Weather - mkalyniuk
advertisement

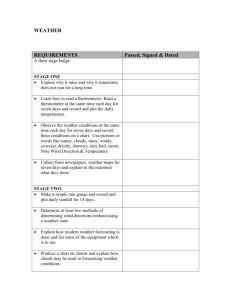
Weather What is Weather? • Weather is the condition of the Earth’s Atmosphere at a given time. • It can change drastically in a 24 hour period. What causes Weather? • All elements of weather are the direct result of energy from the sun. • The sun’s rays hit earth and the land absorbs the heat unevenly. • This uneven heating causes changes in weather. The Water Cycle Read Drippy and the Water Cycle Check it out (video and quiz) http://teacher.scholastic.com/activities/studyjams/water_cycle/ The Water Cycle • The sun heats up the water- evaporation • The water vapor (gas) condenses into clouds • The clouds become saturated and precipitation is the result. • The precipitation pools in lakes, oceans and rivers. Waiting to evaporate again. • Act out the water cycle with instruments and dance • Lable the Water Cycle on page 16 and pg 295 Clouds • Clouds come in many shapes and forms. • Some are high in the sky, while others are so low they touch the ground. • No matter what shape or elevation, clouds form • the same way, by having water vapor condense onto small solid particles like dust, sea salt, and pollution Make A Cloud in A bottle Types of Clouds Two videos Clouds then type of clouds Clouds • Clouds serve several important functions. • They provide rain and snow. • They also help retain heat, so it doesn’t escape quickly back into space. • On hot days, clouds provide shade Types of Clouds • There are Four main types of clouds • Cirrus- found high in the • • • atmosphere Cumulus- found in midatmosphere Stratus- found in the low atmosphere Nimbus- storm clouds. Cirrus • They are thin, wispy clouds blown by high winds into long streamers. • They usually mean fair to pleasant wheather. Cumulus • They are puffy clouds that sometimes look like pieces of floating cotton • They can develop into a giant cumulonimbus, which is a thunderstorm cloud Nimbus (Cumulonimbus) • They are thunderstorm clouds that form if cumulus clouds continue to grow vertically. • Lightning, thunder, and even violent tornadoes are associated with the cumulonimbus. Stratus • are uniform grayish clouds that often cover the entire sky. • They resemble fog that does not reach the ground. • Usually no precipitation falls from stratus clouds, but sometimes they may drizzle. Can you identify these clouds? DO page 13 and Create a cloud poster using cotton balls and labels Matching Game http://eo.ucar.edu/webweather/cloudmat ch.html Precipitation • When there is too much moisture, the water will fall as precipitation. • Precipitation will fall in two main forms: rain or snow depending on the temperature of the air through which the moisture will fall. • Other forms of precipitation are sleet and hail. Forms of Precipitation Rain • When droplets of moisture join together becoming heavy enough to fall to the ground. Snow • If the air is cooled • • below the freezing point of water, the condensing moisture is quickly freeze into ice crystals. The ice crystals join to make snowflakes Snowflakes are always six sided. Hail • Formed in cumulonimbus (storm) clouds. They are frozen droplets of moisture. • BLM #9 Sleet • When falling rain starts off in warmer air, but passes through air below freezing, the rain drops cool and freeze onto surfaces when they hit the ground. Fog • Some clouds do not form in the sky. They form closer to the earth and then everything looks grey. Make it Rain Activity • • • • • • • Large, wide-mouth container, such as a mayonnaise jar Hot water Ice cubes Small plate to hold ice cubes Index card 1. Pour two inches of very hot tap water into the glass container and cover with the plate. Allow water to sit for a few minutes. 2. Place ice cubes on the plate. 3. Watch what happens. The cold plate causes the moisture in the warm air to condense and form water droplets. This is the same thing that happens in the atmosphere as warm, moist air rises and meets colder temperatures high in the atmosphere. Water vapor condenses and forms precipitation that falls to the Earth as rain, sleet, hail, or snow. What does weather include? • • • • • • • • Air temperature Cloud cover Amount of sunlight Relative humidity: The amount of water vapor in the air is referred to as humidity. The more water that is in the air there is, the higher we say that the humidity has risen. Precipitation: The amount of water that falls to the earth in the form of rain, sleet, hail or snow Wind speed Wind direction Air Pressure :The force that is applied on everything on the Earth caused by the weight of the air. • Make Your Own Weather Activity (change humidity and temp) http://www.scholastic.com/kids/weather/ Weather Network (Short and Long Term Predictions) http://www.theweathernetwork.com/?ref=topnav_weather_news_hom epage • Look at Canadian Weather(Very Cool!!!!) http://www.weatheroffice.gc.ca/canada_e.html • Reading A Forecast Tip http://eo.ucar.edu/webweather/forecasttips.html • Read a Weather Report and Complete the Weather Map – http://www.edheads.org/activities/weather/ • Weather Maps as Homework (see handouts) • Create a Weather Report (fill out outline at home and use powerpoint to present) Weather Tools What are they? What do they do? The Most Common Weather Tools Are: • Thermometer • Wind Vane • Anemometer • Barometer • Rain Gauge • Create your own tool at home Thermometer • A thermometer is a weather tool used to measure the temperature. Wind Vane • By observing wind vanes, we can know the direction of the wind. Knowing the direction of the wind is an important part in predicting the weather. • Make Your Own • • • • • • • • Weather Vane You'll need these materials: – – – – – – – – – – a long wooden dowel (about the size of a broom stick) an aluminum pie plate a 12 inch long piece of wood (A sturdy ruler would work) nails a metal washer hammer glue small saw (or serrated knife) wire (for mounting) scissors (strong enough to cut aluminum) Begin with the 12 inch piece of wood. Use the small saw (or serrated knife) to cut a vertical slit at each end of the stick. The slit should be about one half inch deep. At the midpoint (exactly halfway) of the top of the stick, hammer one nail all the way through the stick. Then turn the wood around the nail several times until the stick turns easily around the nail. Refer to the pattern picture and cut the head and tail from the aluminum plate. Glue the head into the slot at one end of the wooden stick. Glue the tail into the other end. Allow time for the glue to dry before you take the vane outside. Attach the weather vane to the long wooden dowel by placing the metal washer on the end of the dowel and then hammering the nail through the wooden stick and into the wooden dowel. (Refer to the picture.) Make sure that the vane moves freely and easily around the nail. Now you are ready to mount your weather vane outside. If you mounted your rain gauge on a fence, you may want to mount your weather vane near it. Position the wooden dowel beside the fence and secure it with wire. Try to get the vane as high above the fence as you can while still keeping the dowel steady and secure. The head of the pointer will always point to the direction from which the wind is blowing. For example, if the head points to the NorthEast, then the wind is blowing from the NorthEast. It's as simple as that. (A common mistake is to think that the wind is blowing toward the NorthEast.) Record your wind direction readings in your weather journal. Anemometer • Wind speed is an important part of weather. • An anemometer is a weather tool that measures wind speed. Barometer • Barometers are important to measuring air pressure. Air pressure can help you predict good or bad weather. • Make a simple barometer Make a Barometer Do you know what the air pressure is today? You can find out for yourself by measuring the air pressure on a barometer. Materials small coffee can plastic wrap scissors straw index card rubber band Instructions COVER the top of the can with plastic wrap. USE a rubber band to hold the plastic wrap in place. The cover should be taut making the can airtight. PLACE the straw horizontally on the plastic wrap so that two-thirds of the straw is on the can. TAPE the straw to the middle of the plastic wrap. TAPE the index card to the can behind the straw. Carefully RECORD the location of the straw on the index card. After 15 minutes, RECORD the new location of the straw on the index card. Continue CHECKING and RECORDING the straw location as often as desired. Be careful not to place your barometer near a window, as the barometer is sensitive to temperature as well as air pressure. What's happening High pressure will make the plastic wrap cave in, and the straw go up. Low pressure will make the plastic wrap puff up, and the straw go down. Check your measurements with a real barometer. What happens to your barometer when a big storm comes? Can you use your barometer to predict a storm? Rain Gauge • A rain gauge is a • weather tool used to collect rain. Using measurements on the side of the rain gauge, you can see how many inches it rained. Temperature • Temperature is amount of heat in a substance. Expressed in degrees Fahrenheit or Centigrade (Celsius) • Temperature is measure by an instrument called a thermometer. • BLM#1-measuring temperature around the room. Assignment • Keep track of the weather using the forecast (http://www.theweathernetwork.com/wea ther/cancitiesmb_en?ref=homeprovince) and compare that to what your tools say • Pg 319 Forecasting the Weather • You have keep track of the weather for ten days. • Was the weather forecast accurate? • Why is it so difficult to predict the weather? Factors that influence weather in different areas. • Land Elevation • Location- lattitude and longitude • The sun • Cloud cover • Air pressure • Earth’s orbit (seasons) Weather Folklore • Weather Folklore • If crows fly low, winds going to blow; If crows fly high, winds going to die. • Whether it’s cold or whether it’s hot; We shall have weather, whether or not! • No weather is ill, if the wind is still. • NEWS and weather; they travel together. • A sunshiny shower won’t last half an hour. • Rain, rain go away; come back another day. • Clear moon, frost soon. • The moon and the weather may change together, but change of the moon does not • • • • • • • • change the weather. From twelve ‘til two tells what the day will do. The more rain, the more rest; fair weather’s not always best. When sea birds fly to land there truly is a storm at hand. To talk of the weather is nothing but folly; when it rains on the hill, it suns in the valley. It rains as long as it takes rain to come. The sharper the blast, the sooner it’s past. Yellow streaks in sunset sky, wind and daylong rain is nigh. • Year of snow, fruit will grow. • The chill is on, near and far, in all the months that have an ‘R’. • Rainbow at noon, more rain soon. • The south wind brings wet weather...the north wind, wet and cold together; the • • • • • • • • • • west wind always brings us rain…the east wind blows it back again. When a cow tries to scratch her ear it means a shower is very near. Onionskin is very thin, mild winter is coming in. Onionskin is thick and tough winter will be cold and rough. Ice in November to walk a duck, the winter will be all rain and muck. Rain before seven, quit by eleven. When the stars begin to huddle the earth will soon begin to puddle. Evening red and morning gray speed the traveler on his way. Evening gray and morning red bring down rain upon his head. Rainbow in the east, sailors at peace. Rainbow in the west, sailors in distress. Pale moon doth rain, red moon doth blow, white moon doth neither rain nor snow. When the dew is on the grass, rain will never come to pass. Rainbow in the morning, shepherds take warning; rainbow at night, shepherds’ delight. A Bunch of Hot Air. • Cold air contracts or sinks. • The air molecules get closer together, which makes the air heavier or more dense. • Hot air expands or rises. The molecules get • further apart, become less dense and they get lighter. Do experiment with 2 paper bags and a light source Warm and Cold Fronts Wild Weather Thunderstorms Hurricanes Tornadoes Research Project • Pick A Wicked Weather – – – – – Flood Tornado(make a twister- http://eo.ucar.edu/webweather/tornact4.html Hurricane Tsunami Thunderstorm make a thunderstorm http://eo.ucar.edu/webweather/tornact2.html Your – – – – – – – – – Project Title Describe it Where does this weather generally occur? Effects on Earth, humans and other living things Safety Resources 5 pictures Worksheet for students Bonus: experiment or hands-on activity Outline • Research It using these sites – http://www.wartgames.com/themes/weather/dangerous-weather.html Flood • Flood Simulator http://library.thinkquest.org/C003603/sims/flooding/index.html Flood of the Century Brandon Flood 2011 Weather vs. Climate • Sort cards from page 290 into weather and or climate zones • Class Activity Stormy Weather Tornado Safety and Trivia Water Cycle Clouds Weather Vocabulary 1pt 1 pt 1 pt 1pt 1 pt 2 pt 2 pt 2pt 2pt 2 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 3 pt 4 pt 4 pt 4pt 4 pt 4pt 5pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt 5 pt Nature’s way of recycling water What is the water cycle? The process of water changing into an invisible gas called water What is evaporation? Amount of water vapor in the air What is humidity? The process of water vapor turning into water droplets What is condensation? Water that is found underground What is groundwater? Gray clouds that cover the lower part of the sky; rain or snow falls from What are stratus clouds? White, puffy clouds that look like piles of cotton; they are known as fairweather clouds What are cumulus clouds? Thin, feathery clouds that appear high in the sky; they are a sign that rain or snow is on the way What are cirrus clouds? Cloud that forms at the earth’s surface What is fog? Tall, dark clouds that mean thunderstorms with heavy rain and strong winds What are cumulonimbus clouds? The state of the air at a certain time and place What is weather? Scientists who study weather Who are meteorologists ? Instrument that shows wind direction What is a wind vane? Measures wind speed What is an anemometer? The weather of a place over a long time What is climate? Most common type of storm What is a thunderstorm? Spinning cloud with a funnel shape What is a tornado? Large, powerful storm that occurs over large bodies of water What is a hurricane? Water overflow that is caused by a large amount of rainfall What is a flood? Another name for a hurricane What is a typhoon? Where you should go during a tornado if you are in a house What is the basement? Where you should go during a tornado if you are in a school or public What is the lowest level of the building? April through June What are the months that the most tornadoes occur? What you should do if you’re in a car during a tornado What is pull over and get out of the vehicle? Scale used rate the damage and speed of tornadoes What is the Fujita scale (F-scale)?