Matrix - FIU Global Learning
advertisement

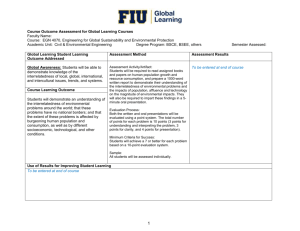
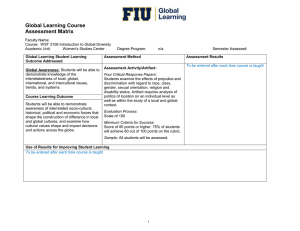
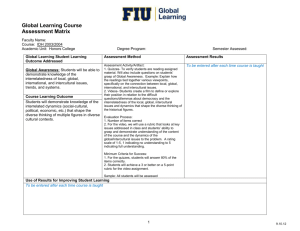
Course Outcome Assessment for Global Learning Courses Faculty Name: Mark D’Alessandro Course: HFT 3894, Global Food and Culture Academic Unit: Hospitality and Tourism Management Degree Program: Hospitality Global Learning Student Learning Outcome Addressed Global Awareness: Students will be able to demonstrate knowledge of the interrelatedness of local, global, international, and intercultural issues, trends, and systems. Course Learning Outcome Students will be able to demonstrate their knowledge of the ways politics, economics, and cultures interact and influence the way food functions in communities across the globe. Semester Assessed: Assessment Method Assessment Results Assessment Activity/Artifact: Students will produce a ten-page research paper (inclusive of a three-page rough draft and thesis statement) that will demonstrate their mastery of local and global issues and elucidate their opinions. To be entered at end of course Evaluation Process: 1. A rubric will be used to assess content, articulation of outcome and demonstration of interrelatedness of food issues across cultures. 2. Students will submit a pre and post research summary that indicates how their understanding of the global issue changed throughout the writing process. Minimum Criteria for Success: 1. Students will be evaluated on how effectively they demonstrate their assimilation of course content in their topic selection, argument and assessment of fact in their paper. 2. Summaries will be analyzed for evidence of the effectiveness of the activity in developing students’ global awareness. Sample: All students will be assessed. Use of Results for Improving Student Learning To be entered at end of course 1 Course Outcome Assessment for Global Learning Courses Faculty Name: Mark D’Alessandro Course: HFT 3894, Global Food and Culture Academic Unit: Hospitality and Tourism Management Degree Program: Hospitality Global Learning Student Learning Outcome Addressed Global Perspective: Students will be able to conduct a multi-perspective analysis of local, global, international, and intercultural problems. Course Learning Outcome Students will be able to analyze the underlying factors that influence the ways consumers and producers across the globe interpret the meaning of food. Semester Assessed: Assessment Method Assessment Results Assessment Activity/Artifact: To be entered at end of course Each team will be tasked with guessing their peers’ food emotions. An interactive class discussion will be held in which students will make evidencebased arguments to explain their guesses. Evaluation Process: A three-point rubric will be used to evaluate student mastery of underlying factors influencing interpretation of food meanings, and method of communicating these meanings. Minimum Criteria for Success: Students will earn a score of at least “2” on the three-point rubric. A score of “2” represents students’ ability to discern diverse underlying cultural and experiential factors influencing the way people across the globe interpret the meaning of food. Sample: All students will be assessed. Use of Results for Improving Student Learning To be entered at end of course 2 Course Outcome Assessment for Global Learning Courses Faculty Name: Mark D’Alessandro Course: HFT 3894, Global Food and Culture Academic Unit: Hospitality and Tourism Management Degree Program: Hospitality Global Learning Student Learning Outcome Addressed Global Engagement: Students will be able to demonstrate willingness to engage in local, global, international, and intercultural problem solving. Course Learning Outcome Students will be able to describe their role in creating change concerning a global food issue. Semester Assessed: Assessment Method Assessment Results Assessment Activity/Artifact: To be entered at end of course Students will reflect in a reaction paper on the impact that learning about the selected issue has had on their attitudes towards affecting change and society. In this paper, they will discuss how the issue has changed their minds, global perception and understanding of culture. Evaluation Process: The two-page reaction paper will be graded with a four-point rubric that will evaluate knowledge/comprehension, analysis of the issue, synthesis of a solution and application. Minimum Criteria for Success: Students should demonstrate deep understanding of the issue and develop a well-thought out course of action for a change. Sample: All students will be assessed. Use of Results for Improving Student Learning To be entered at end of course 3