Here is a study guide
advertisement

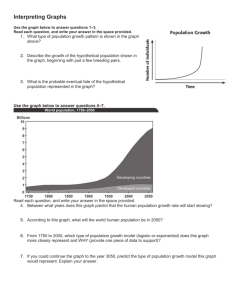
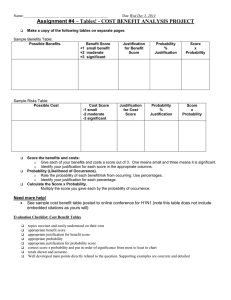
Name ____________________________ Date ______________________ Period ______________ Unit 1: Introduction to Environmental Science Study Guide 1. Be able to define, understand, and apply in context of the class the following words: Sustainability Ecological footprint Carrying capacity Precautionary principle Utilitarian justification Ecological justification Aesthetic justification Moral justification Controlled experiment Deductive reasoning Dependent variable Independent variable Disprovability Control group (or experimental control) Constant variables Hypothesis Inference Inductive reasoning Observations Pseudoscience Theories Ecosystem Exponential growth Feedback Gaia hypothesis Negative feedback Positive feedback Birth rate Death rate Demographic transition Life expectancy Population Biogeochemical cycle Carbon cycle Nitrogen cycle Phosphorus cycle Limiting factor Abiotic factor Biotic factor Food web Food chain Sink Source 2. For the test, you must be able to: Pick out the dependent and independent variable in any given experiment Differentiate between the 8 different justifications for environmental preservation Explain the problem of human population growth, its cause, and possible solutions for it Differentiate between scientific statements and non-scientific statements Recognize accurate food webs Apply the 6 principles of ecology to your eco-column Explain the implications and connections behind sustainability, ecological footprints, and carrying capacity. Justify why studying biogeochemical cycles are important and give specific examples. Define and apply the idea of tragedy of the commons to the real world Apply the 6 themes of environmental science to a given environmental problem