 BCE) nor that he wrote the Shennong bencao jing. The (ca. 320 CE) Baopuzi, written by the Jin Dynasty Daoist scholar Ge Hong, has the first classical discussion of Zhi.[30] Based upon no-longer extant texts, Ge distinguishes five categories of zhi, each with 120 varieties: Shizhi 石芝 "stone Zhi", Muzhi 木芝 "wood Zhi", Caozhi 草芝 "Plant Zhi", Rouzhi 肉芝 "flesh zhi", and junzhi 菌芝 "mushroom zhi. For example, the "mushroom zhi". Tiny excresences. These grow deep in the mountains, at the base of large trees or beside springs. They may resemble buildings, palanquins and horses, dragon and tigers, human beings, or flying birds. They may be any of the five colors. They too number 120 for which there exist illustrations. All are to be sought and gathered while using Yu's Pace [a Daoist ritual walk], and they are to be cut with a bone knife. When dried in the shade, powdered, and taken by the inch-square spoonful, they produce geniehood. Those of the intermediate class confer several thousands of years, and those of the lowest type a thousand years of life.[31] Pregadio concludes, "While there may be no better term than "mushrooms" or "excresences" to refer to them, and even though Ge Hong states that they "are not different from natural mushrooms (ziran zhi 自然芝) (Baopuzi 16.287)", the Zhi pertain to an intermediate dimension between mundane and transcendent reality."[32] The (1596) Bencao Gangmu ("Compendium of Materia Medica") has a zhi 芝 category that includes six types of Zhi (calling the green, red, yellow, white, black, and purple ones from the Shennong bencao jing the liuzhi 六芝 "six mushrooms") and sixteen other fungi, mushrooms, and lichens (e.g., mu'er 木耳 "wood ear" "Cloud ear fungus; Auricularia auricula-judae"). The author Li Shizhen classified these six differently colored Zhi as Xiancao 仙草 "immortality herbs", and described the effects of Chizhi "red mushroom": It positively affects the life-energy, or Qi of the heart, repairing the chest area and benefiting those with a knotted and tight chest. Taken over a long period of time, agility of the body will not cease, and the years are lengthened to those of the Immortal Fairies.[33][34] Stuart and Smith's classical study of Chinese herbology describes the zhi. 芝 (Chih) is defined in the classics as the plant of immortality, and it is therefore always considered to be a felicitous one. It is said to absorb the earthy vapors and to leave a heavenly atmosphere. For this reason it is called 靈芝 (Ling-chih.) It is large and of a branched form, and probably represents Clavaria or Sparassis. Its form is likened to that of coral.[35] The Bencao Gangmu does not list lingzhi as a variety of zhi, but as an alternate name for the shi'er 石耳 "stone ear" "Umbilicaria esculenta" lichen. According to Stuart and Smith, [The 石耳 Shih-erh is] edible, and has all of the good qualities of the 芝 (Chih), being also used in the treatment of gravel, and said to benefit virility. It is specially used in hemorrhage from the bowels and prolapse of the rectum. While the name of this would indicate that it was one of the Auriculariales, the fact that the name 靈芝 (Ling-chih) is also given to it might place it among the Clavariaceae.[36] Chinese pharmaceutical handbooks on Zhi mushrooms were the first illustrated publications in the history of mycology. The historian of Chinese science Joseph Needham discussed a nolonger extant Liang Dynasty (502–587) illustrated text called Zhong Shenzhi 種神芝 "On the Planting and Cultivation of Magic Mushrooms". The pictures of mushrooms in particular must have been an extremely early landmark in the history of mycology, which was a late-developing science in the West. The title of [this book] shows that fungi of some kind were being regularly cultivated – hardly as food, with that special designation, more probably medicinal, conceivably hallucinogenic."[37] The (1444) Ming Dynasty edition Daozang "Daoist canon" contains the Taishang lingbao zhicao pin 太上靈寶芝草品 "Classifications of the Most High Divine Treasure Mushroom Plant",[38] which categorizes 127 varieties of Zhi.[39] A (1598) Ming reprint includes woodblock pictures.[40] In Chinese art, the lingzhi symbolizes great health and longevity, as depicted in the imperial Forbidden City and Summer Palace.[41] It was a talisman for luck in the traditional culture of China, and the goddess of healing Guanyin is sometimes depicted holding a reishi mushroom.[42] Research and therapeutic usage[edit] Lingzhi possesses anti-tumor, anti-cancer, immunomodulatory and immunotherapeutic activities, supported by studies on polysaccharides, terpenes, and other bioactive compounds isolated from fruiting bodies and mycelia of this fungus (reviewed by R. R. Paterson[17] and Lindequist et al.[43]). It has also been found to inhibit platelet aggregation, and to lower blood pressure (via inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme[44]), cholesterol, and blood sugar.[45] Laboratory studies have shown anti-neoplastic effects of fungal extracts or isolated compounds against some types of cancer, including epithelial ovarian cancer.[46] In an animal model, Ganoderma has been reported to prevent cancer metastasis,[47] with potency comparable to Lentinan from Shiitake mushrooms.[48] The mechanisms by which Ganoderma lucidum may affect cancer are unknown and they may target different stages of cancer development: inhibition of angiogenesis (formation of new, tumor-induced blood vessels, created to supply nutrients to the tumor) mediated by cytokines, cytoxicity, inhibiting migration of the cancer cells and metastasis, and inducing and enhancing apoptosis of tumor cells.[17] Nevertheless, Ganoderma lucidum extracts are already used in commercial pharmaceuticals such as MC-S for suppressing cancer cell proliferation and migration. Additional studies indicate that ganoderic acid has some protective effects against liver injury by viruses and other toxic agents in mice, suggesting a potential benefit of this compound in the treatment of liver diseases in humans,[49] and Ganoderma-derived sterols inhibit lanosterol 14α-demethylase activity in the biosynthesis of cholesterol .[50] Ganoderma lucidum compounds inhibit 5-alpha reductase activity in the biosynthesis of dihydrotestosterone.[44] Besides effects on mammalian physiology, Ganoderma lucidum is reported to have antibacterial and anti-viral activities.[51][52] Ganoderma lucidum is reported to exhibit direct antiviral with the following viruses; HSV-1, HSV-2, influenza virus, vesicular stomatitis. Ganoderma lucidum mushrooms are reported to exhibit direct anti-microbial properties with the following organisms; Aspergillus niger, Bacillus cereus, Candida albicans, and Escherichia coli. Other benefits were studied such as the effect of lowering hypertension, cholesterol, and anti-inflammatory benefits through the ganoderic acid properties. Its genome, with about 12,600 genes on 13 chromosomes, was sequenced in 2012.[53] Preparation[edit] Due to its bitter taste, Lingzhi is traditionally prepared as a hot water extract product.[54] Thinly sliced or pulverized lingzhi (either fresh or dried) is added to a pot of boiling water, the water is then brought to a simmer, and the pot is covered; the lingzhi is then simmered for two hours.[citation needed] The resulting liquid is fairly bitter in taste and dark, with the more active red lingzhi more bitter than the black. The process is sometimes repeated for additional concentration. Alternatively, it can be used as an ingredient in a formula decoction or used to make an extract (in liquid, capsule, or powder form). The more active red forms of lingzhi are far too bitter to be consumed in a soup. While hot water extraction seems to be effective to target the polysaccharides, alcohol extraction is another method used to extract the triterpenes element of the Reishi. See also[edit] Medicinal mushrooms References[edit] 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. ^ Jones, Kenneth (1990), Reishi: Ancient Herb for Modern Times, Sylvan Press, p. 6. ^ Karsten PA. (1881). "Enumeratio Boletinearum et Polyporearum Fennicarum, systemate novo dispositarum". Revue mycologique, Toulouse (in Latin) 3 (9): 16–19. ^ Liddell, Henry George and Robert Scott (1980). A Greek-English Lexicon (Abridged Edition). United Kingdom: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-910207-4. ^ R. S. Hseu, H. H. Wang, H. F. Wang and J. M. Moncalvo (1 April 1996). "Differentiation and grouping of isolates of the Ganoderma Lucidum complex by random amplified polymorphic DNAPCR compared with grouping on the basis of internal transcribed spacer sequences" (Abstract). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62 (4): 1354–1363. PMC 167902. PMID 8919797. ^ Pregadio, Fabrizio (2008). "Zhi 芝 numinous mushrooms; excrescences", in The Encyclopedia of Taoism, Fabrizio Pregadio, ed., Routledge, p. 1271. ^ Tr. by E. Bretschneider (1893), Botanicon Sinicum; Notes on Chinese Botany from Native and Western Sources, Kelly & Walsh, p. 40. ^ Groot, Jan Jakob Maria (1892–1910), The Religious System of China: Its Ancient Forms, Evolution, History and Present Aspect, Manners, Customs and Social Institutions Connected Therewith, Brill Publishers, Vol. IV, p. 307. ^ a b c d David Arora (1986). Mushrooms demystified, 2nd edition. Ten Speed Press. ISBN 0-89815169-4. ^ Pregadio (2008), p. 1271. ^ .Hu, Shiu-ying (2006), Food plants of China, Chinese University Press. ^ Bedini, Silvio A. (1994), The Trail of Time, Cambridge University Press, p. 113. ^ Knechtges, David R. (1996), ' Wen Xuan or Selections of Refined Literature, Volume III, Princeton University Press, p. 211. ^ Schipper, Kristofer M. (1993), The Taoist Body, University of California Press, p. 174. ^ Oxford English Dictionary (2009), CD-ROM edition (v. 4.0), s.v. ling chih. ^ Stephen Wootton Bushell (1904), Chinese Art, Victoria and Albert Museum, p. 148. This context describes the lingzhi fungus and ruyi scepter as Daoist symbols of longevity on a jade vase. ^ Names of a Selection of Asian Fungi, multilingual multi-script plant name database. ^ a b c d Paterson RR (2006). "Ganoderma – a therapeutic fungal biofactory". Phytochemistry 67 (18): 1985–2001. doi:10.1002/chin.200650268. PMID 16905165.) ^ Biosci.Biotechnol.Biochem.,68(4),881–887,2004 ^ Medicinal Mushrooms: An Exploration of Tradition, Healing, & Culture (Herbs and Health Series)by Christopher Hobbs (Author), Harriet Beinfield ^ (National Audubon Society; Field Guide to Mushrooms,1993) ^ Pre-Qin and Han texts, Chinese Text Project. ^ Unschuld, Paul U. (1985), Medicine in China: A History of Ideas, University of California Press, p. 112. ^ Tr. by Legge, James (1885), The Li Ki, 2 vols, Oxford University Press, vol. 1, p. 461. 24. ^ Tr. by Hawkes, David (1959), Ch’u Tz'u: The Songs of the South, Clarendon, p. 258. 25. ^ Tr. by Major, John S., Sarah Queen, Andrew Meyer, and Harold D. Roth (2010), The Huainanzi: A Guide to the Theory and Practice of Government in Early Han China, Columbia University Press, p. 634. 26. ^ Tr. Knechtges (1996), 201. 27. ^ 神農本草經, 草上品. 赤芝。 苦, 平, 無毒。胸中結, 益心氣, 補中, 增智慧, 不忘。久食, 輕身不 老, 延年神仙。一名丹芝。 延年神仙。 28. ^ Tr. by Yang Shouzhong (1998) The Divine Farmer's Materia Medica: A Translation of the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing, Blue Poppy, pp. 17–18 29. ^ Reishi mushroom, Reishiessence.com. 30. ^ 抱朴子/卷11; tr. by Ware, James R. (1966). Alchemy, Medicine and Religion in the China of A.D. 320: The Nei Pien of Ko Hung. Dover. pp. 258. 31. ^ Tr. by Ware (1966), p. 185. This word jun [[Wikt:菌|]] means "mushroom; fungus; bacterium; germ" – not "tiny". 32. ^ Pregadio (2008), p. 1273. 33. ^ 本草綱目/菜之三. 胸中結, 益心氣, 補中, 增智慧, 不忘。久食, 輕身不老, 延年神仙。 34. ^ Tr. by Halpern, George M. (2007), Healing Mushrooms, Square One, p. 59. 35. ^ Stuart, G. A. and F. Porter Smith (1911), Chinese Materia Medica, Pt. 1, Vegetable Kingdom, Presbyterian Mission Press. p. 271. 36. ^ Stuart and Smith (1911), p. 274. 37. ^ Tr. by Needham, Joseph and Lu Gwei-Djen (1986), Science and Civilisation in China: Biology and biological technology. Botany, Volume 6, Part 1, p. 261. 38. ^ DZ 1406, 太上靈寶芝草品, Daoist Studies. 39. ^ Tr. "Catalogue of Mushrooms of Immortality" by [author incomplete], Chapter 1, Introduction, NCCU Institutional Repository, p. 107. 40. ^ 太上灵宝芝草品, online Taishang lingbao zhicao pin illustrated reprint. 41. ^ Smith JE, Rowan NJ, and Sullivan R (2001) Medicinal Mushrooms: Their Therapeutic Properties and Current Medical Usage with Special Emphasis on Cancer Treatments Cancer Research UK, p. 28. 42. ^ Halpern (2007), p.59. 43. ^ Lindequist U, Niedermeyer THJ, Jülich WD. (2005). "The pharmacological potential of mushrooms". Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2 (3): 285–299. doi:10.1093/ecam/neh107. PMC 1193547. PMID 16136207. 44. ^ a b Liu J, Kurashiki K, Shimizu K, Kondo R (December 2006). "Structure-activity relationship for inhibition of 5alpha-reductase by triterpenoids isolated from Ganoderma lucidum". Bioorg. Med. Chem. 14 (24): 8654–60. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2006.08.018. PMID 16962782 45. ^ Chinese Herbal Medicine: Materia Medica, Third Edition by Dan Bensky, Steven Clavey, Erich Stoger, and Andrew Gamble (2004) 46. ^ Zhao S, Ye G, Fu G, Cheng JX, Yang BB, Peng C.,"Ganoderma lucidum exerts anti-tumor effects on ovarian cancer cells and enhances their sensitivity to cisplatin." Int J Oncol. 2011 Mar 8; 47. ^ Lee, SS., Chen, FD., Chang, SC., et al. (1984). In vivo anti-tumor effects of crude extracts from the mycelium of Ganoderma lucidum. J. of Chinese Oncology Society 5(3): 22–28. 48. ^ Suga, T.; Shiio, T.; Maeda, YY.; Chihara, G. (1994). "Anti tumor activity of lenytinan in murine syngeneic and autochthonous hosts and its suppressive effect on 3 methylcholanthrene induced carcinogenesis". Cancer Res. 44: 5132. 49. ^ Li YQ, Wang SF (2006). "Anti-hepatitis B activities of ganoderic acid from Ganoderma lucidum". Biotechnol. Lett. 28 (11): 837–841. doi:10.1007/s10529-006-9007-9. PMID 16786250. 50. ^ Hajjaj H, Macé C, Roberts M, Niederberger P, Fay LB (July 2005). "Effect of 26-oxygenosterols from Ganoderma lucidum and their activity as cholesterol synthesis inhibitors". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 71 (7): 3653–8. doi:10.1128/AEM.71.7.3653-3658.2005. PMC 1168986. PMID 16000773. 51. ^ Wang H, Ng TB (January 2006). "Ganodermin, an antifungal protein from fruiting bodies of the medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum". Peptides 27 (1): 27–30. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2005.06.009. PMID 16039755. 52. ^ Moradali MF, Mostafavi H, Hejaroude GA, Tehrani AS, Abbasi M, Ghods S (2006). "Investigation of potential antibacterial properties of methanol extracts from fungus Ganoderma applanatum". Chemotherapy 52 (5): 241–4. doi:10.1159/000094866. PMID 16899973. 53. ^ Chen, Shilin (2012). "Genome sequence of the model medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum". Nature Communications 3. doi:10.1038/ncomms1923. Retrieved 24 July 2012. 54. ^ Smith, Rowan, and Sullivan (2001), p. 31. Further reading[edit] Xie, J.T.; Wang, C.Z.; Wicks, S.; Yin, J.J.; Kong, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.C.; Yuan, C.S. (2006). "Ganoderma lucidum extract inhibits proliferation of SW 480 human colorectal cancer cells". Exp Oncol 28 (1): 25–9. PMID 16614703. Müller, C.I.; Kumagai, T.; O’kelly, J.; Seeram, N.P.; Heber, D.; Koeffler, H.P. (2006). "Ganoderma lucidum causes apoptosis in leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma cells". Leukemia Research 30 (7): 841–848. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2005.12.004. PMID 16423392. Gao, Y.; Tang, W.; Dai, X.; Gao, H.; Chen, G.; Ye, J.; Chan, E.; Koh, H.L.; Li, X.; Zhou, S. (2005). "Effects of water-soluble Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on the immune functions of patients with advanced lung cancer". J Med FoodTimo H. J. 8 (2): 159–168. doi:10.1089/jmf.2005.8.159. Lindequist, U.; Niedermeyer, T.H.J. ; Jülich, W.D. (2005). "The pharmacological potential of mushrooms.". Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2 (3): 285–99. doi:10.1093/ecam/neh107. PMC 1193547. PMID 16136207. Unknown parameter |unused_data= ignored (help) Tanaka, S.; Ko, K.; Kino, K.; Tsuchiya, K.; Yamashita, A.; Murasugi, A.; Sakuma, S.; Tsunoo, H. (1989). "Complete amino acid sequence of an immunomodulatory protein, ling zhi-8 (LZ-8). An immunomodulator from a fungus, Ganoderma lucidum, having similarity to immunoglobulin variable regions.". J. Biol. Chem. 264 (28): 16372–7. PMID 2570780. Unknown parameter |unused_data= ignored (help) Murasugi, A.; Tanaka, S.; Komiyama, N.; Iwata, N.; Kino, K.; Tsunoo, H.; Sakuma, S. (1991). "Molecular cloning of a cDNA and a gene encoding an immunomodulatory protein, Ling Zhi-8, from a fungus, Ganoderma lucidum.". J. Biol. Chem. 266 (4): 2486–93. PMID 1990000. Unknown parameter |unused_data= ignored (help) External links[edit] Media related to Ganoderma lucidum at Wikimedia Commons Retrieved from "http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Lingzhi_mushroom&oldid=557832255" Categories: Fungi of Asia Fungi of Europe Dietary supplements Medicinal fungi Traditional Chinese medicine Ganodermataceae Sequenced genomes Hidden categories: Articles with inconsistent citation formats Articles with 'species' microformats Articles containing traditional Chinese-language text Articles containing Japanese-language text Articles containing Vietnamese-language text Articles containing simplified Chinese-language text Articles containing Korean-language text All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from March 2009 Pages with citations using unsupported parameters Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in Namespaces Article Talk Variants Views Read Edit View history Actions Search Special:Search Navigation Main page Contents Featured content Current events Random article Donate to Wikipedia Interaction Help About Wikipedia Community portal Recent changes Contact Wikipedia Toolbox What links here Related changes Upload file Special pages Permanent link Page information Cite this page Print/export Create a book Download as PDF Printable version Languages Català Česky Deutsch Ελληνικά Español Esperanto Français 한국어 Hrvatski Bahasa Indonesia Italiano Basa Jawa Magyar മലയാളം မြန်ြာဘာသာ 日本語 Norsk bokmål Polski Português Русский Slovenščina Српски / srpski Suomi Svenska தமிழ் ไทย Türkçe Українська Tiếng Việt 中文 Edit links This page was last modified on 1 June 2013 at 13:54. Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License; additional terms may apply. By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Wikipedia® is a registered trademark of the Wikimedia Foundation, Inc., a non-profit organization. Privacy policy About Wikipedia Disclaimers Contact Wikipedia Mobile view