Edexcel Year 10 Biology The variety of life
advertisement

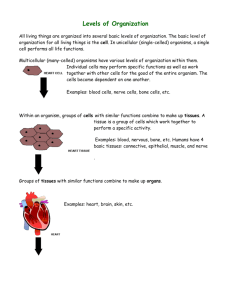
Edexcel Year 10 Biology The variety of life Lesson 2 Levels of Organisation Levels of organisation Syllabus extract Students will be assessed on their ability to: • 2.1 describe the levels of organisation within organisms: organelles, cells, tissues, organs and systems. Levels of organisation Learning Objective: In order to be successful in this lesson you must be able to: Explain how organisms are organised giving explanations of both the nervous system and the circulatory system. Levels of organisation in an organism • Inside of every organism is a precise arrangement of structures which work together to facilitate the functioning of the particular organism. • These systems begin with the smallest structures, called cell organelles. Objective: to order the levels of organisation in an organism Order the words below. Have the smallest on the bottom and work up to the largest. Organelle Organ system Organ Cell Organism Tissue Now draw a pyramid shape in your workbook (with 6 lines ) and write them in order. Objective: to order the levels of organisation in an organism Organism Organ system Organ Tissue Cell Organelle Cell Organelles These are found within cells and allow cells to carry out their functions. • Nucleus: Control centre of the cell, the genes decide which proteins the cell makes. • Cell membrane: allows certain substances to pass through into the cell. • Mitochondria: carry out respiration and provide the cell with energy. • Cell wall: allows the cell to keep its shape • Vacuole: storage area for sugars and other minerals. • Chloroplasts: contain chlorophyll which converts sunlight into sugars for food. The levels of organisation within organisms The basic building blocks of life Cells Cells make up the next level of organisation. The two main types of cell are plant and animal. Tissues Cells which all have a similar function are grouped together to form tissues, e.g. muscles are made up of a group of muscle cells, all specialised to work together to produce a particular function. This group of cells forms muscle tissue. Examples of animal tissues include: • muscular tissue, which can contract to bring about movement • glandular tissue, which can produce substances such as enzymes and hormones • epithelial tissue, which covers some parts of the body. Examples of plant tissues include: • epidermal tissues, which cover the plant • palisade mesophyll, which carries out photosynthesis • spongy mesophyll, which has air spaces to facilitate diffusion of gases • xylem and phloem, which transport substances around the plant. Organs A group of tissues all working together form an organ. An organ is made of a group of tissues all working together to perform a specific function. Examples of organs include: heart, lungs, liver and brain. Plant organs include stems, roots and leaves. Example of an animal organ An example of an animal organ is the stomach, which contains the tissues: • muscular tissue, to allow contents to move through the digestive system • glandular tissue, to produce digestive juices • epithelial tissue, to cover the outside and the inside of the stomach. These tissues all work together to function as the stomach. Organ Systems The final level of organisation is an organ system. This is a group of organs that work together to perform a job. For example: the stomach and intestines are part of the digestive system. The heart and lungs are part of the cardiovascular system. We have lots of different Organ Systems. Can you name these? These are just examples of a few but together all of the organ systems make an organism like you! OR Use the computers and the guided worksheet to produce a presentation showing the levels of organisation in humans. Use the circulatory system or the nervous system as your examples. Objective: To explain the levels of organisation True or false Tissues are made from only one type of cell. Lots of organ systems work together to make an organism. An organelle is bigger than an organ The circulatory system carries electrical messages around the body The spinal cord and brain are organs in the Nervous system Learning Objective: In order to be successful in this lesson you must be able to: Explain how organisms are organised giving explanations of both the nervous system and the circulatory system.