Graphs of Quadratic Functions
advertisement

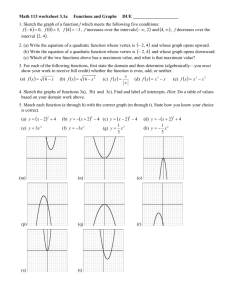
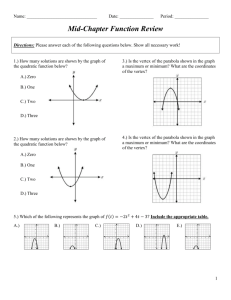
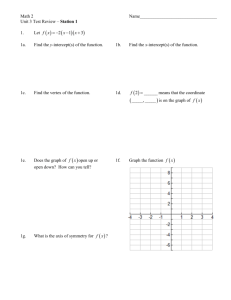
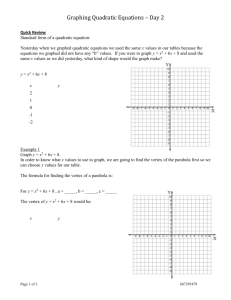
Graphs of Quadratic Functions Focus 10 Learning Goal – (HS.A-REI.B.4, HS.F-IF.B.4, HS.F-IF.C.7, HS.F-IF.C.8) = Students will sketch graphs of quadratics using key features and solve quadratics using the quadratic formula. 4 3 2 1 In addition to level 3, students make connections to other content areas and/or contextual situations outside of math. Students will sketch graphs of quadratics using key features and solve quadratics using the quadratic formula. - Students will be able to write, interpret and graph quadratics in vertex form. Students will be able to use the quadratic formula to solve quadratics and are able to identify some key features of a graph of a quadratic. Students will have partial success at a 2 or 3, with help. 0 Even with help, the student is not successful at the learning goal. Quadratic Graphs Vocabulary Axis of Symmetry: Given a quadratic function in standard form, f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, the vertical line given by the graph of the equation x = -b/2a, is called the axis of symmetry. Vertex: The point where the graph of the quadratic function and its axis of symmetry intersect. Quadratic Graphs Vocabulary End Behavior of a Graph: Given a quadratic function in the form f(x) = ax2 + bx + c or f(x) = a(x-h)2 + k, the quadratic function is said to open up if a > 0 and open down if a < 0. If a > 0, then f has a minimum at the x-coordinate of the vertex (f is decreasing for x-values less than, or to the left of, the vertex, and f is increasing for x-values greater than, or to the right of, the vertex.) If a < 0, then f has a maximum at xcoordinate of the vertex. (f is increasing for x-values less than, or to the left of, the vertex, and f is decreasing for x-values greater than, or to the right of, the vertex.) Architecture Around the World The photographs of architectural features might be closely represented by graphs of quadratic functions. How would you describe the overall shape of a graph of a quadratic function? What is similar or different about the overall shape of the curves to the left? Graphs of Quadratic Functions – Graph A 1. Fill in the table of values based off of the graph. 2. State the x-intercepts: x f(x) -1 8 3. State the vertex: 0 3 4. If we wrote the equation for this graph, what would be the sign of the leading coefficient? 1 0 2 -1 3 4 0 3 5 8 5. Does the vertex represents a minimum or a maximum? Graphs of Quadratic Functions – Graph A Look at the table and the graph, state points of symmetry. (-1, 8) and (5, 8) (0, 3) and (4, 3) What interval is the graph increasing? [2, ∞] What interval is the graph decreasing? [-∞, 2] x f(x) -1 8 0 3 1 0 2 -1 3 0 4 3 5 8 Graphs of Quadratic Functions – Graph B 1. Fill in the table of values based off of the graph. 2. State the x-intercepts: x f(x) -5 -5 3. State the vertex: -4 0 4. If we wrote the equation for this graph, what would be the sign of the leading coefficient? -3 3 -2 4 -1 3 0 0 1 -5 5. Does the vertex represents a minimum or a maximum? Graphs of Quadratic Functions – Graph B Look at the table and the graph, state points of symmetry. (-5, -5) and (1, -5) (-4, 0) and (0, 0) What interval is the graph increasing? [-∞, -2] What interval is the graph decreasing? [-2 , ∞] x f(x) -5 -5 -4 0 -3 3 -2 4 -1 3 0 0 1 -5 Patterns in the tables of values… Table A Table B x f(x) x f(x) -1 8 -5 -5 0 3 -4 0 1 0 -3 3 2 -1 -2 4 3 0 -1 3 4 3 0 0 5 8 1 -5 What patterns do you see in the tables of values? How can we know the xcoordinate of the vertex by looking at two symmetric points? What happens to the yvalues of the functions as the x-values increase to very large numbers? Quadratic Challenge Time! The graph at the left is half of a quadratic function. With a partner, complete the graph by plotting 3 additional points. Be prepared to explain how you found these points. Quadratic Challenge Time! x f(x) Fill in the table of values: -3 -6 What are the coordinates of the x-intercepts? -2 -1 -1 2 0 What are the coordinates of the y-intercept? 3 1 2 2 -1 What are the coordinates of the vertex? Is it a minimum or a maximum? 3 -6 If we knew the equation for this curve, what would the sign of the leading coefficient be and why? Find the equation for the axis of symmetry for the graph of a quadratic function with the given pair of coordinates. If not possible, explain why. 1. (3, 10) and (15, 10) 1. Since these ordered pairs are points of symmetry (same yvalue), you can find the axis of symmetry. 2. The middle of 3 and 15 is 9. 3. The axis of symmetry would be x = 9. 2. (-2, 6) and (6, 4) 1. Since these ordered pairs are not points of symmetry (different y-values), you cannot find the axis of symmetry. Conclusion: Graphs of quadratic functions have a unique symmetrical nature with a maximum or minimum function value corresponding to the vertex. When the leading coefficient of the quadratic expression representing the function is negative the graph opens down and when positive it opens up.