Clam Dissection
advertisement
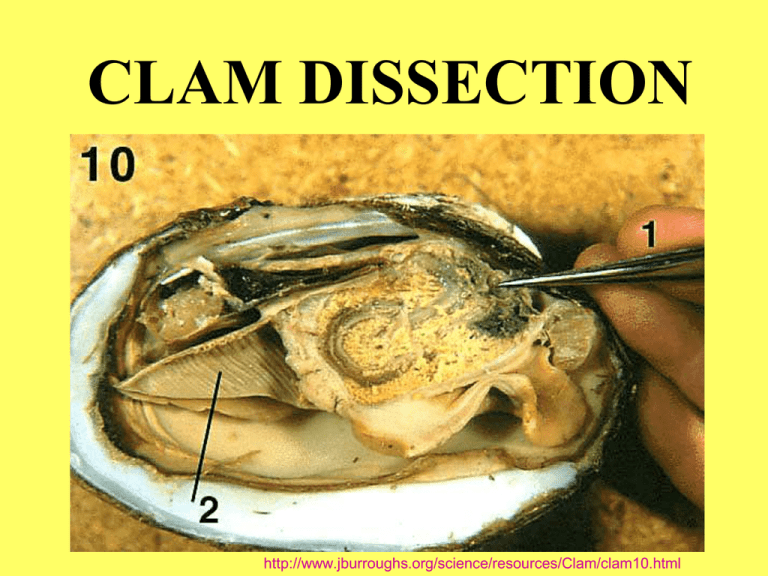
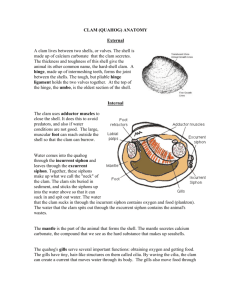
CLAM DISSECTION http://www.jburroughs.org/science/resources/Clam/clam10.html CLAMS ARE: Invertebratesno bones around nerve cord Protostomesblastopore becomes mouth determinate spiral cleavage http://www.zo.utexas.edu/faculty/sjasper/images/so28_04.gif Clam & octopus from: http://www.geocities.com/TheTropics/2428/directory.html CLAM DISSECTION KINGDOM ANIMALIA ___________ MOLLUSCA “Soft” PHYLUM ____________ BIVALVIA CLASS ______________ “2 shells” (Pelecypoda) UMBO tells direction Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral Image by Riedell/Vanderwal © 2005 Clams are SESSILE as ADULTS Don’t move much Stay in one place http://seagrant.gso.uri.edu/factsheets/fsquahog.html LARVA swim with CILIA http://www.okc.cc.ok.us/biologylabs/Images/Evolimages/trochophore.JPG NO CEPHALIZATION (No head) Shell = valve (Bivalvia = 2 shells) Growth rings - increase with age http://wwwbio200.nsm.buffalo.edu/labs/tutor/Clam/ ADDUCTOR MUSCLES Turn POSTERIOR END toward door Cut your adductor muscles to open shell Image from: http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/mollusk_notes_b1.htm ANTERIOR & POSTERIOR ADDUCTORS FOOT – points toward anterior end VISCERAL MASS Contains heart, digestive, excretory, reproductive Mantle cavity (NOT COELOM) Image from: http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/mollusk_notes_b1.htm NO cephalization Gills hang OUTSIDE body in mantle cavity Image modified from: http://www.lander.edu/rsfox/310images/310molluscImage.html Hinge Teeth on dorsal edge lock to keep shells from sliding Smooth lining Irritants are coated by mantle to protect soft body “Pearls” Animation from: http://vilenski.org/science/notebook/unit5/invertebrate/menu.html Mantle produces shell (calcium carbonate makes it hard) INCURRENT & EXCURRENT SIPHONS move food up toward mouth CILIA on gills pull in water Image by: Riedell/VanderWal © 2005 SEXUAL REPRODUCTION SEPARATE SEXES Male & female clams General term for reproductive organs = GONADS SEXUAL REPRODUCTION Marine (salt water) clamsexternal fertilization (sperm or eggs exit through siphon) Freshwater clamsinternal fertilization (sperm enters through siphon; fertilized eggs/larva exit ) Other mollusks GASTROPODS- internal fertilization Land snails = hermaphrodites Aquatic snails = 2 separate sexes CEPHALOPODS- internal fertilization Separate sexes – http://www.geocities.com/TheTropics/2428/directory.html http://www.okc.cc.ok.us/biologylabs/Images/Evolimages/trochophore.JPG Indirect development TROCHOPHORE LARVA Ciliated- can swim ADULTS- Sessile = stay in one place Can put out foot and crawl GILLS Trap food (PALPS move it forward) Ridges for more surface area (like typholosole) Gas exchange Diffusion moves oxygen & CO across membrane GAS EXCHANGE IN GILLS H i Image by Riedell OPEN CIRCULATION • Blood flows loose inside coelom and tissue spaces • Heart pumps blood (HEMOLYMPH) • COELOM = SMALLER mainly around heart = pericardial cavity OPEN CIRCULATION is less efficient way of moving oxygen, nutrients, and nitrogen waste 1. Doesn’t go directly to parts 2. High oxygen and low oxygen blood can mix so it gets diluted HEART & PERICARDIAL CAVITY DIGESTIVE • FILTER FEEDERS (strain food from water) • Food pulled in through incurrent siphon by cilia moving on gills • Food trapped in mucous on gills • Palps move food up and into mouth esophagus stomach Digestive gland Intestine anus http://wwwbio200.nsm.buffalo.edu/labs/tutor/Clam/ DIGESTIVE GLAND Makes BILE to break down fat Finishes digestion http://www.jburroughs.org/science/resources/Clam/clam10.html INTESTINE carries digestive waste to anus 3 Body systems use mantle cavity EXCRETORY - Nitrogen waste from kidney DIGESTIVE – feces released from anus REPRODUCTIVESperm or egg (if external fertilization) Larva (if internal fertilization) Image from: http://sps.k12.ar.us/massengale/mollusk_notes_b1.htm NERVOUS SYSTEM 3 pairs of ganglia 2 pairs of nerve cords http://www.student.loretto.org/zoology/Graphic%20webs/Clam-%20nervous%20system.htm