Facilitator's Guide: Supporting Diverse Learners: Case Studies
advertisement

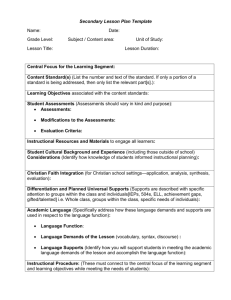
Session 5: Supporting Diverse Learners Sequence of Sessions This training is designed to support high-quality implementation of CKLA. The focus will be on understanding ways CKLA materials can accommodate diverse learners, with an emphasis on strategies, tools and resources for ELLs and children with high-incidence disabilities (e.g., language-related disabilities). All participants will become grounded (or re-grounded) in UDL as a framework for considering accommodations to CKLA lessons. All participants will become grounded (or re-grounded) in UDL as a framework for considering accommodations to CKLA lessons. Teachers, teacher ambassadors, and Network Team members will examine case studies and videos for patterns of lesson accommodations and will gain hands on practice in planning for lesson accommodations, using resources within CKLA (e.g., the A&R guide) as well as introduce tools that can be integrated. Principals will also examine case studies and videos with a focus on recognizing “non-negotiable” of lesson implementation, as well as recognizing allowable accommodations. Overarching Objectives of this May 2014 Network Team Institute: PRINCIPALS 1. Participants will be able to connect principles of universal design for learning (UDL) with meeting the needs of diverse learners within CKLA. 2. Participants will be able to identify lesson “allowable” lesson accommodations within case studies and videos. 3. Participants will gain experience reviewing lesson plans and coaching or providing feedback regarding the accommodations. TEACHERS 4. Participants will be able to connect principles of universal design for learning (UDL) with meeting the needs of diverse learners within CKLA. 5. Participants will be able to identify supplemental resources (the A&R guide, the Supplemental Guide) that can be used to support lesson accommodations. 6. Participants will be identify and apply specific accommodations that can be made to support student learning, in response to case studies. High-Level Purpose of this Session: PRINCIPALS Principals will come out for the first half of this session for an open Q&A in a pull-out session. During this time teachers will examine case studies and creating their lesson plans that reflect accommodations. Principals will return and teachers/groups of teachers will pair with a principal to discuss lesson plans, present accommodations, and hear observations, questions or feedback of the principal. TEACHERS This session is designed to enable educators to apply best practices and concepts of universal design for learning to differentiate instruction to meet specific needs. Related Learning Experiences This training assumes general prior knowledge about CKLA. For schools, teachers, or administrators who are interested in knowing more about Core Knowledge, there are prior training modules posted on EngageNY.org that provide this general support (see . http://www.engageny.org/resource/professional-development-turnkey-kit-ela-p-2-overview for modules of training, on-demand webinars, etc.). It is recommended that anyone new to Core Knowledge look over the material on the program prior to attending this training. Session Outcomes What do we want participants to be able to do as a result of this session? How will we know that they are able to do this? In this session principals and teachers will: 1. Participants will be able to identify specific lessons/activities that can be used to best meet an identified need. Session Overview Section Present Time Overview Planning Instruction ● Using A&R guide in tandem with skills (planning targeted instruction/differentiation) ● uses: progress monitoring; reinforcement, reteaching, and centers ● grouping--WHEN (PP/ GRAIR) and WHO Prepared Resources 1. Facilitator Preparation Participants will plan of small group instruction using their data from either the skills units or progress monitoring, or from a case study scenario of what to do for a newly arrived ELL. Practice Using daily observations of performance, and integrating assessment with Instruction, and providing targeted remediation as quickly as possible will help most struggling students become successful at mastering skills. The A & R guide will help guide teachers to create targeted instruction to satisfy the specific needs of students while in small groups. Debrief 1. 1. Session Roadmap Section 1: Practice Time: __ Planning Instruction Materials used (in slides) ● ● ● Time Using A&R guide in tandem with skills (planning targeted instruction/differentiation) uses: progress monitoring; reinforcement, reteaching, and centers grouping--WHEN (PP/ GRAIR) and WHO Slide #/ Pic of Slide Script/ Activity directions GROUP Slide 1 Slide 2 Key Point: Our objectives for this session include; • working collaboratively to examine case studies of students based on sample data from End-of-Year assessments • Understand how remediation lessons are developed from the Assessment and Remediation Guide to address the specific needs of students • and have the opportunity to build lessons based on the case studies you hear about today or for data that you brought Slide 3 Key Points: • We will follow a pathway as an orientation of how to use the Assessment and Remediation Guide. Our first step is to walkthrough an end-of- year assessment packet for a kindergarten student named Evan, and then for a first grade student named Ella. • For each student you will see the process of gathering, scoring and analyzing the results from the EOY assessments, to determine their specific instructional needs, build an instructional plan and see what a lesson tailored lesson from the A & R guide would look like. • Finally, we will dig into the A & R guide to create instructional plans and aligned lessons for Evan or Ella or for a student from your own data Slide 4 Slide 5 Key Points: • Materials for the assessments including testing instructions, the testing sheets, answer keys, scoring analysis and classroom summary sheets are located in the teacher’s guides. • The student assessments may be included in the teacher’s guides, or the TG will direct you to location of the student assessments in the student workbook along with individual summary score sheets • Extra worksheets are included in the student workbook for students to practice skills while the teacher is administering assessments to students one-on-one Slide 6 Key Points: The End- of -Year Assessments have many different components. It is best to locate them ahead of time and become familiar with them in order to preplan administration. Slide 7 Key Points: • For Kindergarten, the Unit 8 Student Performance Task Assessment is a comprehensive multipart assessment of all letter-sound correspondences, tricky words, and letter names taught in the CKLA program • The results of this assessment will help to determine which students need additional review and reinforcement and/or differentiated instruction Slide 8 Key Points: • CKLA provides an individual summary score sheet to record the results of all of the assessments for the EOY assessments located in K Skills Unit 8. It can help the teacher tailor instruction for the student. • Class summary charts are provided to help compile class data. These lists will help see at a glance who can be grouped together based on similar needs in instruction. Slide 9 Key Points: • Here are the individual end-of-the year results for Evan, a kindergarten student who is below level in some of the key assessments for the end-of the year • The results for each assessment will determine a specific assessment path to follow Slide 10 Key Points: • The word recognition assessment is the first part of the K end of year assessments • The test has 20 words. Students who score 90% or more have strong word skills • Students, such as Evan who score less than 18 correct have difficulty and need further assessment • The next test is psuedoword assessment Slide 11 Key Points: • The 30 word psuedoword assessment is administered one-on-one • Scores 27 or above indicate strong word attack skills. Lower than 27 require a code knowledge diagnostic • A detailed record sheet identifies specific detailed errors. Slide 12 Key Points: • The Code Knowledge Diagnostic Assessment pinpoints specific letter-sound correspondences that students have not yet mastered • In this assessment administered one-on-one, students are asked to identify 35 sounds. • Scores of 22 or less on rows 1-5 and/or scores on rows 1-7 suggest weak letter/sound knowledge. • A detailed record sheet identifies specific detailed errors. Slide 13 Key Points: • CKLA provides detailed scoring and analysis guidance to help the teacher with making decisions about Evan’s level of instructional need. • For Evan, remedial instruction should focus on targeted instruction of the specific letter-sound correspondences that he did not know on the Code Knowledge Diagnostic Assessment, using selected materials from Units 3-7 of the Assessment and Remediation Guide Slide 14 Key Points: • The Lowercase letter name assessment and the tricky word assessments are administered to all students. • The results of both assessments can provide more specific guidance on what to reteach. Slide 15 Key Points: At your table, with a partner, discuss what Evan will need in the way of reteaching. What should his instructional plan look like? Slide 16 Key Points: • Pulling it together, this is what he needs in specifics. Slide 17 Slide 18 Key Points: • Using the summary sheets, you can see exactly what Evan will need to be retaught. • The Code Diagnostic Assessment Remediation sheet is a Cross Reference chart that will help to locate the specific units and lessons where the and organize instructional activities by unit objectives Slide 19 Key Points: • The Assessment and Remediation Guide will include a flow chart to help guide the teacher to create specific targeted instruction for each of the assessments administered, and will direct the instructional planning from specific parts of the A & R guide. Slide 20 Key Points: Slide 21 The K Unit 8 Instructional Flowchart will help to guide instructional planning, aligning the results of the Psuedoword recognition assessment with the exact location of the phonological awareness and phonics sections in the Units and sections of the A & R guide. There are two more sections we would look at. Key Points: Here, the Instructional flowchart will direct you to plan instruction from Units 3-7 of the A & R Guide. Slide 22 Key Points: • Return to Evan’s Summary Score Sheet. Using Evan’s data from his assessments and looking at his specific errors, what level of instruction would you categorize Evan at? • Definitions of each of these levels of instructional need were covered in Session 4. Slide 23 Key Points: • Evan will need to receive explicit reteaching for the specific sounds, letters and words he missed on the assessments. • One letter-sound correspondence will be taught at a time in sequential order, until Evan can decode and read lists of words that include the targeted lettersound correspondence with 90% accuracy. Slide 24 Key Points: • The Lesson Template provides a detailed model of the sequence of instructional steps to be followed when reteaching a particular skill Slide 25 Key Points: • A sample remedial lesson is provided to illustrate how specific skill work, activities, and progress monitoring can be applied to the template • All of the items need to plan are included in the A & R guide • We will come back to lesson planning Slide 26 Slide 27 Key Points: • The assessments for both first and second grade have three parts including silent reading comprehension, fluency, and word reading in isolation. Slide 28 Key Points: Slide 29 Key Points: Slide 30 The End-of-Year assessments, including the instructions for administration, answer keys, scoring and analysis and class summary charts are located in the Teacher’s guide for first grade. The student copies of the assessments and an E-O-Y student summary sheet are located in each student’s individual workbook. The First grade EOY assessments begin with all student receiving a story and comprehension questions to do independently. If the students get more than 2 answers wrong, they will be assessed for fluency or word recognition Key Points: The second step in the EOY assessments in students who show some difficulty with comprehension. A reading record is taken for fluency. Slide 31 Key Points: • The word reading in isolation assessment, Ella read 45 out of 60 words correctly. This puts her at 75% accuracy. Just a little below the 80% benchmark. Slide 32 Key Points: • A scoring sheet is provided to help determine which phonemes the student missed • This remediation guide will help organize the results for each individual student to tailor instruction for specific needs and help to group students with similar needs Slide 33 Slide 34 Key Points: At your table, with a partner, discuss what Ella will need to focus on. What should her instructional plan look like? Slide 35 Key Points: • A scoring sheet is provided to help determine which phonemes the student missed • This remediation guide will help organize the results for each individual student to tailor instruction for specific needs and help to group students with similar needs Slide 36 Key Points: • Ella scored within the 50th percentile for her fluency, and slightly below the 80% benchmark for her grade on word reading. Although these scores indicate an adequate preparedness to move onto second grade, helping Ella to improve before she leaves first grade will off set any summer slide back she may experience Slide 37 Key Points: • Return to Ella’s Summary Score Sheet. Using Ella’s data from her assessments and looking at her specific errors, what level of instruction would you categorize Ella at? Slide 38 Key Points: Slide 39 To help Ella in a dual instructional focus, the comprehensive lesson structure will cover what is needed. Key Points: This lesson has time built in to focus on the reteaching of sounds Ella missed in the word reading assessment and the time to practice fluency. Slide 40 Slide 41 Key Points: While our Case Studies of Evan and Ella gave us a specific entry way into the A & R guide through data from EOY assessments, the A & R guide is set up to be used as a resource when the teacher has observed that the student has been struggling during instruction, or as evidenced from the scores on unit assessments or progress monitoring activities in the A & R guide Slide 42 Key Points: • The steps for navigating- when you aren’t beginning with EOY data necessarily but starting with a sense of student need or some other data, you can go right to the A&G guide to begin problem solving and planning. Slide 43 Key Points: • The Cross Reference Charts and Determining Students Needs Charts will help to establish areas of weakness within the instructional components (phonics, fluency and comprehension, or grammar, confirm the earliest point of weakness and assist in planning for instruction to level of instructional need Slide 44 Key Point: • The A & R Guide will instruct you to use the skills scope and sequence for the grade you are working with to locate the earliest point of weakness within the units of instruction Slide 45 Key Points: • As we demonstrated with the Evan and Ella case studies, the results of the assessments will determine the level of instructional need. • You will need to determine if the student is basically on pace, but just needs reinforcement for a few gaps in code knowledge, or if they need to be explicitly retaught in a specific literacy component, and if they require instruction in multiple literacy areas. Slide 46 Key Points: • Choose aligned exercises that will guide students through warm-ups, guided and independent portions of each structured lesson. Slide 47 Key Points: • Following the exercises section is a Progress Monitoring section. Time is allotted at the end of reteaching ( in both explicit and comprehension lesson templates) to allow for independent practice or progress monitoring Slide 48 Key Points: • The second grade differs from the kindergarten and first grade A & R guides in that it is a comprehensive phonics based guide and includes letter-sound correspondences and words taught over the course of K-2nd grade. Slide 49 Key Points • Use these hyperlinks to access the specific Assessment and Remediation Guide Unit you need Slide 50 Key Point • If you brought your own data to try to work through the case study protocol (of analyzing and creating a differentiated lesson). CKF staff will be on hand to advise around the data they bring (versus that available within the case studies created by CKF), as well as to help participants work through ideas and/or roadblocks to their differentiation. Slide 51 Key Points: • Remember if you have not already done so, please place a dot on the consensogram where you feel you are in terms of 3 areas; your level of proficiency to navigate the A & R guide, the ability determine your student’s level of instructional need, and confidence in being able to plan lessons from the A & R lessons that will meet the specific instructional needs of your students. Slide 52 Key Points: • Take some time to reflect about the process of navigating the A & R guide. What were the most challenging parts? How well do you feel you would be able to do these tasks on your own? What questions do you still have? Slide 53 Key Points: • Look at the consensogram and comment on understandings having deepened (based on how dots have moved). Slide 54 Key Points: • To learn more about the Assessment and Remediation Guide, refer to Session 4 where you will find the link to an Office Hour Recording on the Core Knowledge website • If you need more practice on how to determine a student’s instructional need or how to create lessons using the A & R guide, review slides within this session Use the following icons in the script to indicate different learning modes. Video Reflect on a prompt Turnkey Materials Provided Additional Suggested Resources Active learning Turn and talk