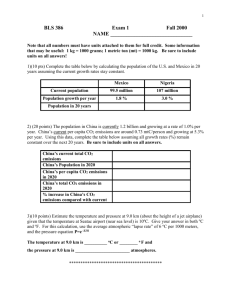
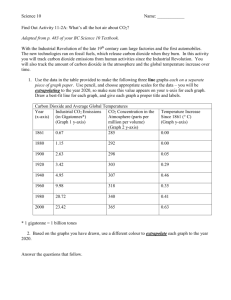
1. The graph is called the - Mercer Island School District
advertisement
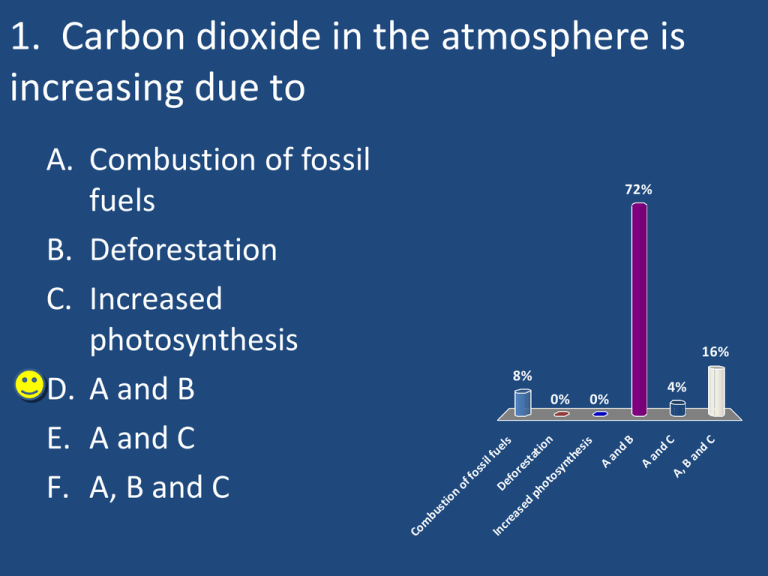
1. Carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is increasing due to 72% 16% 8% 4% d C an d B A, an A A an d C B 0% n to sy nt he s is es ta t io re as ed ph o De fo r In c bu st io n of fo ss il fu el s 0% Co m A. Combustion of fossil fuels B. Deforestation C. Increased photosynthesis D. A and B E. A and C F. A, B and C -Combustion releases carbon dioxide -Deforestation reduced the uptake of carbon dioxide in photosynthesis. 2. The graph is called the A. Gore Graph. B. Keeling Curve. C. Photosynthesis Time-series Curve. D. CO2 Sequence. 72% 16% Se qu en ce . er . .. CO 2 Tim es es is Ke el in g Cu rv e. 4% Ph ot os yn th Go r eG ra ph . 8% 3. The seasonal dips on the previous graph (Keeling Curve of CO2) occur during summer in the ____________ due to____________. No rth er n ... He m isp he re ;s he re ;s ... n. .. isp He m he re ;i So ut he rn He m isp he re ;i er n He m isp No rth So ut he rn A. Southern Hemisphere; increased photosynthesis B. Northern Hemisphere; increased photosynthesis C. Southern Hemisphere; seasonal changes in driving patterns D. Northern Hemisphere; seasonal changes in driving patterns. n. .. 25% 25% 25% 25% Much more of the Earth’s landmass is in the Northern Hemisphere. When it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere there is less photosynthesis so less uptake of carbon dioxide. 4. Which of the following is NOT a greenhouse gas? A. CO2 B. CH4 C. Water Vapor D. N2 E. N2O 50% 27% 15% 8% W at er V N2 O N2 ap or CH 4 CO 2 0% 5. Which type of radiation do greenhouse gases block? 56% 33% 11% ov e bl e Al lo ft he ab Vi si av io le t 0% Ul tr Infrared Ultraviolet Visible All of the above In fra re d A. B. C. D. 6. Which of the following is not a potential effect of a warmer ocean? A. Increased intensity of ocean storms like hurricanes. B. Less ocean productivity. C. Coral reefs dying. D. Ocean conveyor belt will reverse direction. 58% 29% 13% w ill .. . g. yin co n ve yo rb el t re ef sd al ea n pr o ce an Le ss o Co r Oc In c re as ed in te ns ity of oc e. . du ct ivi ty . 0% 7. A component of the environment that stores carbon atoms in other molecules so that there is less CO2 in the atmosphere is called a Carbon sink Carbon cap Carbon reservoir A and B A and C A, B and C 57% 29% 10% 5% C an d B A, d an A an d C B 0% A re se rv oi r p ca bo n bo n Ca r Ca r bo n s in k 0% Ca r A. B. C. D. E. F. 8. The oceans serve as a carbon sink by having A. carbon dioxide dissolved in the water B. carbon in organic molecules in the organisms C. calcium carbonate in shells and limestone D. A and B E. B and C F. A, B and C 57% 17% 13% ca um lci 4% 4% ec rb ul on .. at ei n sh el .. A an d B B an d C A, B an d C m an ic or g ca in rb on ca ca rb on di o xid ed iss ol ol v ed .. 4% 9. As the ocean’s temperature increases its will store a ______ percentage of the atmospheric carbon dioxide emissions. A. increasing B. decreasing C. set 71% 29% se t g de cr ea sin in cr ea sin g 0% As temperature increases, a gas is more likely to come out of solution. This process is why warm soda goes flat faster than cold soda. Note that it is the percentage of atmospheric CO2 dissolved in the water that would decrease, because with higher levels of CO2 in the atmosphere more CO2 dissolves into the water. So increased CO2 and increased temperatures would still mean the total dissolved CO2 would increase, but the oceans would be absorbing a smaller percentage of the overall carbon dioxide (less of a carbon sink). 10. Dissolved CO2 in the ocean A. makes the water more alkaline B. makes the water more acidic C. acts as a buffer to neutralize the pH 76% 20% 4% C. a ct sa sa . ne ut .. bu ffe rt o ea er m or at w es th e ak m m ak es th e w at er m or ea l.. . c.. . 0% Some of the dissolved carbon dioxide reacts with water to form carbonic acid. 11. Which of the following is a potential effect of increased ocean acidity? A. Bleaching of coral reefs. B. Increased dissolution (dissolving) of carbonate shells. C. Plankton not growing properly. D. All of the above. 96% 4% ov e. ab ft he lo Al in ro w no tg kt on Pl an 0% gp . .. s. . . (d i ut io n di ss ol ed re as In c Bl ea c hi n go fc or a lr ee fs . 0% 12. Which of the following are major sources of nitrous oxide (N2O) Agriculture Combustion engines Landfills A and B B and C A, B and C 30% 30% 17% 13% B an d C C A, an d B A an d B s 4% nd fil l La es en gin n bu st io Ag r ic ul tu re 4% Co m A. B. C. D. E. F. Agriculture is the leading source of nitrous oxide, because excess nitrogen in the soil from inorganic nitrogen fertilizers result in the production of N2O The high temperatures of combustion engines also results in nitrous oxide emissions. 13. Inorganic fertilizer usually result in in the production of what other greenhouse gas? A. Methane due to anaerobic fermentation B. Ozone due to volatile organic compound production C. Carbon dioxide due to high energy demands of production D. Water vapor due to evaporation 61% 26% 9% ev a. .. to ap or du e to du e W at er v di bo n Ca r du e Oz on e hi .. . ox id e vo l to to ue ed ha n et M or .. at ile an ae ro bi .. . 4% There is a high energy demand for producing nitrogen compounds from atmospheric N2. 14. Tropospheric ozone (O3) A. protects the earth from harmful UV radiation B. is a strong greenhouse gas C. has harmful health effects D. both B and C 50% 46% fu lh ea l m ar ha sh C an d B bo th ef fe ct s 0% th us e re en ho ng g tro as is pr ot ec ts th e ea rth fro m ... ga s 4% Stratospheric ozone protects the Earth from UV radiation. But tropospheric (ground level) ozone is both a strong greenhouse gas and a harmful air pollutant. 15. The main source of ozone in the troposphere is A. Off-gassing from agriculture B. Aerosol cans and refrigerator coolants C. reactions between nitric oxides (NOx) and volatile organic compounds (VOC’s). D. Off-shore oil wells 38% 38% 21% el ls .. w c. Of f-s h or e oi l tri ni ee n be tw nd re ac t io ns sa ca n Ae ro so l Of f-g as sin gf ro m ag r ic ul re fri ge r.. . tu re 4% Volatile organic compounds are organic compounds (carbon-based molecules produced by living things) that more easily evaporate into the atmosphere. Examples: benzene, butane and methane 16. Which of the following is NOT one of the top three sources of anthropogenic methane? 25% 25% 25% 25% s fa r tle Ca t de st ru nd et la W m ct io n g r il lin ld Oi nd fil l s Landfills Oil drilling Wetland destruction Cattle farms La A. B. C. D. Many oil and coal deposits have a cap of natural gas above them. This natural gas may be released when extracting the other fossil fuels. Methane is also produced when certain anaerobic organisms break down organic matter in no/low O2 environments such as: -the intestines of animals (cellulose broken down) - landfills - wetlands and rice paddies (wetlands are a natural SOURCE of methane because stagnation of water results in low O2 conditions.) 17. When methane is burned, it produces CO2 and nitrous oxide Ozone and nitrous oxide CO2 and water vapor Ozone and water vapor 57% 35% ap or ap or 4% w d an Oz on e an d w at er v at er v so xi CO 2 ni tro u d an Oz on e an d ni tro u so xi de de 4% CO 2 A. B. C. D. Methane over time reacts with O2 in the atmosphere to be broken down into carbon dioxide and water vapor. However these two products are also greenhouse gases. 18. Which of these is true of soot (black carbon/ bc)? 71% 8% 13% C. B an d C. an d B bu r th e is ce A, ... ... co he n so ur n ai m A m el ts fa s te rw in ge co ol Ice re at es a It c 8% 0% ffe ct ... A. It creates a cooling effect on Earth because it blocks sunlight from reaching Earth’s surface. B. Ice melts faster when coated by soot. C. A main source is the burning of biomass. D. A, B and C. E. B and C. Ice and snow are normally very reflective surfaces. But when they are coated with soot they absorb more light. Soot is formed from the incomplete combustion of organic matter (fossil fuels or biomass). Many developing regions use biomass (such as wood or dung) as a source of energy for cooking and heating. Diesel fuel is a major source of soot from developed nations. 19. Which of the following areas will be the least affected by sea level rise? Bangladesh Maldives Seattle Florida 74% 26% Flo r id a 0% Se at t le es di v al M ng l ad es h 0% Ba A. B. C. D. 20. What might also cause sea level to rise besides melting of ice? A. Accelerated erosion of coastlines as climate warms. B. Thermal expansion of the ocean as it warms. C. Decrease in sediment runoff from rivers as rivers dry up. D. Increased ocean floor volcanic activity. 76% 24% n se di In c re as ed in ea se De cr or vo ... oc ea n m ns io 0% flo of en tr th ... ... co of n Th er m al ex pa er os io te d Ac ce le ra un o. . 0% Water becomes less dense as it is heated. It expands. 21. Which of the following is not a potential effect of climate change? A. Increased droughts in certain parts of the world B. Increased pests and diseases. C. Loss of biodiversity. D. Increase in ocean pH. 61% In c pH . re as ei n oc ea n ve rs it y . io di of b nd pe st sa ed re as In c 9% Lo ss ce r. . . in ug ht s dr o ed re as In c 17% di se a. .. 13% 22. Why might global warming cause more methane to be released into the atmosphere? 78% 13% 4% Fr a ck in fra lic g( hy dr au pe ra t ur es c ... ct ... . re le a. em er t ar m er o ar m W W fp go in aw Th ill ce an sw af ro st w i. . 4% er m A. Thawing of permafrost will release methane. B. Warmer oceans will release dissolved methane. C. Warmer temperatures cause cattle metabolic rates to accelerate. D. Fracking (hydraulic fracturing) in location previously inaccessible 23. Which of these is NOT a positive feedback loop that leads to more warming? 50% 27% n. .. at in or e M m os ph er e. .. el ti m gl in ar m CO 2 ea ds t o le ad sd ... e. . ice W el t in go fs ea em pe ra t er t M ar m W 14% 9% ur es l A. Warmer temperatures lead to decreased ocean productivity. B. Melting of sea ice leads darker surfaces and more radiation absorbed by Earth. C. Warming leads to melting of permafrost. D. More CO2 in atmosphere leads to more CO2 absorbed by the ocean. 24. Which of the following is not a reason why climate change might cause a loss of biodiversity? 57% 33% 10% ac id it y ... a. .. In c re as ed fo r ty bi li In a oc ea n ita sp ec ie ts to st o hi ca us e fh ab in go in Sh ift ea se De cr ... .. . 0% in se ct s A. Decrease in insects cause insecteating birds to go extinct. B. Shifting of habitats to higher latitudes and altitudes. C. Inability for species to adapt to a rapidly changing climate. D. Increased ocean acidity endangers the ocean food chain. 25. When did the Kyoto Protocol meeting take place? 1989 1992 1997 2001 74% 17% 9% 20 01 19 97 19 92 0% 19 89 A. B. C. D. 26. How did the Kyoto Protocol aim to reduce CO2 emissions? 67% 19% .. na t io ns ... ll r in ga ev el op ed re qu i By de ve l. . . By re qu i r in gd r in ge ac re qu i r in ge ac By re qu i By 5% h de ve l. . . 10% h A. By requiring each developed nation to reduce emissions by 35%. B. By requiring each developed nation to reduce emissions to pre-1990 levels. C. By requiring developed nations to give aid to developing nations to help them reduce CO2 emissions. D. By requiring all nations to develop a voluntary emissions reduction plan. 27. Which country’s ratification of the treaty finally allowed it to go into effect? 95% an 0% Ja p lia te s St a te d 0% Au st ra 5% Un i Russia United States Australia Japan Ru ss ia A. B. C. D. 28. Which of the following reasons was cited by the US as a reason not to ratify the Kyoto Protocol? A. It would hurt the US economy. B. It wasn’t fair that developing nations would not have to reduce emissions. C. Incomplete state of scientific evidence D. All of the above 52% 33% ov e ab ft he lo Al of sc ie nt ... te st a et e pl om as It w In c n’ tf air th a td ev el o US ec ... tt he hu r ld ou It w 10% ... 5% 29. Which of the following is an example of potential carbon capture technology (carbon sequestration)? A. Pumping CO2 from the smokestacks of coal plants into the ground. B. Trapping the energy in methane emissions from cattle for use as an energy source. C. Invading countries to capture their oil reserves. 65% 25% ... ca o rie st co un t In va d in g he ng t ap pi Tr Pu m pi ng C O2 fro m en er gy i n th e . .. .. . 10% 30. What is cap and trade? 68% 23% 9% ... lb oo k t.. . Tr ng Pu tti ad in ac gy ou ap on co m all ng rs ch oo pa pr od uc ni es t is s io em on im Re qu ir i al ng Pu tti ... .. 0% it A. Putting a limit on emissions and companies who exceed the limit must buy the right to pollute more from companies who are under the limit. B. Requiring all companies to trade a percentage of their profits for the right to emit CO2. C. Putting a cap on production of goods from companies who exceed emission limits, creating more trade with other less-polluting countries. D. Trading your school books for a cap and gown at graduation. 31. How is the Copenhagen Accord different from the Kyoto Protocol? 48% 39% 9% 4% Al lo ft he ab av e. .. na tio ns h de v. .. an d De ve lo pe d ov e. . di ng bi n lly de ve lo pe d eg a Bo th It i sl A. It is legally binding. B. Both developed and developing nations are required to reduce emissions. C. Developed nations have promised money to developing nations to help deal with climate change. D. All of the above. 32. IPCC stands for A. International Policy on Carbon Capture B. Interpretive Programs for Climate Coalitions C. Investing Properly in Carbon Credits D. Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change 68% 32% gP . Pa n el . ... Ca en ta l in In te rg ro pe rly ra m ro g In ve st in eP re t iv ov er nm sf or . .. on icy Po l na l In te rp at io In te rn 0% ... 0% 33. CFC’s have been banned because they A. can easily be replaced by other substances that are not greenhouse gases. B. are known carcinogens. C. increase tropospheric ozone. D. deplete the stratospheric ozone layer. 90% . to sp he ri. . es th de pl et e tro cr ea se in tra po sp he ric rc in ca n no w ek ar 5% oz . .. og en s. ... by ac ed re pl be ea sil y n ca 5% 0% 34. Which of the following is a potential consequence of more rapid and earlier annual snowmelts in the mountains? A. Decreased hydropower B. A longer forest fire season. C. Loss of water supplies for regional inhabitants. D. All of the above ov e ab ft he lo Al su pp l ie sf or .. . so n se a at er of w es tf ir e Lo ss ng e lo A De c re rf or as e d hy dr op ow er . 25% 25% 25% 25% 35. If increased evaporation due to global warming results in thicker cumulus clouds that reflect, this would be an example of 50% positive feedback negative feedback synergism serendipity 32% ity 9% se re nd ip sy n er gi k ive fe ed ba c ac k ne ga t ef ee db sm 9% po s it iv A. B. C. D. Effect of clouds on global warming depends on type of clouds. - feedback A negative feedback loop is when the outcome tends to minimize the effect of an input and stabilize the system. • Cumulus clouds that reflect light and reduce heating would be a negative feedback loop. • Higher, wispy cirrus clouds that aren’t very reflective and yet trap heat would be a positive feedback loop. 36. If the temperature on Earth changes by 2 °C, this is equal to a temperature change of approximately 1.2 °F 2 °F 2.8 °F 3.6 °F 4.8 °F 57% 26% 9% °F 4. 8 °F 3. 6 °F 2. 8 °F 4% 2 °F 4% 1. 2 A. B. C. D. E. 100 °C = 180 °F 1 °C = 1.8 °F 37. The IPCC panel representing climate scientist from around the world have determined that it is _______ that global temperatures have been increasing due to man’s activities. 17% 99 % lik el y (> el y lik Hi g hl y ly 0% 0% ) (9 099 L ik M % el or ) y e ( lik 66 el % yt -8 9% ha No n ) co no ns t( en 50 su ... sc ou ld be r.. . 0% igh Very highly likely (>99%) Highly likely (90-99%) Likely (66%-89%) More likely than not (50%-65 %) No consensus could be reached by the majority of scientists Ve ry h A. B. C. D. E. 83% 38. Which list of greenhouse gases is in order from most powerful heat trapping ability per molecule to least powerful? 50% 23% 23% de .. CO 2, Ni tro u xi HC FC ’s, sO xi (N . .. ... ,M Ni tro us O N2 O) Ni tro us itr Ox id e( HC FC ’s, ou sO xid e( N2 O. . 5% CO 2, N A. CO2, Nitrous Oxide (N2O), Methane (CH4), HCFC’s B. Nitrous Oxide (N2O), Methane (CH4), CO2, HCFC’s C. HCFC’s, Nitrous Oxide (N2O), Methane (CH4), CO2 D. HCFC’s, CO2, Nitrous Oxide (N2O), Methane (CH4) 1. D 2. B 3. B 4. D 5. A 6. D 7. E 8. F 9. B 10.B 11.D 12.D 13.C 14.D 15.C 16.C 17.C 18.E 19.C 20. B 21. D 22.A 23. D 24. B 25. C 26. B 27.A 28. D 29.A 30. A 31. C 32. D 33. D 34. D 35. B 36. D 37.B 38.C