GROUP PRESENTATION: CHAPTER 7: FDI BFMA6043
advertisement

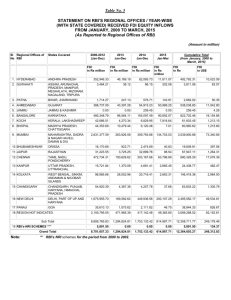
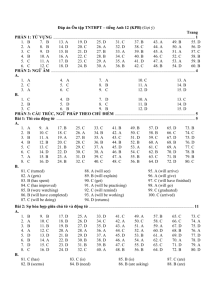
Universiti Utara Malaysia The Eminent Management University COB – COLLEGE OF BUSINESS Master of Business Administration (MBA) Programme GROUP PRESENTATION: CHAPTER 7: FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT BFMA6043 INTERNATIONAL BUSINESS Present by For GROUP B ER SHEAU JIA Matric No. : 803734 SUZANNA A. KOH Matric No. : 000000 TAN YONG SOON Matric No. : 804571 URSULA GLADYS JONGIJI Matric No. : 803739 DR. MOHD SOBRI BIN DON @ A. WAHAB CHAPTER 7: FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT INTRODUCTION FDI IN THE WORLD ECONOMY MAJOR ISSUES THEORIES OF FDI CONCLUSION POLITICAL IDEOLOGY AND FDI BENEFITS AND COSTS OF FDI GOVERNMENT POLICY INSTRUMENT Introduction Inflow Outflow Greenfield Investment Flow of FDI Types Forms M&A Stock of FDI FDI? a firm invests directly in new facilities to produce and/or market in a foreign country FDI - in the world economy TRENDS 2009 FDI Outflows 1982 – 2009 ($ billions) Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy TRENDS National Regulatory Changes 1982 – 2009 (%) Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy DIRECTION FDI Inflows by Region 1982 – 2009 ($ billions) Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy DIRECTION Top Host Economies for FDI in 2010 – 2010 Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy DIRECTION Gross Fixed Capital Formation 1992 – 2007 (%) Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy SOURCE Global FDI Outflows 2008 – 2009 Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy M & A / GREENFIELD INVESTMENT Most cross-border investment is in the form of mergers and acquisitions rather than greenfield investments Firms prefer to acquire existing assets because – mergers and acquisitions are quicker to execute – it is easier and perhaps less risky for a firm to acquire than build them from zero – firms believe that they can increase the efficiency of an acquired unit by transferring capital, technology, or management skills FDI - in the world economy M & A / GREENFIELD INVESTMENT M & A and Greenfield Projects 2005 – 2010 (May) Source: UNCTAD – World Investment Report, 2010 FDI - in the world economy FDI IN SERVICES FDI is shifting away from extractive industries and manufacturing, and towards services The shift to services is being driven by – the general move in many developed countries toward services – the fact that many services need to be produced where they are consumed – a liberalization of policies governing FDI in services – the rise of Internet-based global telecommunications networks Theories of Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) 3 approaches: Why FDI? Pattern of FDI Eclectic Paradig m 1. Why FDI? 1. Exporting - producing goods at home and then shipping them to the receiving country for sale – exports can be limited by transportation costs and trade barriers – FDI may be a response to actual or threatened trade barriers such as import tariffs or quotas 2. Licensing - granting a foreign entity the right to produce and sell the firm’s product in return for a royalty fee on every unit that the foreign entity sells Cont…..Why • FDI? Internalization theory (aka market imperfections theory) suggests that licensing has three major drawbacks compared to FDI – firm could give away valuable technological know-how to a potential foreign competitor – does not give a firm the control over manufacturing, marketing, and strategy in the foreign country – the firm’s competitive advantage may be based on its management, marketing, and manufacturing capabilities 2. Patterns of FDI • Why do firms in the same industry undertake FDI at about the same time and the same locations? • F.T. Knickerbocker - FDI flows are a reflection of strategic rivalry between firms in the global marketplace – multipoint competition -when two or more enterprises encounter each other in different regional markets, national markets, or industries ( i.e. Kodak and Fuji) • Raymond Vernon - firms undertake FDI at particular stages in the life cycle of a product (i.e. Xerox) 3. Eclectic Paradigm • Why is it profitable for firms to undertake FDI rather than continuing to export from home base, or licensing a foreign firm? • According to Dunning’s eclectic paradigm- it is important to consider – location-specific advantages - that arise from using resource endowments or assets that are tied to a particular location and that a firm finds valuable to combine with its own unique assets (i.e. world oil companies) – externalities - knowledge spillovers that occur when companies in the same industry locate in the same area (i.e. silicon valley) Political Ideology & FDI • How does a government attitude affect FDI? RADICAL VIEW PRAGMATIC NATIONALIS M FREE MARKET VIEW hostile……………………………………………………………………… non-interventionist Cont/….Political Ideology & FDI • The Radical View - the multi-national enterprise (MNE) is an instrument of imperialist domination and a tool for exploiting host countries to the exclusive benefit of their capitalistimperialist home countries Cont/….Political Ideology & FDI • The Free Market View - international production should be distributed among countries according to the theory of comparative advantage • embraced by advanced and developing nations including the United States, Britain, Chile, and Hong Kong Cont/….Political Ideology & FDI • Pragmatic Nationalism - FDI has both benefits (inflows of capital, technology, skills and jobs) and costs (repatriation of profits to the home country and a negative balance of payments effect) • FDI should be allowed only if the benefits outweigh the costs • Recently, there has been a strong shift toward the free market stance creating – a surge in FDI worldwide – an increase in the volume of FDI in countries with newly liberalized regimes BENEFITS & COSTS OF FDI HOST COUNTRY BENEFITS • • • • Resource Transfer Effects Employment Effects Balance-of-payments Effects Effects On Competition And Economic Growth 1. RESOURCE TRANSFER EFFECTS • Resources Transferred: CAPITALS TECHNOLOGY R&D MANAGEMENT SKILLS • Improve production process & products, effeciencies 2. EMPLOYMENT EFFECTS • Create job opportunities direct & indirectly • In the case of ACQUISITION, initially employment reduces during restructuring period but later grow faster than the domestic rivals • Because better wage rates & employment qualities are provided 3. BALANCE-OF-PAYMENTS EFFECTS • BALANCE-OF-PAYMENT ACCOUNTS: Track both its payment & receipts from other countries • CURRENT ACCOUNT: Tracks the exports & import of goods & services • Govt. prefers current account surplus (export>import) than current account deficits (import>export) and dislike to see the assets falling into foreign hands. • FDI can help to improve when: – FDI is a substitute for imports – MNE uses a foreign subsidiary to export (i.e. by generating inward FDI) 4. EFFECTS ON COMPETITION & ECONOMIC GROWTH • Greenfield investment: Increase competition, productivity growth, product & process innovations, stimulate capital investment • Looking at the impact on domestic markets, especially important in services, since exporting is often nit an option for services HOST COUNTRY COSTS • Adverse Effects on Competition • Adverse Effects on the Balance of Payments • National Sovereignty & Autonomy 1. ADVERSE EFFECTS ON COMPETITION • Possible to drive indigenous companies put of business & allow MNE to monopolize the market • Acquisitions: Doesn’t show result in a net increase in the no. of players in the market. Therefore, competition effect = neutral • Authorities have to control 2. ADVERSE EFFECTS ON THE BALANCE-OF-PAYMENTS • Outflows of earnings to home country • Foreign subsidiaries import a substantial input fro abroad • Resulted: A debit on the current account of the host country’s balance of payments 3. NATIONAL SOVEREIGNTY AND AUTONOMY • Loss of economic independence • When decisions made by MNE who has no real commitment to the host country might affect host country • Host country’s government das no real control with that HOME COUNRTY BENEFITS • Inward flow of foreign earnings benefits balance of payments account • Outward FDI arise from employment effects • Home country MNEs learn valuable skills from its exposure to foreign markets HOME COUNTRY COSTS • The home country’s balance of payments can suffer – from the initial capital outflow required to finance the FDI – if the purpose of the FDI is to serve the home market from a low cost labor location – if the FDI is a substitute for direct exports • Employment may also be negatively affected if the FDI is a substitute for domestic production • Eg. Toyota OFFSHORE PRODUCTION • FDI undertaken to serve the home market • Stimulate economic growth by freeing home country resources to concentrate on activities when the home country has a competitive advantage • Benefits if prices fall as a result of FDI Government Policy Instruments & FDI Government Policy Instrument Home Country Policies - Host Country Policies Government Policy Instruments & FDI • Home Country Policies – Encourage Outward FDI - Risk reduction policies (financing, insurance, tax incentives) – Restricting Outward FDI - Limit capital outflows, manipulate tax rules or prohibit FDI. Government Policy Instruments & FDI • Host Country Policies – Encourage Inward FDI - Investment incentives - Job creation incentives – Restricting Inward FDI - Ownership extent restrictions (to safeguard host country’s interest) and performance requirement. Conclusion 1 Home Country Benefits -Improvement in balance of payments from foreign earnings * Import substitution * Source of export increase -Increase employment from outward FDI. -Resource/skills transfer 2 Host Country Benefits -Resource transfer effect - Increase employment -Balance –of- payments effects * Import substitution * Source of export increase Conclusion 1 Home Country Costs -Adverse balance-of-payment effects * Initial capital outflow followed by capital inflow + profits -Substitution for domestic production - Employment decreased locally. 2 Host Country Costs -Adverse effect of Balance-of-payment * Capital inflow followed capital outflow + profits. -Perceived loss of national sovereignty. * Loss of economic independence Conclusion • FDI brings lots of benefits to both home countries or host countries. FDI transfers not only economic/ financial resources, but also knowledge/expertise and managerial know-how from home countries to host countries and vice versa.