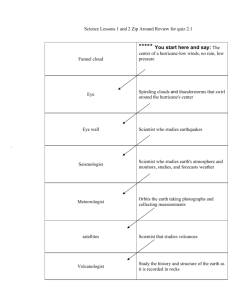
Tornado Frequency by Decade
advertisement

Tornados and Climate Change Michael Pateman And Drew Vankat Introduction • Investigation of tornadic frequency and magnitude in the United States in relation to the El Nino/Southern Oscillation and US climate change Hypothesis • Global warming, along with increased El Nino and La Nina cycles mean more plentiful and powerful tornadoes • But…What role does technology play in increased detection? Research Relevance • If a relationship with climate cycles can be found, perhaps emergency funding can be set aside in advance for victims • Findings can be translated to other weather phenomena such as thunderstorms, flooding, or hurricanes • Authorities can take necessary precautions to minimize economic and human losses • Provide a more convincing argument for the need to rethink the way we treat our environment. What is a tornado? • An intense, rotating column of air extending from the base of a thunderstorm cloud to the ground. www.spc.noaa.gov ENSO • The ENSO (El Nino/ Southern Oscillation) cycle refers to the coherent, largescale fluctuation of ocean temperatures, rainfall, atmospheric circulation, vertical motion and air pressure across the tropical Pacific. http://www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/ What is El Nino? • A disruption of the ocean-atmosphere system in the Tropical Pacific • Development of abnormally warm sea surface temperatures across the eastern tropical Pacific • Consequences can include increased rainfall in some areas and extreme drought in others What is La Nina? • Characterized by unusually cold ocean temperatures in the Equatorial Pacific • USA: warmer southwest winters, colder Northwest Materials and methods • Data retrieved on tornado and ENSO activity • Downloaded into Excel, Statview, and Cricket Graph Tornado Frequency by Decade Spearman Rank Correlation p-values: Texas-Nebraska p=.1096 Texas-Ohio p=.0719 Nebraska-Ohio p=.0719 Frequency of Tornadoes in El-Nino Years Spearman Rank Correlation p-values: Texas-Nebraska p=.4902 Texas-Ohio p=.1837 Texas-USA p=.0170 Nebraska-Ohio p=1983 Nebraska-USA p=.0785 Ohio-USA p=.1223 Tornado Frequency in non-El-Nino Years Spearman Rank Correlation p-values: Texas-Nebraska p=.1096 Texas-Ohio p=.1615 Texas-USA p=.0719 Nebraska-Ohio p=.3173 Nebraska-USA p=.2301 Ohio-USA p=.0719 Tornado Frequency in La Nina Years Spearman Rank Correlation p-values: Texas-Nebraska p=.0422 Texas-Ohio p=.1474 Texas-USA p=.0376 Nebraska-Ohio p=.1117 Nebraska-USA p=.0751 Ohio-USA p=.0438 Tornado Frequency in non-La-Nina Years Spearman Rank Correlation p-values: Texas-Nebraska p=.0719 Texas-Ohio p=.0719 Texas-USA p=.0455 Nebraska-Ohio p=.1096 Nebraska-USA p=.0719 Ohio-USA p=.0719 Texas Tornado Frequency 350 300 Count 250 200 150 100 50 0 195 0 196 0 197 0 198 0 Yea r 199 0 200 0 Nebraska Tornado Frequency 120 100 Count 80 60 40 20 0 195 0 196 0 197 0 198 0 Yea r 199 0 200 0 Ohio Tornado Frequency 70 60 Coun t 50 40 30 20 10 0 195 0 196 0 197 0 198 0 year 199 0 200 0 Data • http://www4.ncdc.noaa.gov/cgiwin/wwcgi.dll?wwEvent~Storms • All Tornado Data downloaded from this site. Tentative conclusions • Overall increase in tornado frequency • P-values indicate little relationship in frequency for El-Nino years • P-Values indicate a relationship in frequency for La-Nina years Still To Come… • Spearman Rank Correlations for tornado frequency per year in each state • Analyze magnitude Future Research • Incorporate climate change and global warming • Any questions or suggestions?