Inflammation 3
Inflammation
Dr. Ahmad Hameed
MBBS,DCP, M.Phil
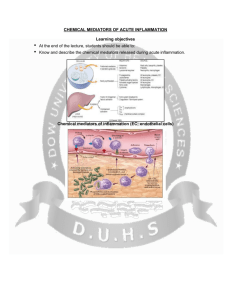
Chemical Mediators and regulators of inflammation
Chemical mediators that are responsible for vascular and cellular events of inflammation.
Mediators may be produced locally by cells at inflammation, or may be derived from circulating precursors (typically synthesized by the liver) that are released at the site of inflammation.
.
Cell-derived mediators are
Sequestered intracellular granules or synthesized de novo
Plasma derived mediators are inactive which undergo proteolytic cleavage to acquire biologic activity.
Chemical Mediators and regulators of inflammation
Most mediators act by binding to specific receptors on different target cells.
Diverse action
Direct action
The actions of most mediators are tightly regulated and short lived
Quickly decay
Inactivated by enzymes
Eliminated inhibited
Cell Derived
Preformed mediators in secretory granules
Newly synthesized
Mediators
Histamine
Source
Mast cells, basophils, platelets
Actions
Vasolidation, increased vascular permeability, endothelial activation
Serotonin Platelets
Prostaglandins All leukocytes, mast cells
Vasoconstriction
Vasodilation, pain, fever
Leukotrienes All leukocytes, mast cells Increase vascular permeability, chemotaxis, leukocyte adhesion and activation
Plateletactivitating factor
All leukocytes, EC Vasodilation, increase vascular permeability, leukocyte adhesion, chemotaxis, degranulation, oxidative burst.
Killing microbes, tissue damage Reactive oxygen species
Nitric oxide
All leukocytes
Cytokines
Macrophages, EC
Macrophages,lymphocytes,
EC, mast cells
Local; endothelial activation
(expression of adhesion molecules) systemic: fever, metabolic abnormalities, hypotension (shock)
Neuropeptides Leukocytes, nerve fibers
Vascular smooth muscle relaxation; killing of microbes
Plasma proteinderived
Compliment activation
Factor XII (hageman factor) activation
Mediators Source
)
C3a
(anaphylatoxins
)
C5a
(anaphylatoxins
C3b
C5b-9
(membrance attack complex)
Kinin system
(bradykinin)
Plasma
(Liver)
Plasma
(Liver)
Plasma
(Liver)
Plasma
(Liver)
Plasma
(Liver)
Coagulation / fibrinolysis sytem
Plasma
(Liver)
Actions
Leukocyte chemotaxis and activation, direct target killing (MAC), yasodilation (mast,cell stimulation)
Increased vascular permeability, smooth muscle contraction, vasodilation, pain
Cell-Derived Mediators
Tissue macrophages, mast cells, and endothelial cells, leukocytes
Vasoactive Amines
HISTAMINE
Richest source
Mast cells ( C.T , B.V)
Basophils
Platelets
Release in response to
1.
Physical injury (trauma, cold, heat)
2.
3.
Immune reactions (Antibody to mast cells)
Anaphylatoxins (C3a & C5a)
1.
2.
Histamine Releasing protein (H.R.P) from leucocytes
Neuropeptides (Substance P )
3.
Cytokines ( IL-1, IL-8)
Action
Immediate transient response (main)
Dilatation of arterioles
Increase permeability of venules
Contricts large arteries
Acts on microcirculation / bind to H1 receptors on endothelial cells
SEROTONIN
5HT
Similar action
Present in platelets, entero chromaffin cells & neurons
Neurotrasmitter and regulate intestinal motility
When platelet aggregation occurs release serotonin
Mast cells PAF platelet aggregation
Archidonic Acid Metabolites:
Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Lipoxins
Microbial Products + Mediators of Inflammation
↓
Arachidonic Acid
Prostaglandins Leukotrienes
AA Metabolites
Cyclooxygenase pathway
PGs are Produced by mast cells, macrophages, endothelium and others
PGE
2
,PGD
2
,PGF
2 α
Vasodilation
Potentiates Edema formation
Involved in pathogenesis of pain and fever
PGI
2
Produced by prostacyclin synthase in endothelial cell
Vasodilation, Inhibits Platelet aggregation
TXA
2
Produced by Thromboxane synthase in platelets
Vasoconstriction & stimulates platelets aggregation, unstable and converts to TXB
2
Production of arachidonic acid metabolites and their roles in inflammation.
Lipoxygenase Pathway
LTs are secreted mainly by leukocytes and chemoattractants for leukocytes.
LTA
4
LTB
4
Produced by neutrophils & some macrophages
Chemotactic agent for neutrophils
LTC
4
LTD
4
& LTE
4
Produced by mast cells
Vasocontriction + bronchospasm + Intravascular
Permeability
Anti-inflammatory Drugs that
Block Prostagladin Production
NSAID
Inhibit cyclooxygenase
Prevent biosynthesis of all PG
Treat pain and fever
Cyclooxygenase inhibitor
Two isoforms - COX-1/COX-2
COX-1
Expressed on most tissues produced in response to inflammation stimulate prostaglandins
COX-2
Absent most tissues
Developed that they will not affect protective function of prostaglandins
Increased risk of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular events
Lipoxygenase Pathway
Lipoxins (Anti inflammatory mediators )
Endogenous antagonists of Leukotrienes ie inhibit neutrophil chemotaxis and adhesion to endothelium
Platelet adherent to neutrophils from LXA
4 and
LXB
4
Cortisol
Reduces vascular permeability and edema
Decreases prostglandin production by preventing release of AA by inhibiting phospholipase A
2
Platelet-Activating Factor
It is generated from a lipid complex stored in cell membranes; Produced by WBCs & endothelial cells induces platelet aggregation;
Causes Vasoconstriction, Bronchoconstriction
It activates neutrophils and is a potent eosinophil chemoattractant;
It contributes to extravascularization of plasma proteins and so, to edema.